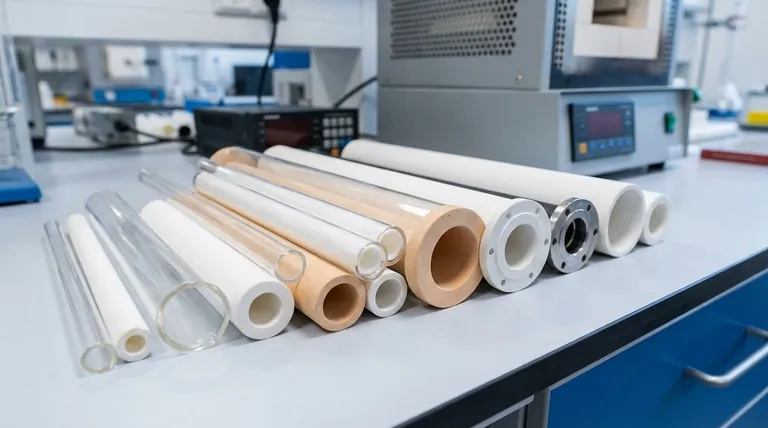
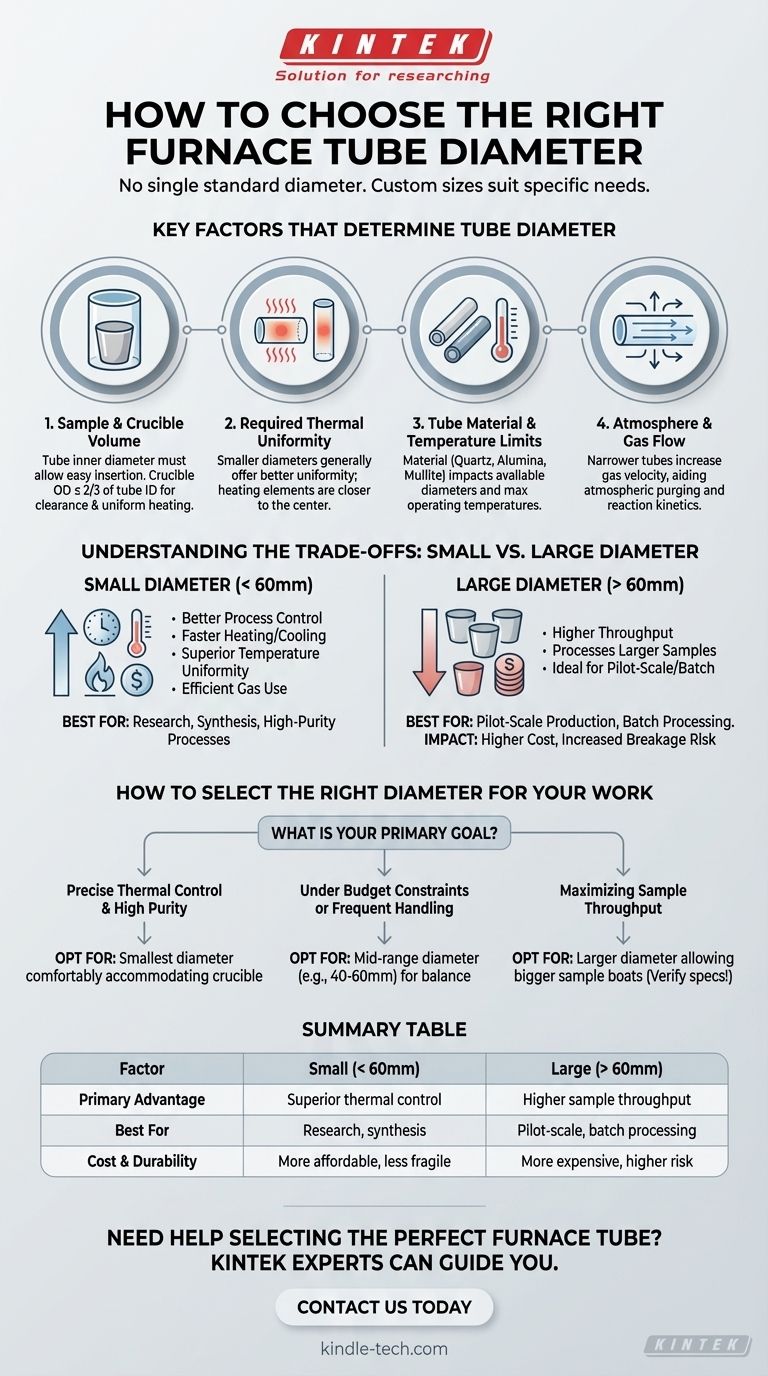
To be precise, there is no single standard diameter for a furnace tube. Instead, they are available in a range of sizes to suit different scientific and industrial applications. While a common range for laboratory-scale tube furnaces is between 25 mm (approx. 1 inch) and 100 mm (approx. 4 inches), the specific diameter is always chosen based on the requirements of the process.
Choosing the right furnace tube diameter is not about finding a standard size, but about matching the tube's capacity and material properties to your specific sample, temperature, and atmospheric requirements.

Key Factors That Determine Tube Diameter
Selecting a furnace tube is a critical decision based on the parameters of your experiment or process. The diameter is a function of several interdependent factors.
Sample and Crucible Volume
The most immediate consideration is the physical size of your sample and its container. The tube's inner diameter must be large enough to allow a crucible or sample boat to be inserted and removed easily.
As a general rule of thumb, the outer diameter of your crucible should not exceed two-thirds of the inner diameter of the furnace tube. This ensures adequate clearance and promotes uniform heating.
Required Thermal Uniformity
The diameter of the tube directly impacts the temperature uniformity across your sample.
Smaller diameter tubes generally offer a more uniform heated zone. The closer proximity of the heating elements to the central axis ensures the sample receives more consistent radiant heat from all sides.
Tube Material and Temperature Limits
The material of the tube—most commonly quartz, alumina (corundum), or mullite—influences the available diameter options, especially for high-temperature applications.
Large-diameter quartz tubes, for example, can be more susceptible to thermal shock and may have lower maximum operating temperatures compared to their smaller counterparts or tubes made from more robust ceramics like alumina.
Atmosphere and Gas Flow
If your process involves a controlled atmosphere or flowing gas, the tube diameter plays a role in efficiency.
A narrower tube results in a higher linear gas velocity for a given flow rate, which can be beneficial for purging the atmosphere or for processes where reaction kinetics depend on gas exposure.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Small vs. Large Diameter
The choice between a smaller or larger diameter tube involves a clear set of engineering and process trade-offs. Understanding these is key to making an informed decision.
Advantages of a Smaller Diameter (< 60mm)
Tubes with a smaller diameter typically provide better process control. They heat up and cool down faster, offer superior temperature uniformity, and use process gases more efficiently. They are often the preferred choice for research, material synthesis, and high-purity applications.
Advantages of a Larger Diameter (> 60mm)
The primary benefit of a larger diameter is throughput. It allows for the processing of larger individual samples or the use of bigger boats that can hold a greater quantity of material, making it ideal for pilot-scale production or batch processing.
The Impact on Cost and Durability
Larger diameter tubes, particularly those made from high-purity quartz, are significantly more expensive and fragile than smaller tubes. The risk of breakage during handling or due to thermal stress increases with size, adding to the total cost of ownership.
How to Select the Right Diameter for Your Work
Base your decision on the primary goal of your application.
- If your primary focus is precise thermal control and high purity: Opt for the smallest diameter tube that comfortably accommodates your sample crucible to ensure maximum temperature uniformity and efficient atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is maximizing sample throughput: Select a larger diameter tube that allows for bigger sample boats, but carefully verify that its material and temperature specifications meet the demands of your process.
- If you are working under budget constraints or require frequent handling: A mid-range diameter tube (e.g., 40-60mm) often provides a good balance of capacity, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Ultimately, the right diameter is the one that best serves your specific experimental and operational goals.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Small Diameter (< 60mm) | Large Diameter (> 60mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Advantage | Superior thermal control & efficiency | Higher sample throughput |
| Best For | Research, synthesis, high-purity processes | Pilot-scale production, batch processing |
| Cost & Durability | More affordable, less fragile | More expensive, higher risk of breakage |
Need help selecting the perfect furnace tube for your lab? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific needs. Whether you require precise thermal control for research or high-throughput capabilities for production, our experts can guide you to the ideal solution. Contact us today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-purity alumina lining required for high-temperature tube furnaces? Ensure Accurate Biomass Research
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?



















