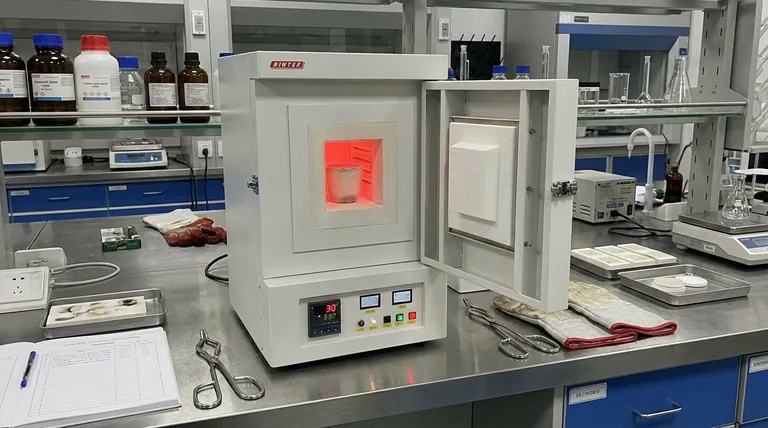
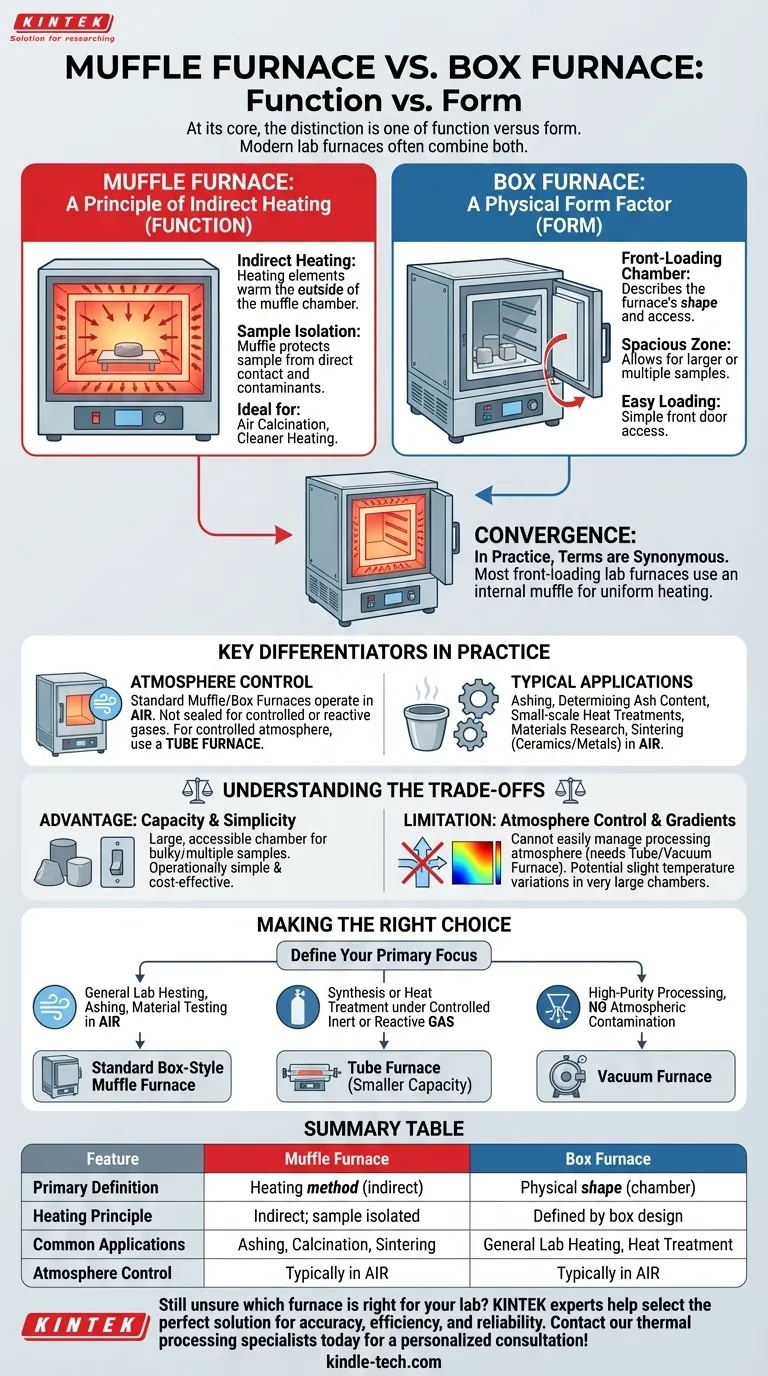
At its core, the distinction is one of function versus form. A "muffle furnace" describes how a sample is heated—indirectly, inside a protective chamber. A "box furnace" describes the physical shape of the equipment—a front-loading chamber. In modern practice, these terms are often used interchangeably because most laboratory box furnaces are, by design, muffle furnaces.
The critical takeaway is that "muffle" refers to the internal heating method (isolating the sample), while "box" refers to the furnace's external shape (a chamber). Because these two concepts are almost always combined in a single piece of equipment, the terms "box furnace" and "muffle furnace" usually describe the same device.

Defining the Core Concepts
To make an informed decision, you must understand the principle behind each term. The confusion arises because one term describes a component, and the other describes a chassis.
The Muffle: A Principle of Indirect Heating
A muffle is an internal, box-like chamber made of a high-temperature-resistant material.
Heating elements warm the outside of this muffle. The muffle then radiates heat uniformly to the sample placed inside it.
This indirect heating method protects the sample from direct contact with the heating elements and any contaminants from combustion, ensuring a cleaner heating environment. It is ideal for processes like air calcination.
The Box Furnace: A Physical Form Factor
A box furnace simply refers to a furnace with a front-loading door and a chamber (or "box") where samples are placed.
This design is valued for its spacious heating zone and the ease with which operators can place and remove samples. Its shape is what distinguishes it from other forms, like a tube furnace or a bottom-loading furnace.
Where the Terms Converge
Most standard, front-loading laboratory furnaces are built with an internal muffle to provide the uniform, protected heating environment described above.
Therefore, when someone refers to a "box furnace," they are almost always talking about a furnace that uses the muffle principle. The terms have become synonymous in common lab parlance.
Key Differentiators in Practice
While the terms often overlap, understanding their distinct applications and limitations is crucial for selecting the right equipment for your process.
Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle or box furnace is designed to operate in an air atmosphere.
These furnaces are not inherently sealed for processing under a controlled inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) or a reactive atmosphere. For that specific requirement, a tube furnace is the appropriate tool.
Typical Applications
Due to their simple design and ability to heat in air, box-style muffle furnaces excel at specific tasks.
Common applications include ashing materials, determining ash content, performing small-scale heat treatments, materials research, and the sintering of ceramics and metals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every equipment choice involves balancing advantages and limitations. The box-style muffle furnace is a workhorse, but it is not the solution for every thermal processing need.
Advantage: Capacity and Simplicity
The primary benefit of a box furnace is its large, accessible chamber. This allows for the processing of bulky samples or multiple samples at once, something that is difficult in a narrow tube furnace. They are also operationally simple and generally more cost-effective.
Limitation: Lack of Atmosphere Control
The most significant limitation is the inability to easily manage the processing atmosphere. Heating in anything other than air requires a different type of furnace, such as a tube or vacuum furnace, which is specifically designed for gas flow or evacuation.
Limitation: Potential for Temperature Gradients
While the muffle design promotes uniformity, very large chambers can sometimes exhibit slight temperature variations from the center to the corners. For applications requiring extreme temperature precision across the entire sample, this must be considered.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on your specific material, process, and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is general lab heating, ashing, or material testing in air: A standard box-style muffle furnace is the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is synthesis or heat treatment under a controlled inert or reactive gas atmosphere: A tube furnace is the necessary tool, despite its smaller sample capacity.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing without any atmospheric contamination: A vacuum furnace is required to remove air and other gases entirely.
Understanding this distinction between heating method and physical form empowers you to select the precise tool for your scientific or industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Box Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Definition | A heating method (indirect, via a chamber) | A physical shape (front-loading chamber) |
| Heating Principle | Indirect; sample is isolated in a muffle | Defined by the furnace's box-like chamber design |
| Common Applications | Ashing, calcination, sintering in air | General lab heating, heat treatment in air |
| Atmosphere Control | Typically operates in air | Typically operates in air |
| Key Takeaway | Terms are often used interchangeably for modern lab furnaces. |
Still unsure which furnace is right for your lab's needs?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment for your application. Whether you require a standard muffle furnace for ashing or a specialized tube furnace for atmosphere control, our experts can help you select the perfect solution to ensure accuracy, efficiency, and reliable results.
Contact our thermal processing specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of muffle furnace in pharmaceutical industry? Ensure Drug Purity and Quality
- Is a furnace endothermic or exothermic? Uncover the Science of Home Heating
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of muffle furnace? Achieve Absolute Purity and Control in Your Lab
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a blast furnace? Precision vs. Production
- How is heat transferred in a furnace? Master Radiation, Convection & Conduction



















