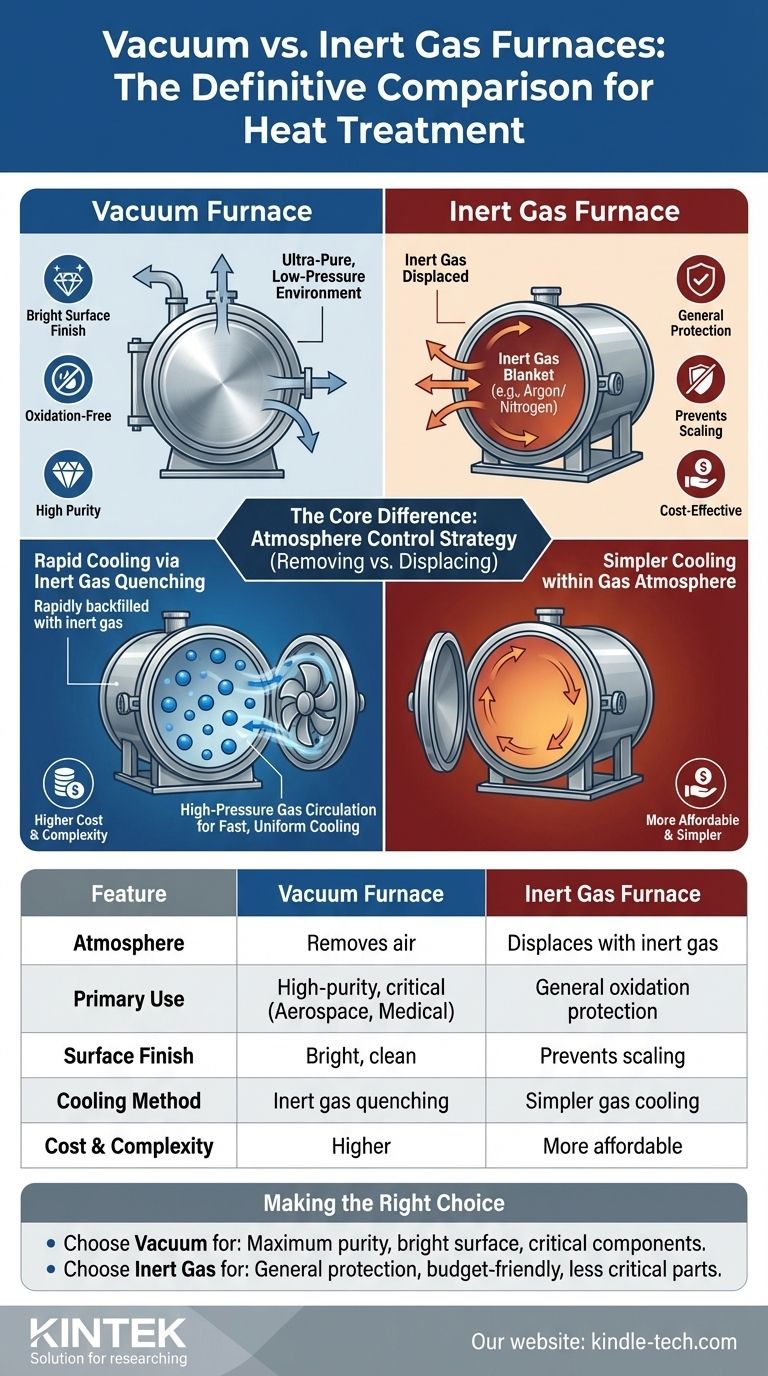
At its core, the difference lies in the type of atmosphere used during the heat treatment process. A vacuum furnace operates by removing nearly all atmospheric gases to create a controlled, low-pressure environment, while an inert gas furnace (a type of atmosphere furnace) displaces the air with a non-reactive gas like argon or nitrogen. The confusion often arises because modern vacuum furnaces frequently use inert gas as a critical tool for rapid cooling after the heating cycle is complete.
The choice is not a simple "either/or." A vacuum furnace provides the purest environment by removing reactive elements, while inert gas is a tool used within that environment (or in a simpler furnace) to control the process—most notably, to achieve rapid and uniform cooling.

The Critical Role of Atmosphere in Heat Treatment
When metals are heated to high temperatures, their reactivity increases dramatically. The gases in our normal atmosphere, particularly oxygen, will readily react with the hot metal surface.
The Problem: Unwanted Reactions
These reactions cause undesirable effects like oxidation (scaling) and decarburization (the loss of carbon from the surface of steel), which can degrade the mechanical properties and surface finish of the component.
The primary goal of a controlled atmosphere furnace is to prevent these reactions from occurring.
The Vacuum Furnace Approach: Ultimate Purity
A vacuum furnace addresses this challenge by physically removing the reactive molecules. Powerful pumps evacuate the air from a sealed chamber before the heating process begins.
This creates an extremely pure environment, preventing any significant reaction with the workpiece. This is why vacuum heat treatment is known for producing parts with a bright, clean surface finish, free from oxidation.
The Atmosphere Furnace Approach: Controlled Displacement
An atmosphere furnace works by replacing the air with a different, controlled gas. If that gas is non-reactive, it is called an inert gas furnace.
Gases like argon and nitrogen are used to purge the oxygen from the chamber, blanketing the workpiece in a protective environment that prevents oxidation. This is a simpler and often more cost-effective method than creating a deep vacuum.
Where the Lines Blur: Inert Gas in Vacuum Furnaces
The most advanced heat treatment processes often combine both technologies, which is the source of most confusion. A vacuum is not just an atmosphere; it's also an excellent thermal insulator.
The Challenge: Cooling in a Vacuum
While being an insulator is beneficial for efficient heating, it makes cooling a slow process. For many metallurgical processes like hardening, rapid cooling (quenching) is absolutely essential to achieve the desired material properties.
The Solution: Inert Gas Quenching
To solve this, modern vacuum furnaces perform a crucial step after the heating cycle. The furnace chamber is rapidly backfilled with a high-pressure inert gas, typically argon or nitrogen.
This gas is then circulated at high speed by a powerful fan, transferring heat away from the hot component and through a heat exchanger. This gas quenching process allows for very fast, yet highly controllable, cooling in a way that cooling in a vacuum cannot achieve.
The Best of Both Worlds
This combination provides the ultimate process control: the unparalleled purity of a vacuum during the critical heating and soaking phases, followed by the rapid, uniform cooling enabled by the inert gas.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a process requires balancing technical requirements with operational realities. No single method is perfect for every application.
Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more expensive and complex. They require robust chambers, high-performance seals, and sophisticated pumping and control systems. An inert atmosphere furnace is a comparatively simpler and more affordable machine.
Process Speed and Throughput
While gas quenching is fast, the overall cycle time for a vacuum furnace can be longer due to the time required to pump the chamber down to the required vacuum level. A simple atmosphere furnace can often achieve a higher throughput for less-demanding jobs.
Application Specificity
The purity of a vacuum furnace is non-negotiable for high-performance, sensitive materials used in industries like aerospace, medical implants, and high-end tool steel. For general-purpose annealing or stress relieving of less critical parts, an inert gas furnace is often perfectly sufficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be driven by the metallurgical requirements of your material and the desired final properties of the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and a bright, unoxidized surface for critical components: A vacuum furnace that uses inert gas for quenching is the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is general protection from oxidation on a budget: A standard inert gas atmosphere furnace is a highly effective and economical solution.
- If your primary focus is a surface modification process like carburizing or nitriding: You need a specialized active atmosphere furnace that uses reactive gases, as both vacuum and inert gas would prevent the desired chemical changes.
Ultimately, understanding your process means choosing the right atmospheric control strategy to achieve your desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Furnace | Inert Gas Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Removes air to create a low-pressure environment | Displaces air with non-reactive gas (Argon/Nitrogen) |
| Primary Use | High-purity processes (aerospace, medical) | General oxidation protection |
| Surface Finish | Bright, clean, oxidation-free | Prevents scaling, but may not achieve same purity |
| Cooling Method | Inert gas quenching for rapid cooling | Simpler cooling within gas atmosphere |
| Cost & Complexity | Higher cost, more complex | More affordable, simpler operation |
Need help selecting the right furnace for your lab's heat treatment processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance on vacuum furnaces, inert gas furnaces, and more. We help you achieve precise temperature control, superior material properties, and optimal process efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover the perfect solution for your applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish



















