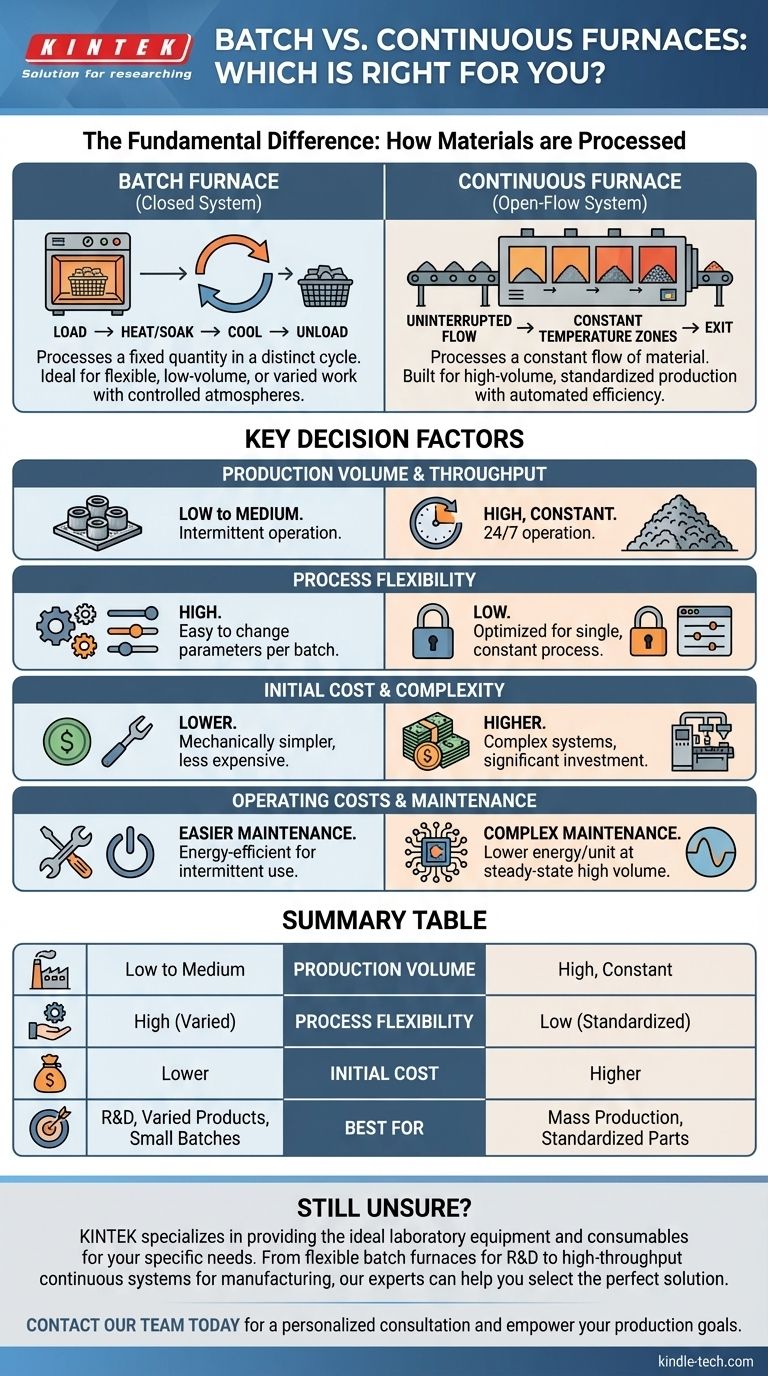
The fundamental difference between a batch furnace and a continuous furnace lies in how materials are processed. A batch furnace processes a fixed quantity of material in a distinct, start-to-finish cycle, while a continuous furnace processes a constant, uninterrupted flow of material through different heating zones.
The choice is not about which furnace is technologically superior, but which operational model best aligns with your production volume and process requirements. Batch furnaces offer flexibility for varied or low-volume work, whereas continuous furnaces are built for high-volume, standardized production.

The Fundamental Operating Principle
To select the right furnace, you must first understand the core difference in how each one works. This operational model dictates everything from cost and complexity to throughput and energy use.
How Batch Furnaces Work
A batch furnace is a closed system. A specific quantity of product—a "batch"—is loaded into the furnace, often using fixtures like baskets or racks.
The furnace is then sealed, and the entire chamber is brought through a specific thermal cycle (heating, soaking, cooling). Once the process is complete, the doors are opened, and the finished batch is unloaded.
This method is ideal for processes requiring a controlled, inert atmosphere or cleanroom standards, as the chamber is completely sealed during operation.
How Continuous Furnaces Work
A continuous furnace is an open-flow system. Material is constantly fed into one end of the furnace, travels through different temperature zones on a conveyor or by being unrolled, and exits the other end.
The furnace maintains a constant temperature profile along its length, and the processing time is controlled by the speed of the material's movement.
This design eliminates the need for fixtures and manual loading/unloading for each cycle, making it highly efficient for mass production of a single product type.
Comparing Key Decision Factors
Your decision will ultimately depend on how each furnace type aligns with your specific operational and financial goals.
Production Volume and Throughput
This is the most critical factor. Continuous furnaces are designed for high-volume, constant production where the investment is justified by high throughput.
Batch furnaces are better suited for lower or uncertain production volumes. Their ability to operate intermittently makes them more cost-effective when production is not running 24/7.
Process Flexibility
Batch furnaces offer superior flexibility. You can easily change the temperature, duration, and atmospheric conditions for each new group of parts.
Continuous furnaces are far more rigid. They are optimized to run at a constant temperature and speed, making them unsuitable for applications that require frequent changes to the thermal process.
Initial Cost and Complexity
Due to their intricate conveyor systems and zone controls, continuous furnaces are significantly more complex and have a much higher upfront cost.
Batch furnaces are mechanically simpler, making them less expensive to purchase and install.
Operating Costs and Maintenance
Batch furnaces are generally easier and less costly to maintain due to their simpler design. For intermittent production, they are more energy-efficient because they can be shut down between cycles.
Continuous furnaces require more frequent and complex maintenance. However, in high-volume scenarios, their steady-state operation can lead to lower overall energy consumption per unit produced because they avoid repeated heat-up and cool-down cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither furnace is a perfect solution. Recognizing their inherent compromises is key to making an objective decision.
The Batch Furnace Compromise
With a batch furnace, you gain flexibility and a lower initial investment. However, you sacrifice throughput and may require more manual labor for loading and unloading. You also need to manage work-in-process inventory as parts queue up to form a full batch.
The Continuous Furnace Compromise
With a continuous furnace, you gain massive throughput and automation at scale. The trade-off is a loss of flexibility, a significantly higher capital investment, and more complex maintenance requirements. It is an investment in standardization, not versatility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Select the furnace that directly supports your primary production goal.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, consistent production: The automation and throughput of a continuous furnace will deliver the lowest cost per part.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility for varied products: A batch furnace provides the control needed for different parts, temperatures, and special atmospheres.
- If your primary focus is managing initial investment and lower volumes: The simplicity, lower cost, and operational efficiency of a batch furnace make it the most practical choice.
By understanding this core distinction between processing in static groups versus a constant flow, you can confidently select the furnace that serves as the right tool for your manufacturing goals.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Batch Furnace | Continuous Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Production Volume | Low to Medium | High, Constant |
| Process Flexibility | High (Easy to change per batch) | Low (Optimized for one process) |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Best For | Varied products, R&D, lower volumes | Mass production, standardized parts |
Still unsure which furnace is right for your lab or production line?
KINTEK specializes in providing the ideal laboratory equipment and consumables for your specific needs. Whether you require the flexibility of a batch furnace for R&D or the high throughput of a continuous system for manufacturing, our experts can help you select the perfect solution to optimize your process efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and let KINTEK empower your production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results



















