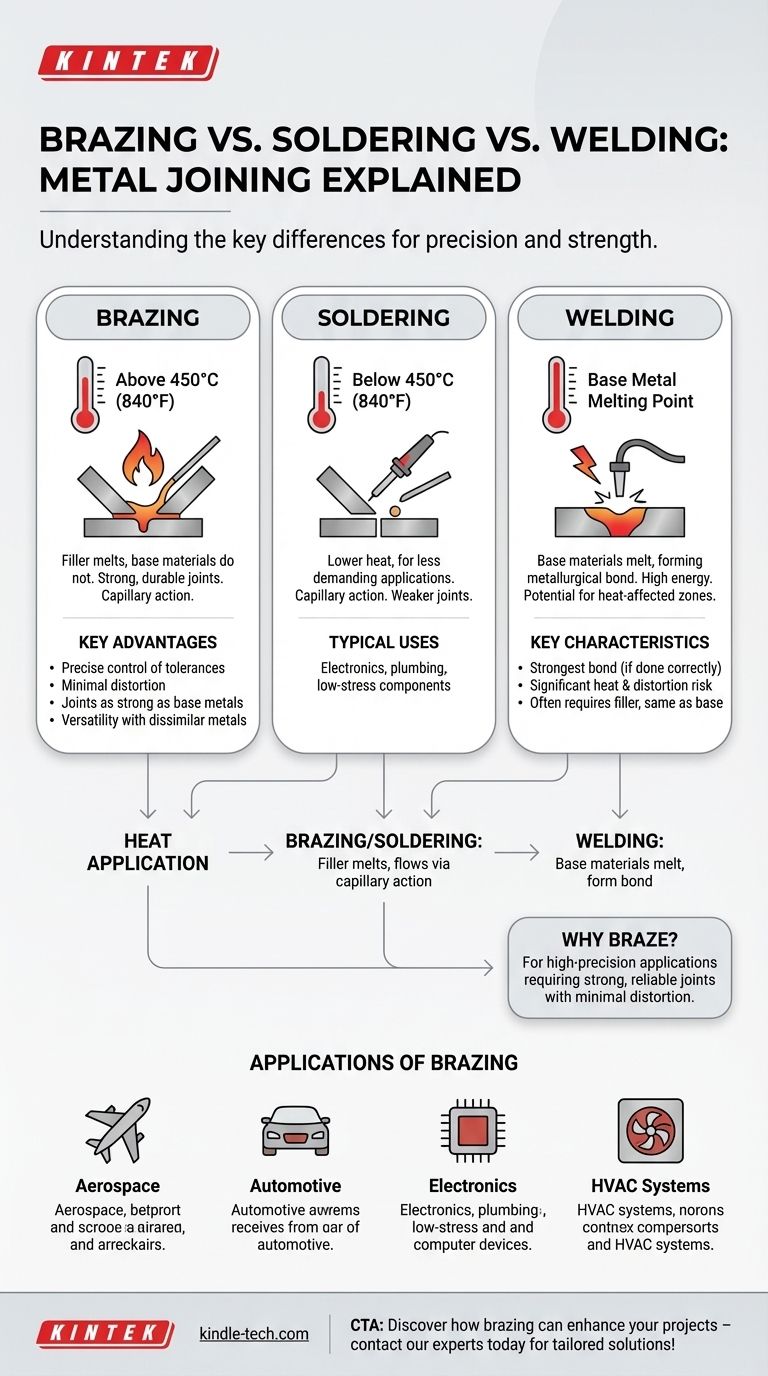
Brazing is a metal-joining process that uses a filler metal with a melting point above 450°C (840°F) to bond two or more base materials without melting them. It is distinguished from soldering, which uses filler metals with lower melting points, and welding, which involves melting the base materials. Brazing offers advantages such as precise control of tolerances, minimal distortion, and joints as strong as the base metals, making it suitable for high-precision applications. The process involves capillary action to distribute the filler metal, creating strong, durable joints. Understanding the differences between brazing, soldering, and welding helps in selecting the appropriate joining method for specific applications.

Key Points Explained:
-
Definition and Temperature Range of Brazing:
- Brazing is a metal-joining process that uses a filler metal with a melting point above 450°C (840°F). This distinguishes it from soldering, which uses filler metals with lower melting points.
- The filler metal in brazing has a lower melting point than the base materials being joined, ensuring that the base materials do not melt during the process.
-
Comparison with Soldering:
- Soldering uses filler metals with melting points below 450°C (840°F), making it suitable for applications requiring lower heat.
- Both brazing and soldering rely on capillary action to distribute the filler metal, but brazing creates stronger joints due to the higher melting point and stronger filler materials used.
-
Comparison with Welding:
- Welding involves melting the base materials, often with a filler material, to create a metallurgical bond. This process requires high energy and can result in significant heat-affected zones.
- Brazing, on the other hand, does not melt the base materials, allowing for more precise control of tolerances and minimal distortion.
-
Advantages of Brazing:
- Precision and Minimal Distortion: Since the base materials do not melt, brazing allows for precise control of tolerances and minimal distortion, making it ideal for high-precision applications.
- Joint Strength: Brazed joints are as strong as the base metals, providing durable and reliable connections.
- Versatility: Brazing can join dissimilar metals and is suitable for a wide range of applications, including those requiring high strength and precision.
-
Process and Mechanism:
- Brazing involves heating the base materials and the filler metal to a temperature above the filler's melting point but below the melting point of the base materials.
- The filler metal is drawn into the joint by capillary action, creating a strong bond as it cools and solidifies.
- This process can be performed using various heat sources, including torches, furnaces, and induction heating.
-
Applications of Brazing:
- Brazing is widely used in industries requiring strong, precise, and durable joints, such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, and HVAC systems.
- It is particularly useful for joining dissimilar metals and creating complex assemblies with minimal distortion.
By understanding these key points, equipment and consumable purchasers can make informed decisions about when and how to use brazing, ensuring optimal results for their specific applications.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Filler metal melts above 450°C (840°F), base materials remain solid. |
| Comparison with Soldering | Soldering uses lower melting points (<450°C), brazing creates stronger joints. |
| Comparison with Welding | Welding melts base materials, brazing avoids melting for minimal distortion. |
| Advantages | Precise tolerances, minimal distortion, strong joints, versatile for dissimilar metals. |
| Applications | Aerospace, automotive, electronics, HVAC, and more. |
Discover how brazing can enhance your projects—contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is graphite resistant to heat? Unlocking Its Exceptional Thermal Stability
- What is the thermal property of graphite? Mastering Extreme Heat Management
- Why is a high-vacuum graphite heating element furnace used for HAp sintering? Achieve Pure, High-Bond Coatings
- Why does graphite have a high melting point? The Power of Its Giant Covalent Structure
- How does a high-temperature furnace contribute to the post-synthesis heat treatment of Fe-Cr-Mn-Mo-N-C composites?



















