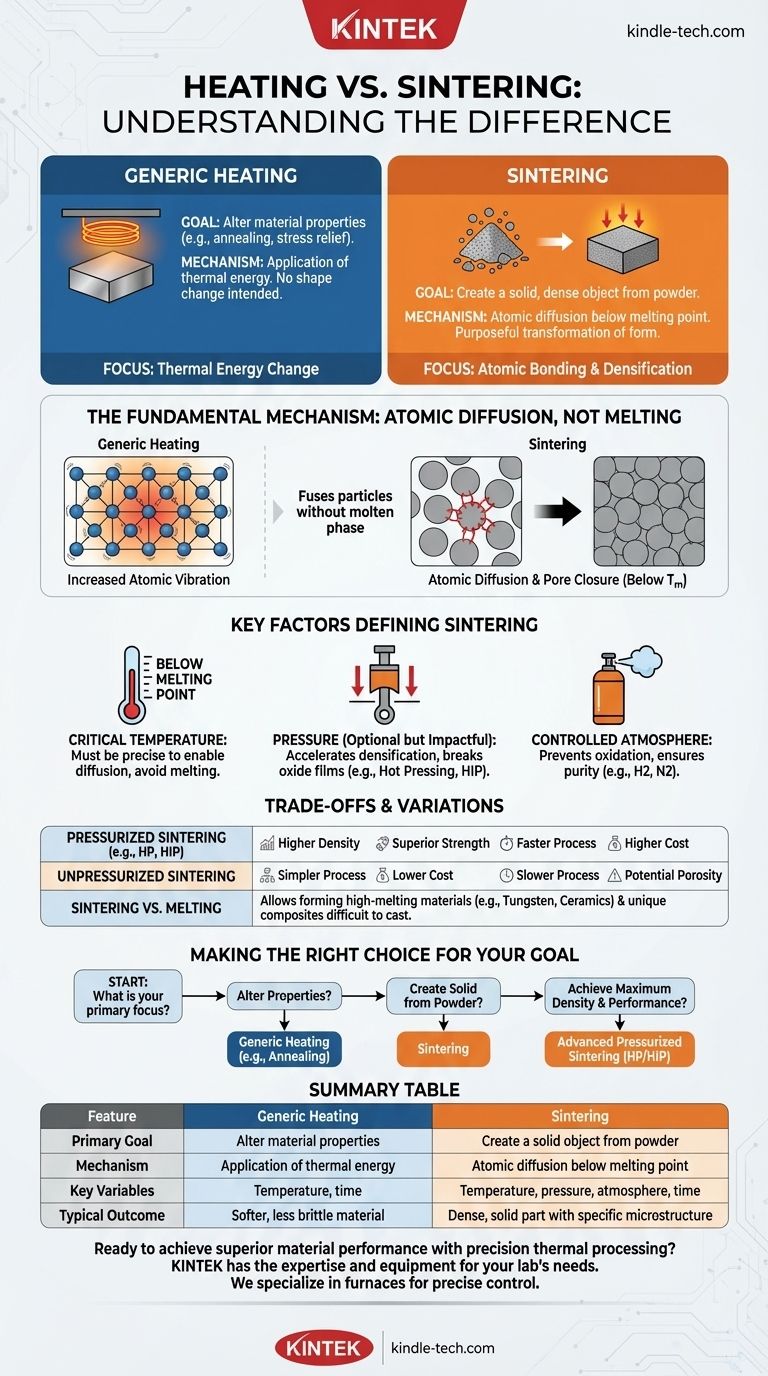
At its core, heating is the general act of increasing a material's temperature, while sintering is a specific manufacturing process that uses heat to bond particles together into a solid object without melting them. Sintering is a purposeful transformation of form—turning a powder into a solid—whereas heating is simply a change in thermal energy that can be used for many different purposes.
The crucial distinction is one of intent and mechanism. Heating is a tool. Sintering is a goal-oriented process that uses that tool, along with pressure and a controlled environment, to achieve atomic-level bonding and create a dense, solid part from a powder.

The Fundamental Goal: From Particles to a Solid Mass
To truly grasp the difference, we must look beyond the heat source and focus on the intended outcome for the material.
What is Generic Heating?
Heating is the application of thermal energy to an object. Its purpose can vary widely.
For example, a process like annealing involves heating a metal and then cooling it slowly. The goal is not to create a new shape but to alter the material's internal crystal structure, making it softer and less brittle.
What is Sintering?
Sintering is a manufacturing method used to create objects from powdered material. This is a cornerstone of powder metallurgy and ceramic fabrication.
The process involves taking a powder, often compacted into a desired shape (a "green part"), and heating it in a controlled furnace. The key is that the temperature is kept below the material's melting point.
The Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion, Not Melting
Sintering works through a phenomenon called atomic diffusion. At high temperatures, the atoms in the individual powder particles become agitated and begin to migrate across the boundaries where the particles touch.
This atomic movement closes the gaps between particles, fusing them together and causing the object to shrink and increase in density. This is fundamentally different from melting processes like soldering or welding, which use a molten phase to join parts.
Key Factors that Define the Sintering Process
Sintering is a highly engineered process, not just simple heating. Several factors must be precisely controlled to achieve the desired outcome.
The Critical Role of Temperature
The sintering temperature is a carefully selected value within a specific range.
If the temperature is too low, diffusion will not occur, and the particles will not bond. If it is too high, the material will begin to melt, losing its shape and desired microstructure.
The Impact of Pressure
Sintering can be broadly divided into two categories: unpressurized and pressurized.
Unpressurized sintering relies solely on heat to drive diffusion. In pressurized sintering, an external force is applied during heating. This pressure helps break down surface oxide films on the powder, accelerates densification, and can result in superior material properties. Processes like Hot Pressing (HP) and Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) fall into this category.
The Importance of Atmosphere
The gas environment inside the furnace is critical. Many materials, especially non-oxide ceramics and metals, require a specific atmosphere to prevent unwanted chemical reactions.
For instance, sintering metals or carbides may require a hydrogen or nitrogen atmosphere to prevent oxidation and help achieve a fully dense, pure final part.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
Choosing a thermal process depends entirely on the starting material and the desired end product. The differences between methods highlight critical trade-offs in manufacturing.
Pressurized vs. Unpressurized Sintering
Unpressurized sintering is generally simpler and less expensive. However, it can be a slower process and may not achieve the same level of density as pressurized methods.
Pressurized sintering, while more complex and costly, significantly reduces process time and produces parts with higher density and superior mechanical strength. The pressure actively aids the diffusion process, making it an "activated" form of sintering.
Sintering vs. True Melting Processes
The primary advantage of sintering is its ability to create objects from materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten or ceramics. Melting and casting these materials would be incredibly difficult and energy-intensive.
Sintering also allows for the creation of unique material blends and composites that would be impossible to form through melting.
Common Pitfalls: Incomplete Densification
The main challenge in sintering is achieving full density. If the temperature, pressure, or atmosphere are not optimized, the resulting part can be porous and mechanically weak.
Pores are defects that act as stress concentrators, compromising the strength and performance of the final component. This is why the process parameters must be so tightly controlled.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice between simple heating and a complex sintering process is dictated by your final objective.
- If your primary focus is changing a material's properties (like softening it): A specific heating and cooling cycle, such as annealing, is the correct approach.
- If your primary focus is creating a solid, dense object from a powder: Sintering is the necessary manufacturing process.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and superior mechanical performance from a powder: Advanced, pressurized sintering methods like Hot Pressing or HIP are required.
Ultimately, understanding this distinction is the key to mastering material transformation and selecting the right process for the job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Generic Heating | Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Alter material properties (e.g., annealing) | Create a solid object from powder |
| Mechanism | Application of thermal energy | Atomic diffusion below melting point |
| Key Variables | Temperature, time | Temperature, pressure, atmosphere, time |
| Typical Outcome | Softer, less brittle material | Dense, solid part with specific microstructure |
Ready to achieve superior material performance with precision thermal processing?
Whether your goal is annealing metals or creating high-density components through advanced sintering, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory's needs. We specialize in lab furnaces and consumables for precise temperature control and controlled atmosphere applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your sintering or heating processes for stronger, more reliable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between DC sputtering and RF sputtering? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material
- Is lab-grown diamond business profitable? Navigate Falling Prices & Build a Profitable Brand
- What is the advantage of sputtering? Achieve Superior, High-Purity Thin Films from Any Material
- Is heat treatment necessary? A Guide to Making the Right Engineering Choice
- How much pressure is required in DC sputtering? Optimize Your Thin-Film Deposition Process
- How does a laboratory forced-air drying oven process ternary nanocomposite products? Ensure Nanostructural Integrity
- What is used for sintering? A Guide to Materials, Equipment, and the Process
- How hot can a metal surface get in the sun? The Surprising Science Behind Extreme Heat



















