In short, the efficiency of induction melting is exceptionally high because it transfers energy directly into the metal without combustion. This results in fast melting rates, minimal material loss from oxidation, and precise temperature control. Rather than a single percentage, its true efficiency is best understood as a combination of superior energy conversion, high product yield, and operational speed.
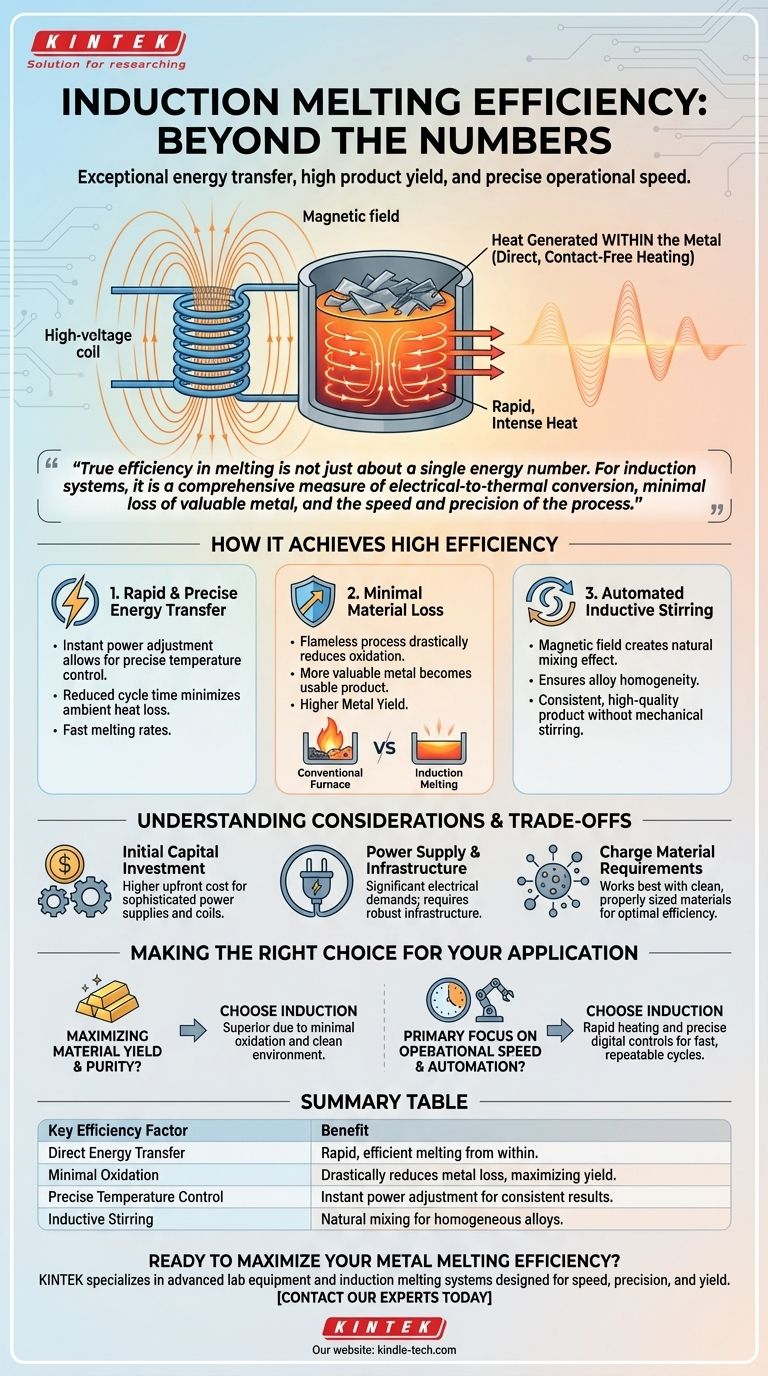
True efficiency in melting is not just about a single energy number. For induction systems, it is a comprehensive measure of electrical-to-thermal conversion, minimal loss of valuable metal, and the speed and precision of the process.

How Induction Melting Achieves High Efficiency
Induction melting is not efficient by accident; it is a direct result of its fundamental operating principle. Unlike fuel-fired furnaces that heat a chamber and then the metal, induction turns the metal itself into the source of the heat.
The Principle: Direct, Contact-Free Heating
An induction furnace uses a powerful, high-voltage coil to generate a strong magnetic field. When conductive material like metal is placed inside this field, the field induces a high-current, low-voltage electrical flow directly within the metal.
This internal electrical resistance generates rapid and intense heat, causing the metal to melt from the inside out. This method of heat transfer is fundamentally more efficient than external heating.
Factor 1: Rapid and Precise Energy Transfer
Because the heat is generated within the charge material, melting is extremely fast. The power can be adjusted instantly, allowing for precise temperature control that is difficult to achieve with combustion-based systems.
This speed and control reduce the total energy consumed per cycle, as there is less time for ambient heat loss.
Factor 2: Minimal Material Loss
In conventional furnaces, the open flame and direct exposure to air cause significant oxidation, turning valuable metal into worthless slag. This is a major source of financial loss.
Induction melting is a clean, flameless process. This drastically reduces oxidation losses, meaning more of the metal you put into the furnace comes out as usable product. This improvement in metal yield is a critical component of its overall efficiency.
Factor 3: Automated Stirring for Alloy Homogeneity
The magnetic field that heats the metal also creates a natural stirring or mixing effect within the molten bath. This inductive stirring is a unique and valuable feature.
It ensures that alloys are mixed evenly and thoroughly, leading to a higher-quality, more consistent final product without the need for mechanical stirring. This enhances the efficiency of the alloying process itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While highly efficient, induction melting is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Initial Capital Investment
Induction furnaces require sophisticated high-frequency power supplies and carefully engineered, water-cooled coils. This technology generally represents a higher upfront capital cost compared to simpler cupola or crucible furnaces.
Power Supply and Infrastructure
These systems are entirely electric and can have significant power demands. Your facility's electrical infrastructure must be capable of supporting the high-voltage and high-current requirements of the furnace.
Charge Material Requirements
Induction works best with relatively clean and properly sized charge materials. Very fine, loose scrap or materials contaminated with non-conductive substances can melt less efficiently.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use induction melting should be based on your specific production goals.
- If your primary focus is maximizing material yield and purity: Induction is the superior choice due to its minimal oxidation and clean melting environment.
- If your primary focus is operational speed and automation: The rapid heating and precise digital controls of induction systems allow for fast, repeatable production cycles.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance and operator safety: Induction is ideal, as it produces no combustion byproducts and eliminates the hazards of storing and handling fossil fuels.
Ultimately, induction melting delivers its value by transforming electrical energy into high-quality molten metal with unparalleled precision and minimal waste.
Summary Table:
| Key Efficiency Factor | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Direct Energy Transfer | Heat is generated within the metal itself for rapid, efficient melting. |
| Minimal Oxidation | Flameless process drastically reduces metal loss, maximizing yield. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Instant power adjustment ensures consistent, high-quality results. |
| Inductive Stirring | Natural mixing effect creates homogeneous alloys without mechanical parts. |
Ready to maximize your metal melting efficiency?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including induction melting systems. Our solutions are designed to deliver the speed, precision, and material yield your laboratory demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how an induction furnace can transform your metal processing workflow and boost your productivity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity



















