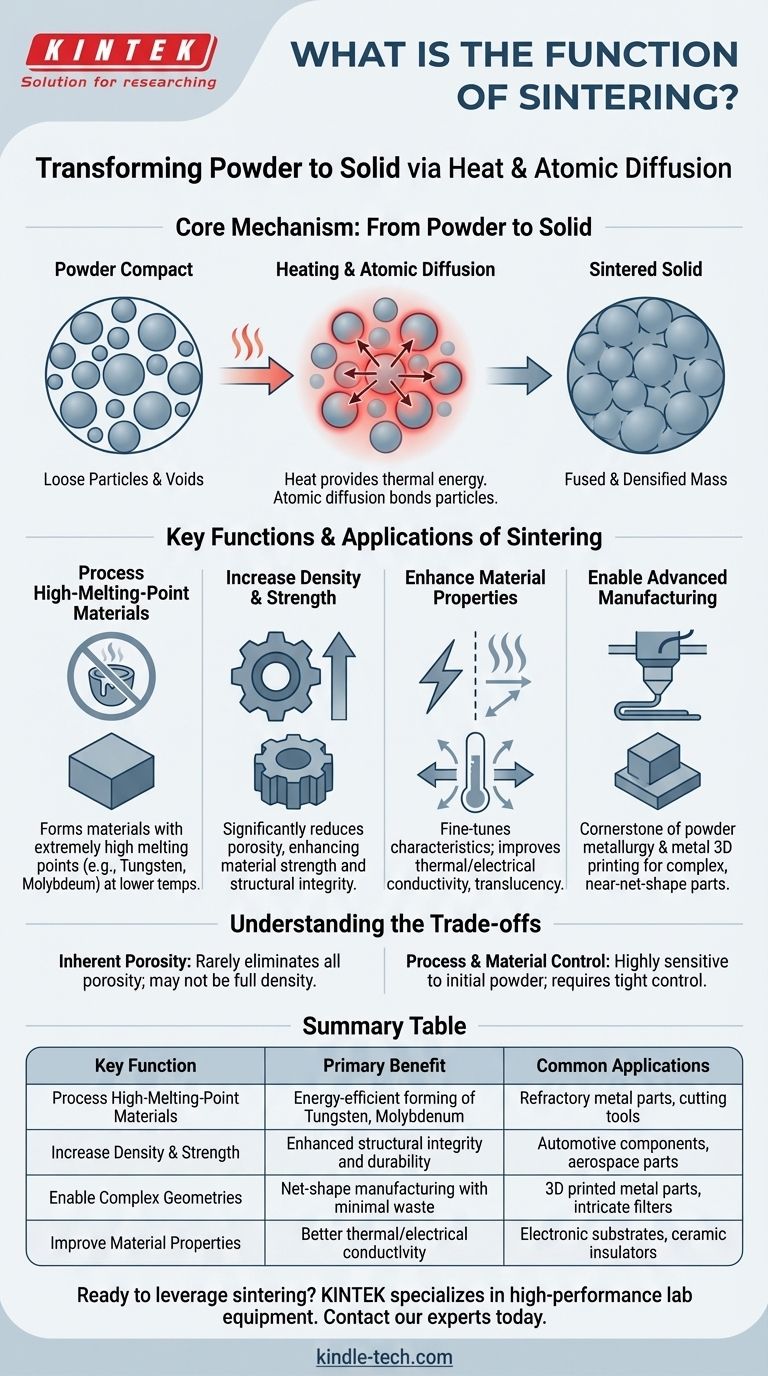
The primary function of sintering is to transform a mass of powder into a solid, coherent object using heat. This process occurs at temperatures below the material's melting point, relying on atomic diffusion to fuse individual particles together, which increases the material's strength, density, and integrity.
Sintering allows us to create strong, solid components from metal or ceramic powders without having to melt them. This makes it an indispensable and energy-efficient tool for processing materials with extremely high melting points and for advanced manufacturing techniques like 3D printing.
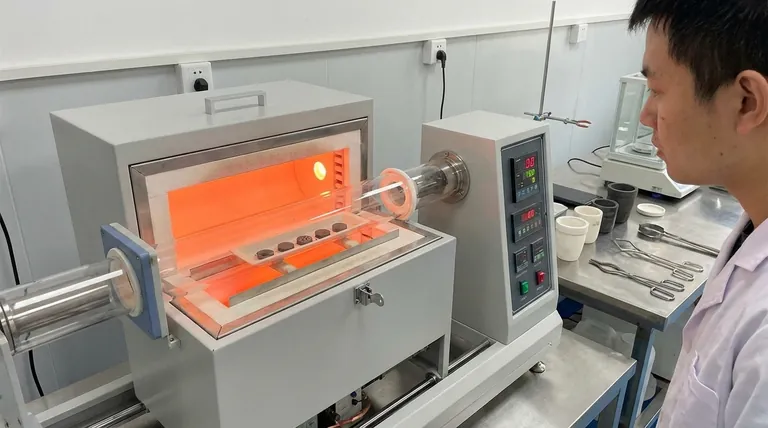

The Core Mechanism: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is fundamentally a thermal transformation process. It takes a compacted or loose collection of particles and uses controlled heating to bond them into a single, densified piece.
The Role of Heat and Pressure
Heat is the primary driver of sintering. It provides the necessary thermal energy for atoms within the particles to become mobile.
While not always required, pressure is often applied to press the powder particles into close contact, which reduces the distance atoms need to travel and accelerates the bonding process.
Atomic Diffusion: The Key to Fusion
Instead of melting, sintering relies on atomic diffusion. At elevated temperatures, atoms migrate across the boundaries of adjacent particles.
This atomic movement effectively fills the voids between particles and creates strong metallurgical bonds, fusing the separate grains into a single, solid mass with a more refined microstructure.
Key Functions and Applications of Sintering
Engineers and manufacturers choose sintering for several distinct and powerful advantages over other methods like casting.
Processing High-Melting-Point Materials
This is one of sintering's most critical functions. For metals like tungsten and molybdenum, which have extremely high melting points, melting them is impractical and prohibitively expensive.
Sintering allows these materials to be formed into solid, usable parts at much lower temperatures, saving significant energy and overcoming technical hurdles.
Increasing Material Density and Strength
The initial powder compact is porous. The sintering process significantly reduces this porosity by pulling the particles together.
Reducing the empty space between particles dramatically increases the object's overall density, which directly contributes to higher material strength and structural integrity.
Enhancing Material Properties
By controlling the sintering process, it's possible to fine-tune a material's final characteristics.
Proper sintering can significantly improve thermal and electrical conductivity, as the fused particle boundaries create a more efficient path for energy to travel. For some ceramics, it can even increase translucency.
Enabling Advanced Manufacturing
Sintering is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, particularly in powder metallurgy and metal 3D printing.
It allows for the creation of complex, near-net-shape parts directly from a powder bed, minimizing waste and the need for subsequent machining.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the sintering process has inherent characteristics that must be considered for any application.
Inherent Porosity
Although sintering significantly densifies a material, it rarely eliminates porosity completely. A sintered part may not be as fully dense as one that was cast from a liquid state.
This residual porosity can be a limiting factor for applications requiring the absolute maximum mechanical strength or hermetic sealing.
Process and Material Control
The final properties of a sintered part are highly sensitive to the characteristics of the initial powder, including particle size and shape.
Achieving consistent, repeatable results requires tight control over temperature, time, and atmospheric conditions during the entire sintering cycle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting sintering depends entirely on the material you are using and the final properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is working with high-temperature materials: Sintering is the most practical and energy-efficient method for forming parts from metals like tungsten.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, net-shape parts: Sintering, especially in 3D printing, excels at producing intricate designs with minimal material waste.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific material properties: Sintering provides a unique level of control over a part's final density, conductivity, and strength.
Ultimately, sintering serves as a foundational process for engineering advanced materials with precision and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Primary Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Process High-Melting-Point Materials | Energy-efficient forming of tungsten, molybdenum | Refractory metal parts, cutting tools |
| Increase Density & Strength | Enhanced structural integrity and durability | Automotive components, aerospace parts |
| Enable Complex Geometries | Net-shape manufacturing with minimal waste | 3D printed metal parts, intricate filters |
| Improve Material Properties | Better thermal/electrical conductivity | Electronic substrates, ceramic insulators |
Ready to leverage sintering for your laboratory or manufacturing needs? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for material processing. Whether you're working with advanced ceramics, metal powders, or developing new sintering protocols, our solutions deliver precise temperature control and consistent results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your research and production goals with reliable sintering furnaces and accessories.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry
- What are the primary functions of high-precision tube furnaces in graphene growth? Achieve Defect-Free GS Synthesis
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- How does an industrial tube furnace ensure the required process conditions for supercritical fluid experimental devices?



















