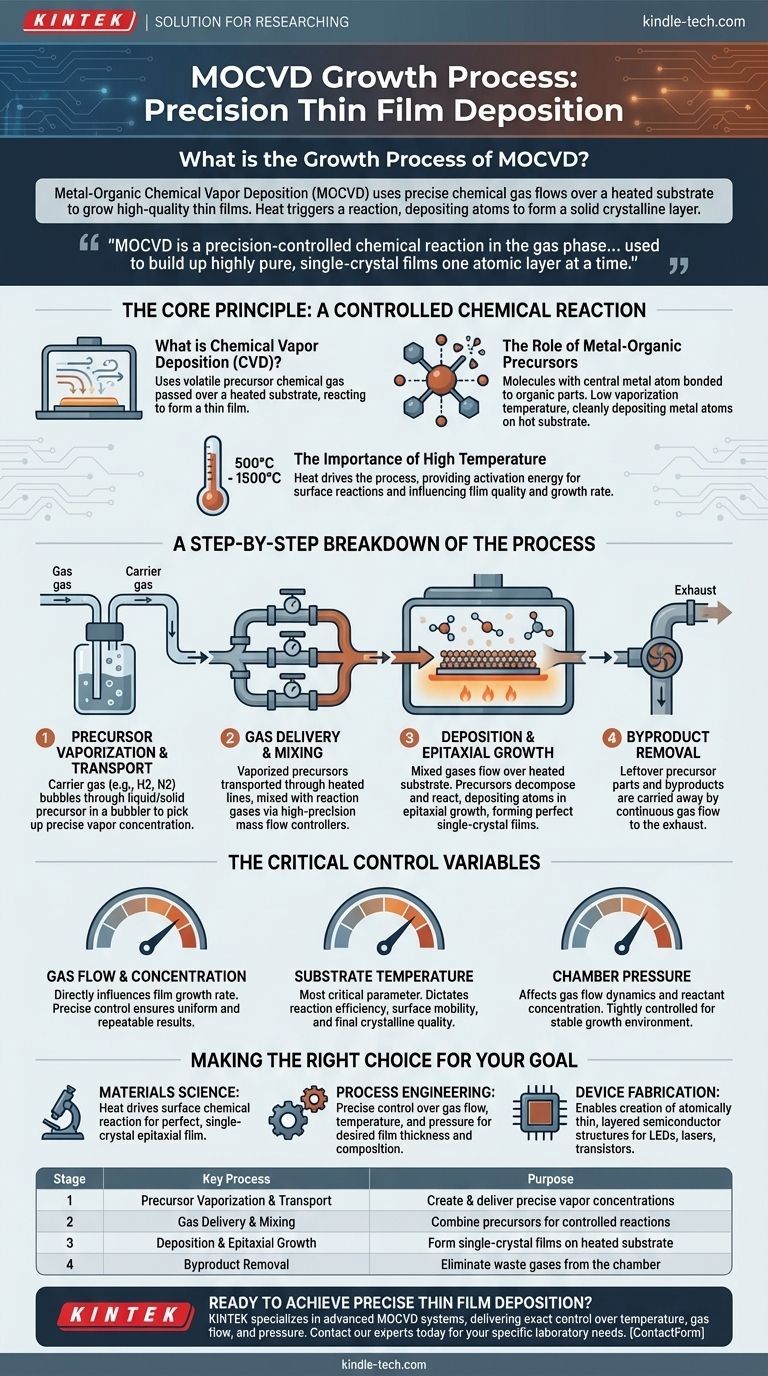
In essence, the Metal-Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD) process grows high-quality thin films by flowing specific chemical gases over a heated surface, known as a substrate. The heat triggers a chemical reaction, causing atoms from the gas to deposit onto the surface and form a new, solid crystalline layer. This process is broken down into four key stages: precursor vaporization and transport, gas delivery and mixing, chemical deposition on the substrate, and the removal of byproducts.
MOCVD is fundamentally a precision-controlled chemical reaction in the gas phase. It uses heat to "crack" metal-organic precursor molecules on a substrate, allowing engineers to build up highly pure, single-crystal films one atomic layer at a time, which is the foundation for manufacturing many modern electronic and optoelectronic devices.

The Core Principle: A Controlled Chemical Reaction
What is Chemical Vapor Deposition?
MOCVD is a specific type of a broader industrial process called Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). The fundamental idea behind any CVD process is to use a volatile, or gaseous, precursor chemical that contains the atoms you want to deposit.
This gas is passed over a heated substrate, and the thermal energy causes the precursor to decompose or react, leaving behind a thin film of the desired material on the surface.
The Role of Metal-Organic Precursors
The "MO" in MOCVD stands for metal-organic. These are specially designed molecules that contain a central metal atom (like gallium, aluminum, or indium) bonded to organic molecules.
The key advantage of these precursors is that they can be turned into a vapor at relatively low temperatures. When they reach the hot substrate, the bonds break, cleanly depositing the metal atom while the organic parts are carried away as gaseous byproducts.
The Importance of High Temperature
Heat is the engine of the MOCVD process. The substrate is typically heated to temperatures between 500 and 1500 degrees Celsius.
This intense heat provides the necessary activation energy for the chemical reactions to occur directly on the substrate's surface. The specific temperature is a critical variable that influences the film's quality, crystal structure, and growth rate.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process
Step 1: Precursor Vaporization and Transport
The process begins with the metal-organic sources, which are often liquids or solids. To transport them, a carrier gas (like hydrogen or nitrogen) is bubbled through the liquid precursor in a device called a bubbler.
This picks up a precise, reproducible concentration of the precursor vapor, which is then carried from the bubbler toward the reaction chamber. Controlling this concentration is the first step in controlling the final film.
Step 2: Gas Delivery and Mixing
The vaporized metal-organic precursors are transported through temperature-controlled lines. Before entering the main chamber, they are mixed with other necessary reaction gases.
These gases are all controlled by high-precision mass flow controllers to ensure the exact chemical mixture required for the specific material being grown enters the reactor.
Step 3: Deposition and Epitaxial Growth
The precisely mixed gases flow over the heated substrate inside the reaction chamber. The high temperature causes the precursors to decompose and react on the surface, depositing a thin layer of atoms.
This process typically results in epitaxial growth, meaning the deposited atoms align with the underlying crystal structure of the substrate. This creates a perfect, single-crystal film, which is essential for high-performance devices.
Step 4: Byproduct Removal
As the desired atoms deposit on the surface, the leftover parts of the precursor molecules (ligands) and other reaction byproducts are formed.
These waste products, along with any unreacted precursor gases, are simply carried away by the continuous gas flow and removed from the chamber's exhaust system.
The Critical Control Variables
Gas Flow and Concentration
The rate at which precursor gases are delivered to the chamber directly influences the growth rate of the film. Precise and stable control over gas flow is necessary for uniform and repeatable results.
Substrate Temperature
Temperature is arguably the most critical parameter. It dictates the reaction efficiency, the surface mobility of the atoms, and the final crystalline quality of the film. Too low a temperature results in a poor-quality film, while too high can cause unwanted side reactions.
Chamber Pressure
The pressure inside the reaction chamber affects the gas flow dynamics and the concentration of reactants at the substrate surface. It is another key variable that must be tightly controlled to ensure a stable and predictable growth environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the MOCVD process is about seeing how chemistry and engineering work together to create advanced materials.
- If your primary focus is materials science: The key takeaway is how heat energy drives a surface chemical reaction to create a perfect, single-crystal epitaxial film.
- If your primary focus is process engineering: The key takeaway is that MOCVD is a system demanding precise and repeatable control over gas flow, temperature, and pressure to achieve a desired film thickness and composition.
- If your primary focus is device fabrication: The key takeaway is that this process enables the creation of the atomically thin, layered semiconductor structures that form the basis of LEDs, lasers, and high-power transistors.
Ultimately, MOCVD is a powerful technique for building materials from the atom up, enabling the technology that defines our modern world.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Precursor Vaporization & Transport | Create and deliver precise vapor concentrations |
| 2 | Gas Delivery & Mixing | Combine precursors for controlled reactions |
| 3 | Deposition & Epitaxial Growth | Form single-crystal films on heated substrate |
| 4 | Byproduct Removal | Eliminate waste gases from the chamber |
Ready to achieve precise thin film deposition in your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced MOCVD systems and lab equipment, delivering the exact control over temperature, gas flow, and pressure that your semiconductor research or production requires. Our solutions empower you to grow high-quality epitaxial layers for next-generation optoelectronic devices. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What are the methods used to synthesize graphene? Master Scalable Production with CVD
- What is a primary challenge in producing usable graphene sheets after CVD? Overcoming the Transfer Bottleneck
- What is the construction and working of chemical vapour deposition? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Film Coating
- What is an example of chemical vapor deposition CVD? Creating the Microchips That Power Our World
- What is hot filament chemical vapor deposition? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond Film Growth
- What is LPCVD advantages and disadvantages? Balancing Film Quality and Thermal Budget
- How does pressure affect deposition? Mastering the Key to High-Quality Film Growth
- How are optical coatings applied? Achieve Precision with Advanced Vacuum Deposition Methods



















