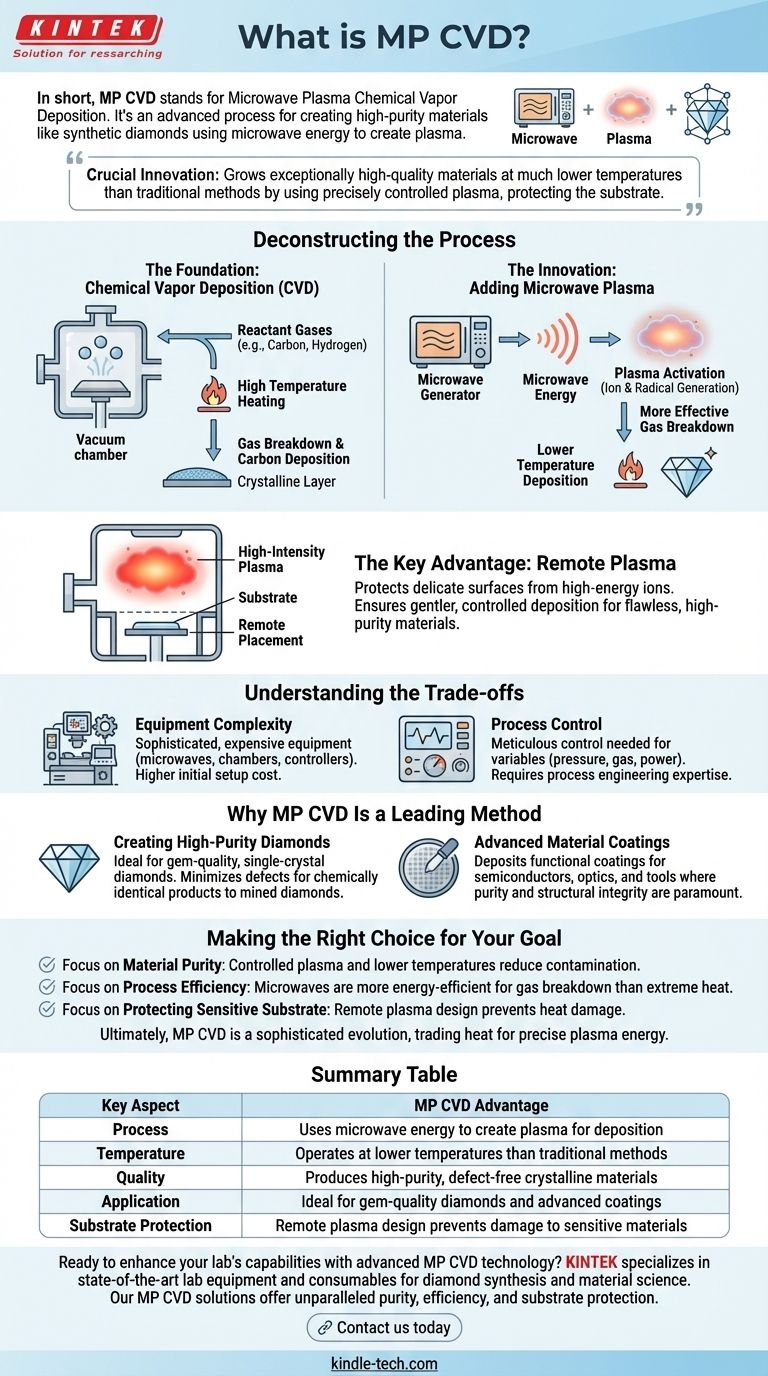
In short, MP CVD stands for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition. It is a highly advanced process used to create synthetic diamonds and other high-purity crystalline materials inside a controlled laboratory environment. This method uses microwave energy to excite a gas into a plasma state, which then breaks down and deposits onto a substrate, layer by layer.
The crucial innovation of MP CVD is its ability to grow exceptionally high-quality materials at much lower temperatures than traditional methods. It achieves this by using a precisely controlled plasma to activate the chemical reaction, rather than relying on brute-force heat, which protects the substrate from potential damage.

Deconstructing the Process
To understand MP CVD, it's best to break it down into its core components: the foundational method (CVD) and the key innovation (Microwave Plasma).
The Foundation: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
The general CVD process involves placing a substrate, often a small diamond seed, into a vacuum chamber.
Reactant gases, typically a mixture of a carbon source like methane and hydrogen, are then introduced into this chamber.
The chamber is heated to a very high temperature, causing the gas molecules to break down and deposit their carbon atoms onto the substrate, slowly building up a new crystalline layer.
The Innovation: Adding Microwave Plasma
MP CVD enhances this process by adding microwave energy. This energy "activates" the reactant gases, turning them into a plasma—an energized cloud of ions and radicals.
This plasma is far more effective at breaking down the reactant molecules than heat alone. This allows the deposition to occur at significantly lower temperatures.
The Key Advantage: Remote Plasma
A critical feature of many MP CVD systems is that the substrate is not placed directly within the most intense part of the plasma discharge.
This "remote" placement protects the delicate growing surface from being damaged by high-energy ions. It ensures a gentler, more controlled deposition, which is essential for creating flawless, high-purity materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the MP CVD method is not without its complexities. A clear understanding of its trade-offs is necessary for a complete picture.
Equipment Complexity
MP CVD systems require sophisticated and expensive equipment, including microwave generators, vacuum chambers, and precise gas flow controllers. This makes the initial setup more costly than simpler thermal CVD methods.
Process Control
Managing a stable plasma requires meticulous control over variables like pressure, gas composition, and microwave power. Any deviation can impact the quality and uniformity of the final product, demanding significant process engineering expertise.
Why MP CVD Is a Leading Method
The advantages of the MP CVD process make it a dominant technique, particularly in the production of high-quality synthetic diamonds.
Creating High-Purity Diamonds
The lower-temperature, highly controlled environment is ideal for growing gem-quality, single-crystal diamonds. This minimizes the risk of structural defects or impurities, resulting in a product that is chemically and physically identical to a mined diamond.
Advanced Material Coatings
Beyond diamonds, MP CVD is used to deposit a wide range of functional coatings. These thin films are used in semiconductors, optics, and wear-resistant tools where purity and structural integrity are paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the principles of MP CVD allows you to recognize its purpose in different applications.
- If your primary focus is material purity: MP CVD is superior because the controlled plasma and lower temperatures reduce the risk of contamination and structural flaws.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Using microwaves to generate a plasma is a more energy-efficient way to break down precursor gases compared to relying solely on extreme heat.
- If your primary focus is protecting a sensitive substrate: The remote plasma design is the critical feature, preventing heat damage and ensuring the integrity of the material being coated.
Ultimately, MP CVD represents a sophisticated evolution of material science, trading simple heat for precise plasma energy to achieve unparalleled quality and control.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | MP CVD Advantage |
|---|---|
| Process | Uses microwave energy to create plasma for deposition |
| Temperature | Operates at lower temperatures than traditional methods |
| Quality | Produces high-purity, defect-free crystalline materials |
| Application | Ideal for gem-quality diamonds and advanced coatings |
| Substrate Protection | Remote plasma design prevents damage to sensitive materials |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with advanced MP CVD technology? KINTEK specializes in providing state-of-the-art lab equipment and consumables for diamond synthesis and material science. Our MP CVD solutions offer unparalleled purity, efficiency, and substrate protection for your research and production needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can accelerate your material innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
People Also Ask
- How plasma is used in diamond coating films? Unlock the Power of MPCVD for Superior Coatings
- How does a microwave plasma reactor facilitate the synthesis of diamond? Master MPCVD with Precision Technology
- What is the difference between MPCVD and HFCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- How does Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapour Deposition (MPCVD) work? Your Guide to High-Purity Diamond Film Growth
- What is the frequency of MPCVD? A Guide to Choosing 2.45 GHz vs. 915 MHz for Your Application


















