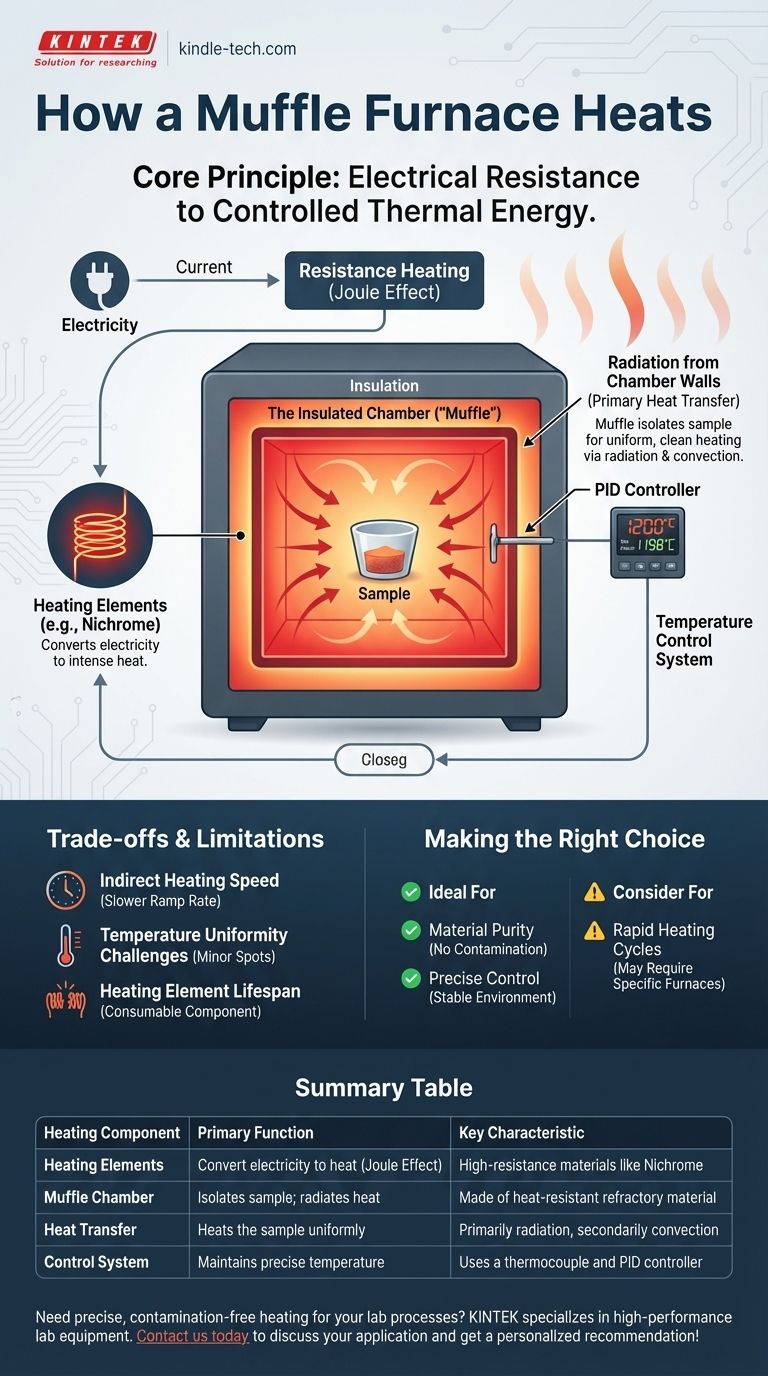
At its core, a muffle furnace heats materials using electrical resistance. It converts electrical energy into intense, controlled thermal energy within an insulated chamber. This design isolates the sample from the raw heating elements, ensuring uniform heating without direct contact or contamination from the heat source.
A muffle furnace is not defined by a single heating method but by its architecture. It uses electric resistance coils to heat a sealed inner chamber (the "muffle"), which then transfers that heat to the sample inside primarily through radiation and natural convection, ensuring a clean and uniform high-temperature environment.

The Fundamental Principle: From Electricity to Heat
The entire operation begins with a simple, powerful principle of physics. Understanding this foundation is key to grasping how the furnace achieves such high temperatures with precision.
Resistance Heating (Joule Effect)
A muffle furnace is a type of electric furnace. Its heat source is generated by the Joule effect, also known as resistance heating.
When an electric current passes through a conductor with electrical resistance, electrical energy is converted directly into heat energy. This is the fundamental energy conversion that powers the furnace.
The Role of Heating Elements
To create this heat, the furnace uses specialized heating elements, often made of high-resistance materials like Nichrome wire.
These elements are designed to withstand extremely high temperatures and efficiently convert the flow of electricity into the thermal energy needed to heat the furnace chamber.
How the Furnace Architecture Delivers Heat
The way a muffle furnace is constructed is just as important as how it generates heat. The architecture is designed to contain, control, and uniformly deliver that heat to a sample.
The Insulated Chamber (The "Muffle")
The central feature is the heating chamber, or muffle. This chamber is made of a heat-resistant refractory material that prevents heat from escaping.
Crucially, it acts as a barrier, separating the sample from the actual heating elements. This isolation is the defining characteristic of a muffle furnace, preventing any chemical contamination from the elements.
Radiation from Chamber Walls
The heating elements heat the outside walls of the muffle chamber. These walls absorb the energy and become extremely hot.
The primary method of heat transfer is then thermal radiation. The hot interior walls of the muffle radiate heat evenly inward, bathing the sample in thermal energy from all directions.
Convection Within the Chamber
A secondary heating mechanism is natural convection. The air (or atmosphere) sealed inside the muffle chamber gets heated by the hot walls.
This heated air circulates within the chamber, transferring additional heat to the surfaces of the sample and helping to ensure a uniform temperature throughout.
The Temperature Control System
Modern furnaces provide precise control. A thermocouple acts as a sensor, constantly measuring the temperature inside the chamber.
This sensor feeds data to a PID controller (Proportional-Integral-Derivative), which acts as the furnace's brain. It intelligently adjusts the electrical power sent to the heating elements to maintain the desired temperature with high accuracy.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the design of a muffle furnace presents inherent trade-offs that are important to recognize for effective use.
Indirect Heating Speed
Because the heat is transferred indirectly (element → chamber → sample), the time it takes to reach the target temperature, or the "ramp rate," can be slower than direct heating methods.
Temperature Uniformity Challenges
While designed for uniformity, slight temperature variations can still exist. Loading the furnace improperly or the aging of heating elements can create minor hot or cold spots within the chamber.
Heating Element Lifespan
The heating elements operate under extreme thermal stress. Over time, they degrade and will eventually fail, requiring repair or replacement. They are a consumable component of the furnace system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the heating mechanism allows you to align the furnace's capabilities with your specific thermal processing needs.
- If your primary focus is material purity and avoiding contamination: The muffle furnace is ideal, as its core design isolates your sample from the heating elements.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature control: The combination of a PID controller, robust insulation, and indirect heating provides a highly stable and repeatable thermal environment.
- If your primary focus is rapid heating cycles: Be aware that the standard ramp-up time can be a limitation, and you may need to look for furnaces specifically designed for high ramp rates.
By understanding this mechanism, you can leverage the muffle furnace not just as a tool, but as a precise instrument for achieving your material processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Heating Component | Primary Function | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Elements | Convert electricity to heat (Joule Effect) | High-resistance materials like Nichrome |
| Muffle Chamber | Isolates sample; radiates heat | Made of heat-resistant refractory material |
| Heat Transfer | Heats the sample uniformly | Primarily radiation, secondarily convection |
| Control System | Maintains precise temperature | Uses a thermocouple and PID controller |
Need precise, contamination-free heating for your lab processes?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including a range of muffle furnaces designed for accuracy and durability. Our experts can help you select the perfect furnace to meet your specific material processing goals.
Contact us today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the heating mechanism of a muffle furnace? Achieve Clean, Uniform High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a chamber furnace? Understand the Key Distinctions for Your Lab
- What is the maximum temperature of muffle furnace? A Guide from 1100°C to 1800°C
- What is the difference between hot air oven and muffle furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Thermal Needs
- How is heat transferred in a furnace? Master Radiation, Convection & Conduction



















