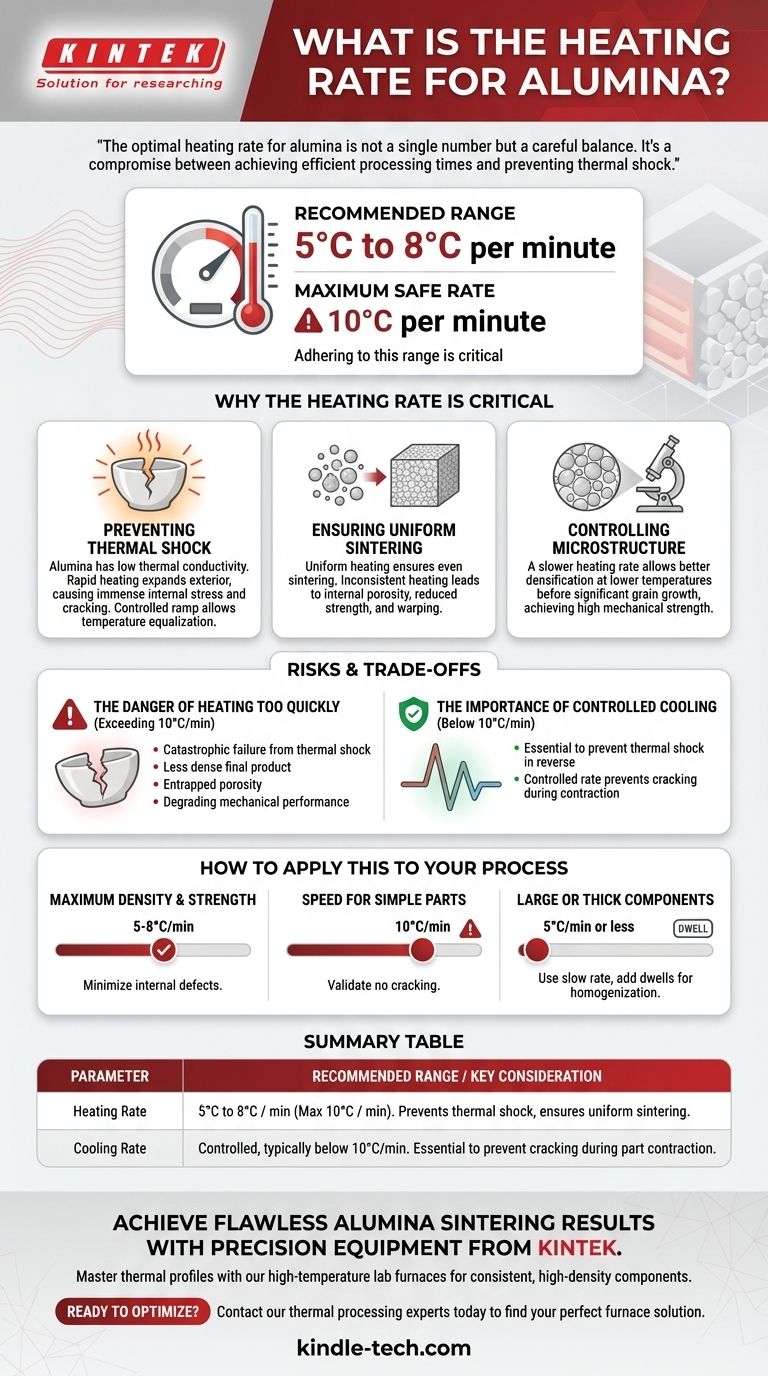
For processing alumina, the generally recommended heating rate is between 5°C to 8°C per minute, with a maximum safe rate of 10°C per minute. Adhering to this range is critical for achieving the desired material properties and preventing catastrophic failure of the part due to thermal stress.
The optimal heating rate for alumina is not a single number but a careful balance. It's a compromise between achieving efficient processing times and preventing thermal shock, which can cause cracking and compromise the final integrity of the ceramic component.

Why the Heating Rate is Critical
The rate at which you heat alumina directly influences the final quality of the component. This is not a step to be rushed; it is a fundamental process parameter that controls the material's transformation at a microscopic level.
Preventing Thermal Shock
Alumina, like most ceramics, has low thermal conductivity. This means heat does not travel through it quickly.
If you heat the exterior too rapidly, it expands while the interior remains cool and unexpanded. This difference in expansion creates immense internal stress, which can easily lead to cracks or complete fracture. A slow, controlled ramp rate allows the temperature to equalize throughout the part.
Ensuring Uniform Sintering
Sintering is the process where individual ceramic particles fuse together at high temperatures, creating a dense, solid part.
Uniform heating ensures this process happens evenly throughout the component. If some areas heat faster than others, you will get inconsistent densification, leading to internal porosity, reduced strength, and dimensional warping.
Controlling Microstructure
The final properties of the alumina—such as its hardness, strength, and translucency—are determined by its microstructure, specifically its grain size.
A slower heating rate generally allows for better densification at lower temperatures before significant grain growth occurs, which is often desirable for achieving high mechanical strength.
The Risks and Trade-offs
Choosing a heating rate involves balancing process speed against material quality. Deviating from the recommended range has significant consequences.
The Danger of Heating Too Quickly
Exceeding the 10°C/min maximum is highly inadvisable. The primary risk is catastrophic failure from thermal shock, especially in larger or more complex geometries.
Even if the part doesn't visibly crack, rapid heating can lead to a less dense final product with entrapped porosity, severely degrading its mechanical performance.
The Importance of Controlled Cooling
The cooling process is just as critical as the heating process. Never stop a furnace program at a high temperature.
A controlled cooling rate, typically below 10°C/min, is essential to prevent thermal shock in reverse. As the part cools, it contracts, and a rapid, uncontrolled drop in temperature will induce the same internal stresses that cause cracking during heating.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your specific goal will dictate where you operate within the recommended range. Use these principles as a starting guide for your application.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength: Stick to the lower end of the range, around 5-8°C/min, to ensure uniform sintering and minimize internal defects.
- If your primary focus is processing speed for simple, small parts: You may be able to operate closer to the 10°C/min maximum, but you must validate that it does not introduce cracking.
- If you are working with large or thick components: Always use a slow rate of 5°C/min or less and consider adding dwells (holding at a constant temperature) to allow the temperature to fully homogenize.
Ultimately, controlling the thermal cycle is fundamental to success in ceramics processing.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Maximum Safe Rate | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heating Rate | 5°C to 8°C per minute | 10°C per minute | Prevents thermal shock and ensures uniform sintering |
| Cooling Rate | Controlled, typically below 10°C/min | - | Essential to prevent cracking during part contraction |
Achieve flawless alumina sintering results with precision equipment from KINTEK.
Mastering the thermal profile is critical for producing high-density, strong alumina components free from cracks and warping. KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab furnaces that deliver the precise, controlled heating and cooling rates your ceramic processing demands.
Our furnaces are engineered for exceptional temperature uniformity and programmability, giving you complete control over your sintering cycle to achieve the desired material properties consistently.
Ready to optimize your alumina processing? Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your specific application requirements and find the perfect furnace solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How does a quartz tube facilitate fractional condensation in a horizontal tube vacuum gasification furnace? Expert Guide
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation



















