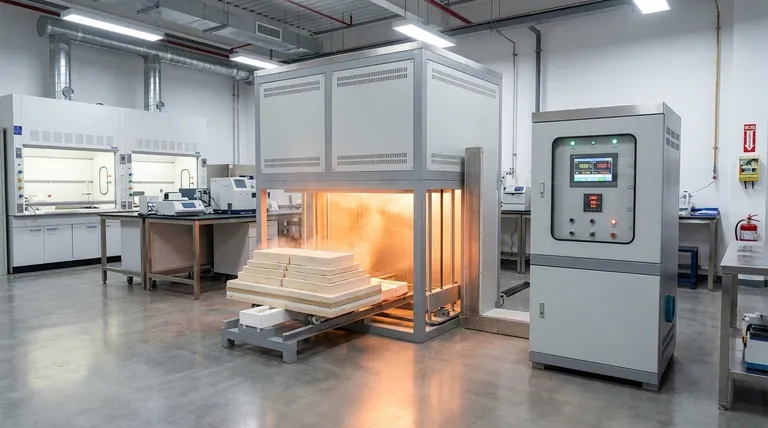
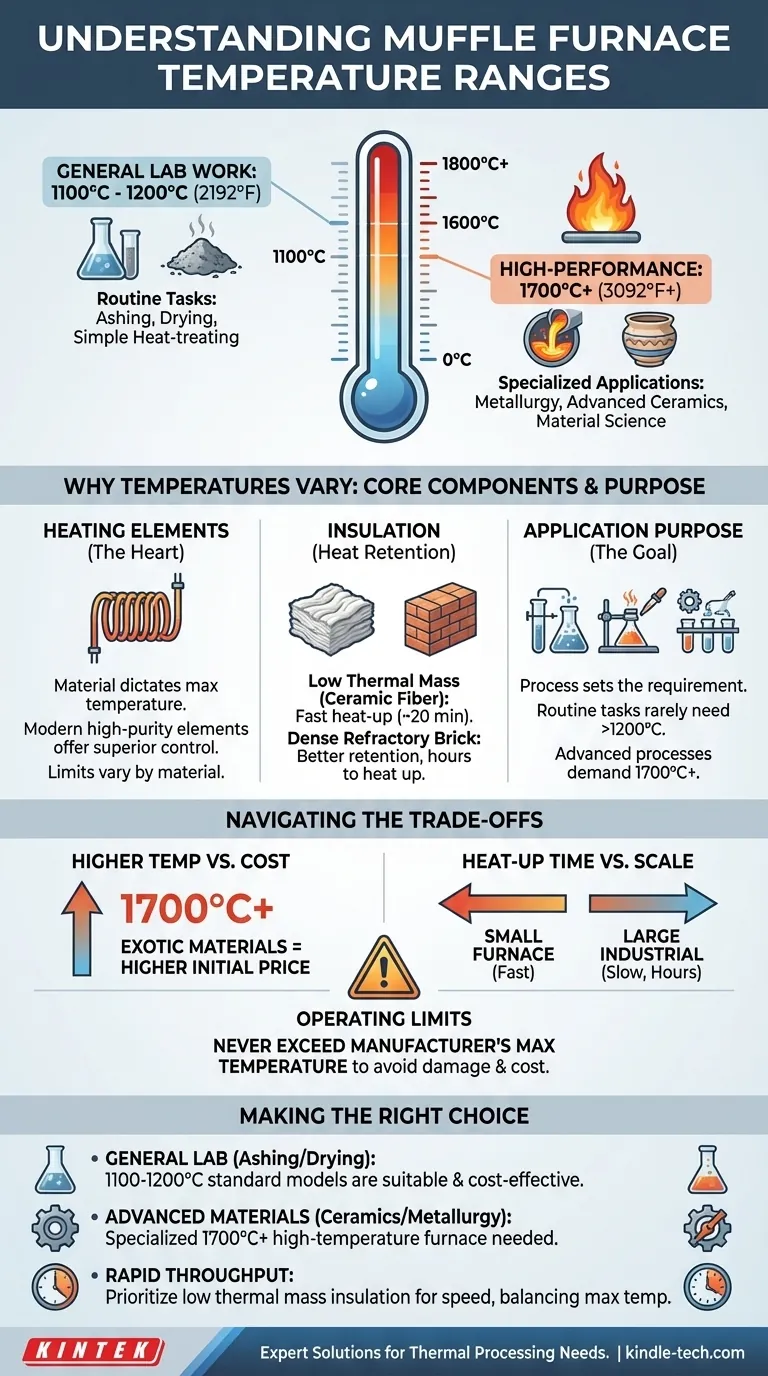
The maximum temperature of a muffle furnace is not a single value but falls within a range determined by its design and intended use. While many general-purpose laboratory furnaces operate up to 1100°C or 1200°C (2192°F), high-performance models designed for specialized applications like metallurgy or ceramics can reach 1700°C (3092°F) or even higher.
The key takeaway is that a muffle furnace's maximum temperature is a direct function of its construction—specifically its heating elements and insulation—which are chosen to meet the demands of a particular industrial or scientific process.

Why Maximum Temperature Varies So Widely
A muffle furnace provides a controlled, high-temperature environment isolated from combustion byproducts. This is achieved by placing the workload inside a sealed chamber, or "muffle." The temperature it can achieve is not a universal standard but depends entirely on its core components.
The Role of Heating Elements
The heart of an electric muffle furnace is its heating element, and the material used directly dictates the maximum achievable temperature.
Modern furnaces use high-purity electric elements, which offer superior temperature uniformity and control compared to older flame-based models. Different materials have different operating limits.
The Impact of Insulation
Insulation determines how effectively the furnace retains heat and how quickly it can reach its target temperature.
A furnace with low thermal mass insulation, like ceramic fiber, can heat up rapidly—sometimes in as little as 20 minutes. Conversely, a larger furnace built with dense refractory brick will retain heat better at steady temperatures but may take several hours to heat up.
The Purpose of the Application
Ultimately, the required temperature is set by the process. Routine laboratory tasks like ashing, drying, or simple heat-treating rarely require temperatures above 1200°C.
Processes involving advanced ceramics, certain metal alloys, or specialized material science research demand the higher thermal capabilities of a 1700°C+ furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace involves balancing performance with practical limitations. Simply choosing the highest possible temperature is often inefficient and unnecessary.
Higher Temperature vs. Cost
Furnaces capable of reaching extreme temperatures (above 1200°C) require more exotic and expensive materials for both their heating elements and insulation. This significantly increases the initial purchase price.
Heat-Up Time vs. Furnace Scale
The time required to reach maximum temperature is a critical operational factor. A small laboratory furnace may be ready for use quickly, but a large industrial furnace can take hours. This delay must be factored into any production or testing schedule.
Operating Limits vs. Equipment Longevity
It is critical to never exceed the manufacturer's specified maximum temperature. Doing so can cause permanent damage to the heating elements and insulation, leading to costly repairs and compromising the safety and accuracy of the furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct furnace, you must first define your thermal processing needs. The goal is to match the furnace's capabilities to your specific task.
- If your primary focus is general lab work like ashing or drying: A standard furnace with a maximum temperature of 1100°C to 1200°C is perfectly suitable and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials, ceramics, or metallurgy: You will need a specialized high-temperature furnace capable of reaching 1700°C or more.
- If your primary focus is rapid throughput and efficiency: Prioritize a furnace with low thermal mass insulation for faster heat-up times, while ensuring its maximum temperature still meets your needs.
By aligning the furnace's technical specifications with your specific goal, you ensure safe, efficient, and accurate thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Application Type | Typical Max Temperature | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| General Lab Work (e.g., ashing, drying) | 1100°C - 1200°C | Cost-effective, suitable for most routine tasks |
| Advanced Materials (e.g., ceramics, metallurgy) | 1700°C+ | Higher cost, specialized heating elements & insulation |
| Rapid Throughput & Efficiency | Varies (e.g., 1200°C) | Prioritize low thermal mass insulation for fast heat-up |
Selecting the right muffle furnace is critical for your lab's efficiency and accuracy. KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, offering a range of muffle furnaces tailored to your specific thermal processing needs—whether for routine testing or advanced materials research. Our experts can help you balance performance, cost, and operational requirements. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the 3 types of heat transfer? Master Conduction, Convection & Radiation for Your Lab
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a chamber furnace? Understand the Key Distinctions for Your Lab
- What is the maximum temperature of muffle furnace? A Guide from 1100°C to 1800°C
- What is ashing in a muffle furnace? Isolate Inorganic Content with Precision
- What is the heating mechanism of a muffle furnace? Achieve Clean, Uniform High-Temperature Processing



















