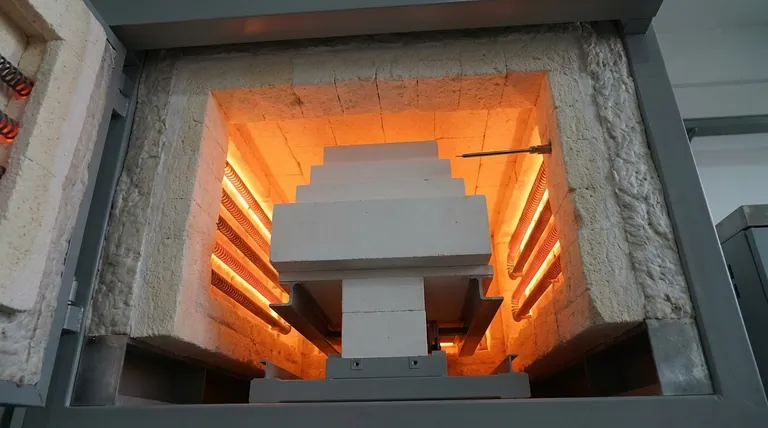
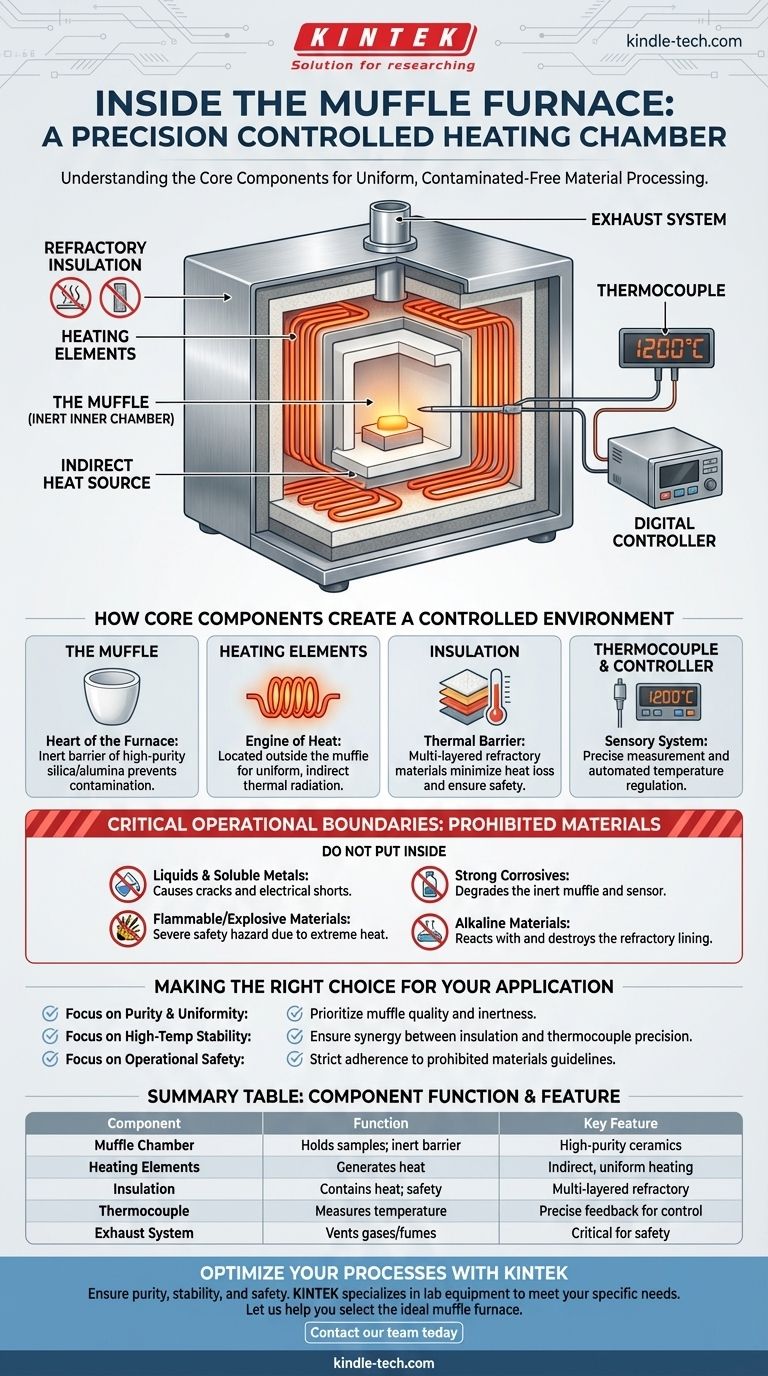
At its core, the inside of a muffle furnace is a specialized, high-temperature chamber designed for material processing. The critical internal components are the muffle itself (an inert inner chamber), heating elements that surround it, dense refractory insulation, and a thermocouple for precise temperature measurement. These parts work in concert to create a uniform, controlled, and uncontaminated heating environment.
The essential principle of a muffle furnace isn't just what's inside, but how the components are arranged. The design intentionally separates the material being heated from the direct radiation of the heating elements, ensuring purity and uniform temperature exposure.

How Core Components Create a Controlled Environment
A muffle furnace's effectiveness comes from the specific function and interaction of each internal part. The goal is to generate, contain, and precisely control extreme heat within a chemically non-reactive space.
The Muffle: The Heart of the Furnace
The "muffle" is the central refractory-lined chamber that holds the samples. It acts as a crucial barrier, or shield, between the items being heated and the raw heat source.
This chamber is typically made from durable, inert materials like high-purity silica and alumina ceramics. This construction prevents chemical reactions or contamination of the sample at high temperatures.
Heating Elements: The Engine of Heat
The heating elements are responsible for generating the furnace's high temperatures. They are almost always located outside the muffle chamber, embedded within the furnace's insulating walls.
These elements are often made from robust alloys like iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl). By placing them outside the muffle, the furnace provides indirect heat, which protects samples from direct thermal radiation and ensures a more uniform temperature profile throughout the chamber.
Insulation and Refractory Lining: The Thermal Barrier
Multi-layered insulation is what allows a muffle furnace to reach and maintain extreme temperatures efficiently and safely. This includes dense refractory materials that line the chamber and surround the heating elements.
This insulation minimizes heat loss, which improves energy efficiency and temperature stability. It also keeps the external casing of the furnace at a safe temperature for operators.
The Sensory System: Thermocouple and Controller
To manage the heat, a sensor called a thermocouple is placed inside the furnace chamber. It constantly measures the internal temperature with high accuracy.
This thermocouple sends its readings to an external digital temperature controller. The controller then adjusts the power sent to the heating elements, turning them on and off to maintain the exact temperature set by the user.
The Exhaust System: Managing Byproducts
Some muffle furnaces include a small release hole or a dedicated exhaust system. This feature is critical for safely venting gases, fumes, or moisture that may be released from samples during the heating process.
Critical Operational Boundaries: What Not to Put Inside
A muffle furnace is a powerful tool, but its internal components are sensitive. Introducing prohibited materials can cause permanent damage to the refractory lining and heating elements, leading to costly repairs and inaccurate results.
Prohibited Materials
You must never place certain substances inside the furnace chamber. These include:
- Liquids and Soluble Metals: Spills can seep into the porous refractory material, causing cracks and electrical shorts upon heating.
- Flammable or Explosive Materials: The extreme heat will ignite these substances, creating a severe safety hazard.
- Strongly Corrosive Materials: Acids and other corrosives will degrade the inert muffle chamber and the thermocouple sensor.
- Alkaline Materials: These can react with and melt the silica-based refractory lining, destroying the furnace's core.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding the function of each internal component helps you use the furnace effectively and for the correct purpose.
- If your primary focus is material purity and uniform heating: The quality and inertness of the muffle chamber are your most important considerations.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability: The synergy between the dense insulation and the precision of the thermocouple/controller system is paramount.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Strict adherence to guidelines on prohibited materials is essential for protecting the furnace's internal components.
By understanding how these internal parts function together, you can ensure the long-term reliability and accuracy of your high-temperature applications.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Muffle Chamber | Holds samples; provides inert barrier | Made from high-purity ceramics (e.g., alumina) |
| Heating Elements | Generates heat | Located outside muffle for indirect, uniform heating |
| Insulation | Contains heat; ensures safety | Multi-layered refractory materials |
| Thermocouple | Measures temperature | Provides feedback to digital controller for precision |
| Exhaust System | Vents gases/fumes | Critical for safety and sample integrity |
Optimize your high-temperature processes with the right equipment.
Understanding the internal components of a muffle furnace is the first step to achieving precise, contamination-free results in your lab. The correct furnace ensures material purity, uniform heating, and operational safety.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the ideal muffle furnace for your specific application, whether your priority is material purity, high-temperature stability, or safety.
Let us help you ensure the long-term reliability and accuracy of your work. Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the precautions for heat in the laboratory? Essential Safety Rules to Prevent Burns and Fires
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and an incubator? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab
- What is the purpose of calcination? Transform and Purify Materials for Industrial Use
- What are the safety precautions for heat experiment? Essential Steps to Prevent Lab Burns and Accidents
- What precautions should you take while using a muffle furnace? Ensure Safe High-Temperature Processing in Your Lab



















