The single most important takeaway when selecting a lab freeze dryer is to let your application's requirements—specifically the critical temperature of your samples—dictate the necessary technical specifications of the machine. Do not start by comparing features or prices. Start by defining the exact needs of what you are drying, and then find the equipment that meets those non-negotiable requirements.
Instead of asking "Which freeze dryer is best?", the correct approach is to first define your sample's unique properties and your lab's throughput needs. Only then can you effectively evaluate which machine specifications are essential, which are secondary, and which you can ignore.

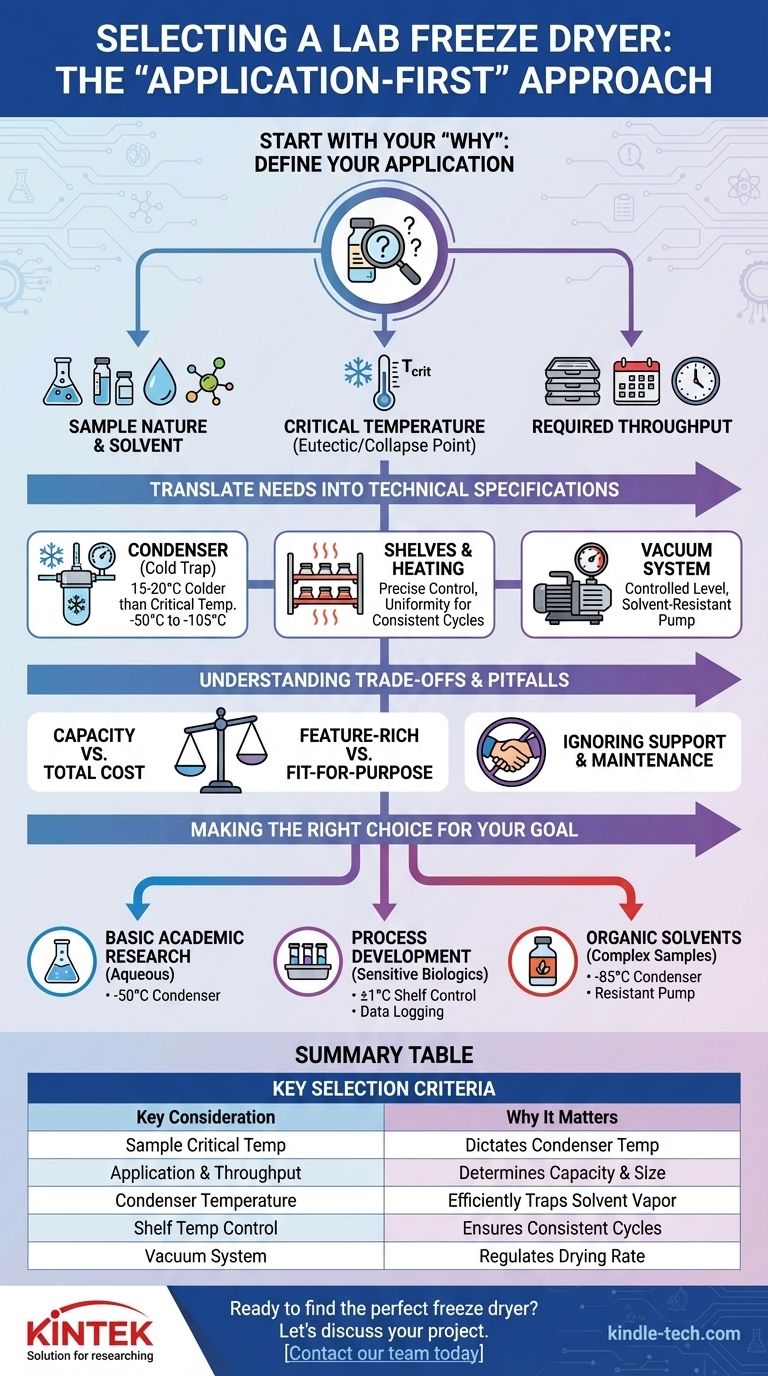
Start with Your "Why": Defining Your Application
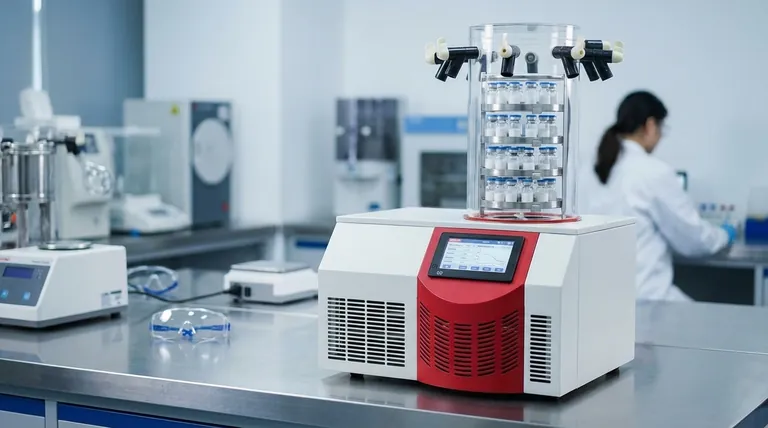
Before you look at a single product sheet, you must perform a comprehensive assessment of your own process. The answers to these questions will form the blueprint for your ideal machine.
What Is the Nature of Your Samples?
The physical form and chemical composition of your samples are the primary drivers. Are you drying material in flasks, vials on a shelf, or in bulk trays?
Most importantly, what solvents are you removing? An aqueous (water-based) solution has very different requirements than a sample containing organic solvents like acetonitrile or t-butanol.
What is Your Sample's Critical Temperature?
This is the most crucial technical detail. For crystalline samples, this is the eutectic point; for amorphous samples, it's the collapse temperature.
This temperature is the point at which your frozen product will lose its structure and melt or "collapse" during drying, ruining the final product. Your freeze dryer's components must be able to maintain conditions that protect your sample from reaching this temperature.
What is Your Required Throughput?
You must quantify your needs. How many samples do you need to process per cycle, and how many cycles do you anticipate running per week?
This calculation determines the required shelf space (for tray dryers) or the number of ports (for manifold dryers) and the necessary condenser capacity, which must be able to hold all the sublimated ice from a full batch.
Translating Needs into Technical Specifications
Once you have defined your application, you can intelligently evaluate the key components of a freeze dryer.
The Condenser (Cold Trap)
The condenser’s job is to trap the solvent vapor that leaves your sample, turning it back into a solid. Its temperature is a critical specification.
A general rule is that the condenser must be 15-20°C colder than your sample's eutectic point or collapse temperature. For most aqueous samples, a -50°C to -55°C condenser is sufficient. However, for samples with low eutectic points or those containing organic solvents, a -85°C or even a -105°C condenser is non-negotiable.
The Shelves and Heating System
For anything beyond basic manifold drying of robust samples, you need controlled shelves. Shelf temperature control is essential for managing the rate of sublimation (primary drying) and removing bound water (secondary drying).
Look for temperature uniformity across the shelf. Inconsistent temperatures can lead to some samples finishing drying before others, compromising batch consistency. The ability to precisely ramp and hold temperatures is vital for developing an optimized and repeatable drying cycle.
The Vacuum System
The vacuum pump removes air from the system to reduce the pressure, allowing the frozen solvent in your sample to sublimate directly into a vapor.
The key is not simply achieving the deepest vacuum, but controlling the vacuum level. Precise vacuum control helps regulate the drying rate and shelf temperature, preventing product collapse. The pump must also be appropriate for the solvents you are using (e.g., an oil-free or hybrid pump for corrosive solvents).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
A freeze dryer is a significant investment, and focusing only on the primary specifications can lead to costly mistakes.
Capacity vs. Total Cost of Ownership
A larger-capacity machine costs more upfront and also consumes more electricity and may require dedicated facility upgrades like enhanced power or water-cooling lines.
Over-specifying your capacity "just in case" can be an expensive error. A realistic assessment of your throughput is essential to balance capability with budget and operating costs.
Feature-Rich vs. Fit-for-Purpose
Modern freeze dryers offer advanced features like programmable recipes, sophisticated data logging for GMP compliance, and pressure-rise tests.
These are invaluable if you are in pharmaceutical development or need strict process control. However, if you are in a basic research setting drying stable samples, a simpler, manual unit may be far more cost-effective and easier to maintain.
Ignoring Manufacturer Support and Maintenance
Your relationship with the manufacturer does not end at purchase. Consider the availability of technical support for application development, as well as the cost and speed of service and preventative maintenance.
A machine that is down for weeks waiting for a part can be more costly than a more expensive but better-supported alternative.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluate your options based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is basic academic research on aqueous samples: Prioritize a reliable unit with an appropriately sized -50°C condenser and choose between manifold or tray configurations based on sample type.
- If your primary focus is process development for sensitive biologics: Invest in a unit with precise shelf temperature control (±1°C), programmable cycles, data logging, and a condenser at least 20°C below your product's collapse temperature.
- If your primary focus is handling samples with organic solvents: You must select a machine with a very low-temperature condenser (-85°C or lower) and a solvent-resistant vacuum pump.
Ultimately, a freeze dryer is a tool, and the right choice is the one that reliably and repeatedly performs the specific job you require.
Summary Table:
| Selection Criteria | Key Consideration | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Critical Temperature | Eutectic or Collapse Temperature | Dictates the required condenser temperature to prevent product failure. |
| Application & Throughput | Samples per cycle, solvent type | Determines machine capacity (shelf space/ports) and condenser size. |
| Condenser Temperature | Must be 15-20°C below sample's critical temp | Essential for efficiently trapping solvent vapor. |
| Shelf Temperature Control | Uniform heating and precise ramping | Ensures consistent, repeatable drying cycles across all samples. |
| Vacuum System | Control, not just ultimate pressure | Regulates drying rate and protects sensitive samples. |
Ready to find the perfect freeze dryer for your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing lab equipment and consumables tailored to your unique laboratory needs. Our experts can help you analyze your sample requirements and throughput to recommend a freeze dryer that ensures reliable, repeatable results—avoiding costly over-specification or under-performance.
Let's discuss your project. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can support your research and development goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- Why is freeze drying a good method for preserving fruits and vegetables? Unlock Superior Food Preservation
- What is the importance of ultimate vacuum in a freeze dryer? A Key Diagnostic for Efficient Drying
- What are the main components of a lab freeze dryer? Unlock the Secrets of Lyophilization
- What is the role of the refrigeration system in a freeze dryer? It's the Heart of the Sublimation Process
- What are the key steps in the freeze drying process? A Guide to Mastering Sublimation



















