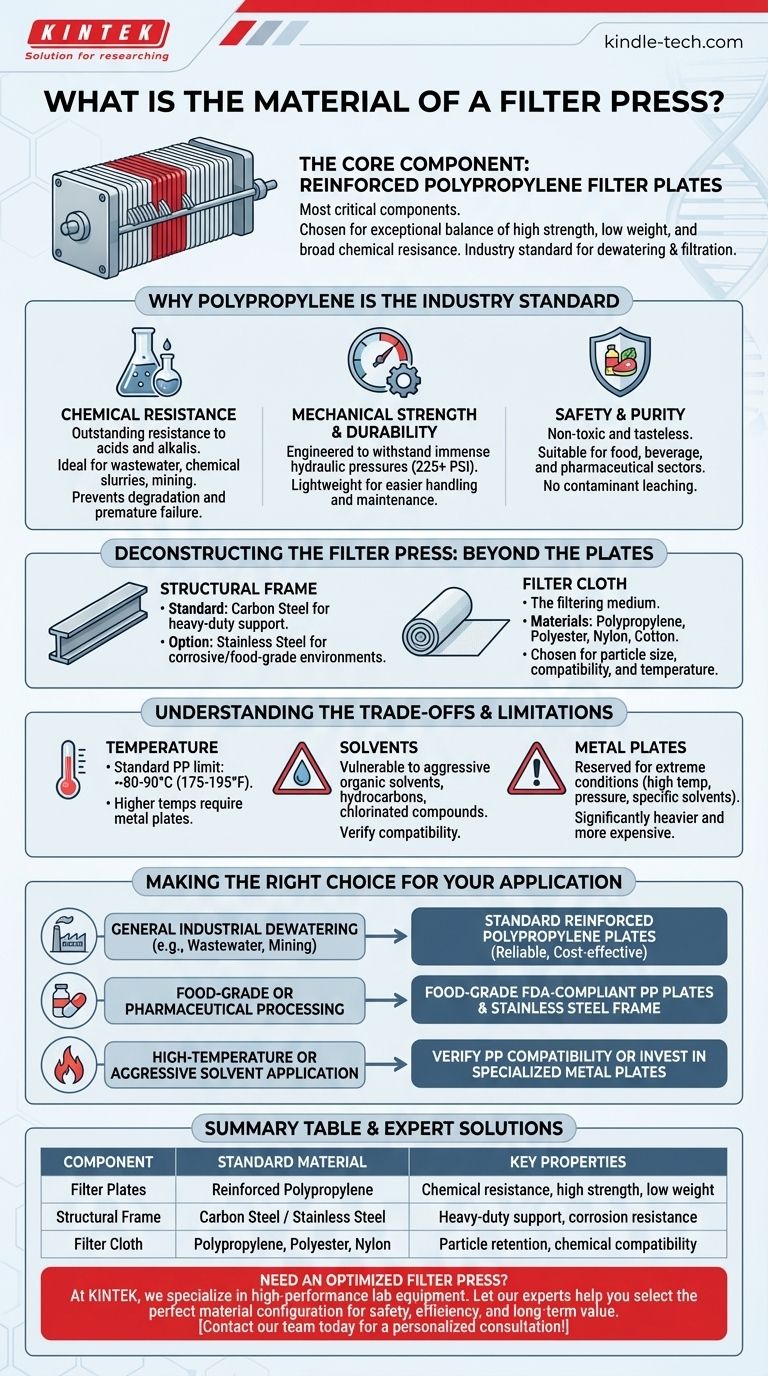
In modern filter presses, the most critical components—the filter plates—are almost universally constructed from reinforced polypropylene. This material is chosen for its exceptional balance of high strength, low weight, and broad chemical resistance, making it suitable for the vast majority of industrial dewatering and filtration applications.
The selection of reinforced polypropylene is not an accident; it is a deliberate engineering choice. It provides the best combination of chemical resilience, mechanical durability, and operational safety for most filtration tasks, far surpassing traditional materials in both performance and cost-effectiveness.

Why Polypropylene is the Industry Standard
The properties of reinforced polypropylene directly address the demanding environment inside a filter press. It is the default material because it solves several challenges simultaneously.
Chemical Resistance: The Core Advantage
Polypropylene offers outstanding resistance to a wide range of chemicals, particularly acids and alkalis. This makes it ideal for treating industrial wastewater, chemical slurries, and mining tailings without degrading.
This inherent inertness ensures the filter press has a long service life even when exposed to corrosive substances, preventing premature failure and costly replacements.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
The "reinforced" aspect is crucial. The polypropylene is engineered to withstand the immense hydraulic pressures—often exceeding 225 PSI—used to squeeze liquid from the solids.
Despite its strength, it is significantly lighter than older materials like cast iron. This low weight makes the filter plates easier for operators to handle during cake discharge and maintenance, improving safety and efficiency.
Safety and Purity
For sensitive industries, material safety is non-negotiable. Polypropylene is non-toxic and tasteless, making it a suitable choice for applications in the food and beverage or pharmaceutical sectors.
This ensures that the material of the press itself does not leach contaminants into the final product, preserving its purity.
Deconstructing the Filter Press: More Than Just Plates
While the plates are the heart of the system, a complete filter press assembly relies on other materials for structure and function.
The Structural Frame
The heavy-duty skeleton frame that holds the plates under pressure is typically fabricated from carbon steel. For more corrosive environments or food-grade applications, the frame may be made of stainless steel or sheathed in it for added protection.
The Filter Cloth
The filter cloth is the actual filtering medium, and its material is selected specifically for the application. Common materials include polypropylene, polyester, nylon, and cotton, chosen based on particle size, chemical compatibility, and temperature requirements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While polypropylene is the dominant material, it is not universally perfect. Understanding its limitations is key to avoiding misapplication.
Temperature Limitations
Standard polypropylene has an upper operating temperature limit, typically around 80-90°C (175-195°F). For processes involving higher temperatures, alternative materials for the plates, such as cast iron or stainless steel, must be considered.
Solvent Compatibility
While excellent with acids and bases, polypropylene can be vulnerable to certain aggressive organic solvents, hydrocarbons, and chlorinated compounds. In these specific cases, material compatibility must be verified, and a different polymer or metal plate might be necessary.
When to Consider Metal Plates
Filter plates made from cast iron or stainless steel are reserved for niche, extreme applications. They are used for processes involving very high temperatures, extreme pressures, or specific solvents that are incompatible with polypropylene. However, they are significantly more expensive, much heavier, and require more effort to operate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your process requirements dictate the correct material specification. Use these guidelines to inform your decision.
- If your primary focus is general industrial dewatering (e.g., wastewater, aggregates, mining): Standard reinforced polypropylene plates are the most reliable and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is food-grade or pharmaceutical processing: Specify food-grade, FDA-compliant polypropylene for the plates and consider stainless steel for the structural frame and piping.
- If your primary focus is a high-temperature or aggressive solvent application: You must verify polypropylene's chemical and thermal compatibility and be prepared to invest in specialized metal plates if necessary.
Understanding these material choices empowers you to select a filter press that is not just functional, but optimized for safety, efficiency, and long-term value.
Summary Table:
| Component | Standard Material | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Filter Plates | Reinforced Polypropylene | Chemical resistance, high strength, low weight |
| Structural Frame | Carbon Steel / Stainless Steel | Heavy-duty support, corrosion resistance |
| Filter Cloth | Polypropylene, Polyester, Nylon | Particle retention, chemical compatibility |
Need a filter press optimized for your specific application? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including filtration systems. Our experts can help you select the perfect material configuration—whether it's standard polypropylene for industrial dewatering or specialized metals for extreme conditions—ensuring safety, efficiency, and long-term value for your laboratory. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy



















