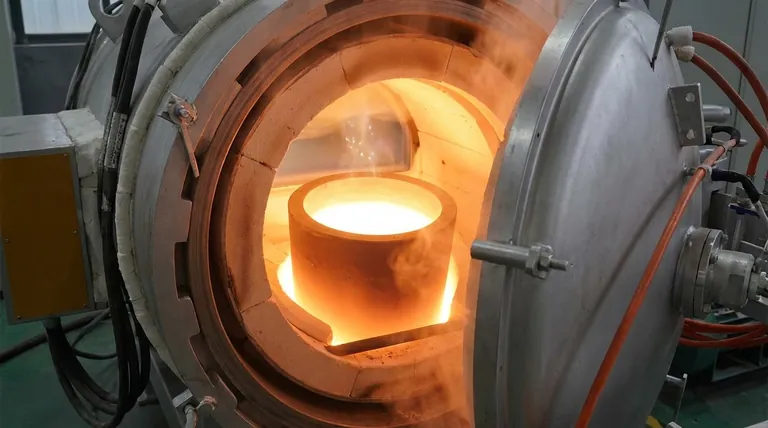
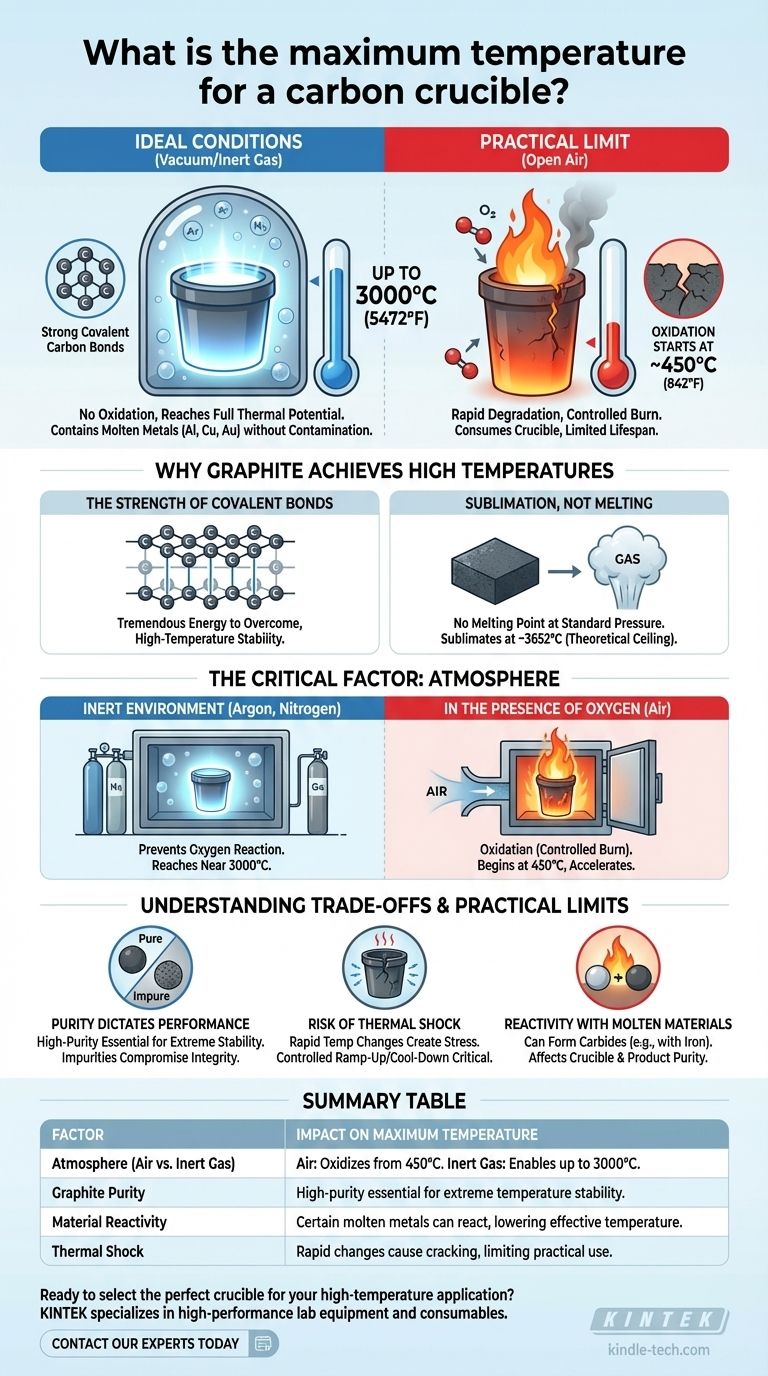
Under ideal conditions, a high-purity graphite crucible can withstand an exceptionally high temperature, reaching up to 3000°C (5472°F). This remarkable thermal stability allows it to contain molten metals like aluminum, copper, and gold without degrading or contaminating the melt. However, this maximum temperature is only achievable under very specific circumstances.
The theoretical temperature limit of a carbon crucible is dictated by its material properties, but its practical, usable temperature is almost always determined by the atmosphere it's heated in.

Why Graphite Achieves Such High Temperatures
The incredible heat resistance of a graphite crucible is not magic; it is a direct result of its atomic structure and the nature of carbon itself.
The Strength of Covalent Bonds
Graphite is an allotrope (a specific structural form) of carbon. Within its layers, carbon atoms are linked by extremely strong covalent bonds. A tremendous amount of thermal energy is required to overcome these bonds, giving the material its high-temperature stability.
Sublimation, Not Melting
Unlike metals that melt into a liquid state, graphite does not have a melting point at standard pressure. Instead, it sublimates, turning directly from a solid into a gas. This sublimation point is incredibly high, around 3652°C, which forms the absolute theoretical ceiling for its use.
The Critical Factor: Atmosphere
The 3000°C figure is only relevant in a controlled, non-reactive environment. In practice, the surrounding atmosphere is the single most important factor limiting the crucible's performance.
In an Inert Environment
To reach temperatures near 3000°C, a graphite crucible must be used in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen). This prevents oxygen from reacting with the carbon, allowing the material to reach its full thermal potential without being consumed.
In the Presence of Oxygen
When heated in the presence of air, carbon reacts with oxygen in a process called oxidation. This is essentially a controlled burn. Oxidation of graphite can begin at temperatures as low as 450°C (842°F), and it accelerates rapidly as the temperature increases. Using a graphite crucible in open air will cause it to degrade and wear away long before it reaches its sublimation point.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Practical Limits
Beyond the core issue of atmosphere, several other factors influence the performance and lifespan of a carbon crucible.
Purity Dictates Performance
The 3000°C value applies specifically to high-purity graphite. Lower-purity crucibles or those made from other forms of carbon may contain impurities that will melt or react at much lower temperatures, compromising the crucible's structural integrity.
Risk of Thermal Shock
While highly resistant to heat, graphite can be susceptible to thermal shock. Heating or cooling the crucible too rapidly can create internal stresses that lead to cracks or complete failure. A controlled ramp-up and cool-down cycle is critical for longevity.
Reactivity with Molten Materials
Although generally non-reactive, carbon can react with certain molten materials. For example, it can form carbides with metals like iron or titanium at very high temperatures, which can affect both the crucible and the purity of the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right operating parameters depends entirely on your specific goal and equipment.
- If your primary focus is reaching maximum possible temperatures: You must use a high-purity graphite crucible inside a vacuum or inert gas furnace.
- If your primary focus is general melting in open air: You must accept a much lower effective temperature limit and account for the gradual consumption of the crucible due to oxidation.
- If your primary focus is material purity: You must verify the compatibility of your molten material with carbon to avoid the formation of unwanted carbides.
Ultimately, understanding that the crucible's environment is as important as the crucible itself is the key to achieving successful high-temperature work.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Maximum Temperature |
|---|---|
| Atmosphere (Air vs. Inert Gas) | Air: Oxidizes from 450°C. Inert Gas/Vacuum: Enables up to 3000°C. |
| Graphite Purity | High-purity graphite is essential for extreme temperature stability. |
| Material Reactivity | Certain molten metals (e.g., iron) can react with carbon, lowering effective temperature. |
| Thermal Shock | Rapid temperature changes can cause cracking, limiting practical use. |
Ready to select the perfect crucible for your high-temperature application?
The right lab equipment is crucial for achieving precise and reliable results. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a range of crucibles designed for specific thermal and atmospheric conditions.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements. We'll help you choose the right solution to enhance your lab's efficiency, ensure material purity, and achieve your temperature goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can graphite withstand high-temperature? Maximizing Performance in Controlled Atmospheres
- Why can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking Its Extreme Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What are the properties of graphite at high temperatures? Unlock Its Strength and Stability in Extreme Heat
- Is graphite good in high temperature? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential
- Is a graphite melting point high or low? Discover Its Extreme Thermal Resilience



















