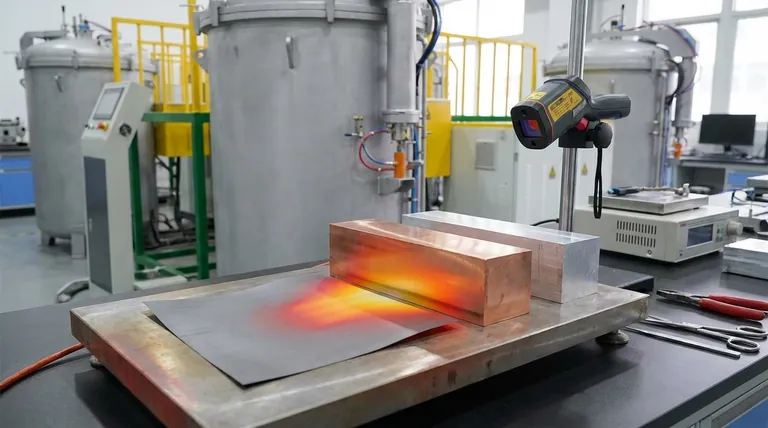
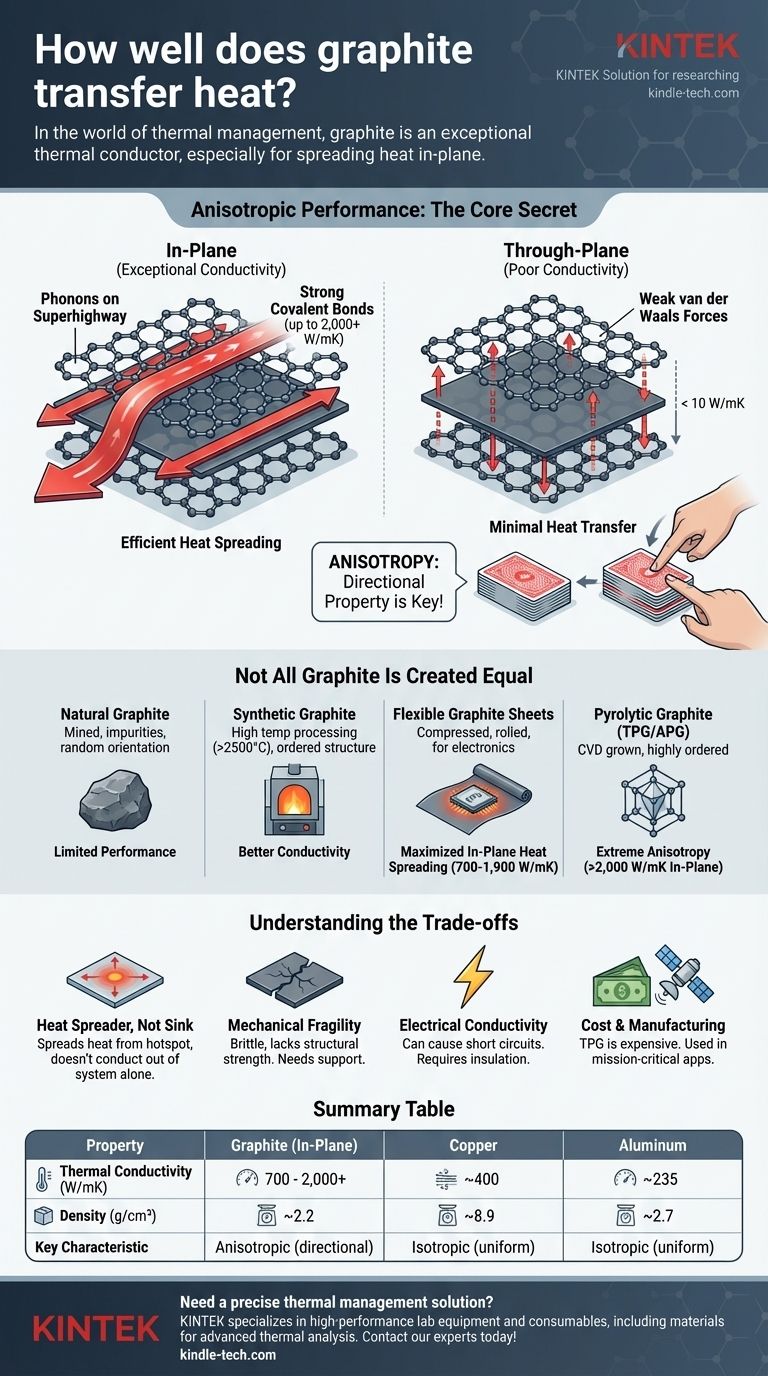
In the world of thermal management, graphite is an exceptional thermal conductor. Depending on its form and purity, its ability to transfer heat along a specific plane can significantly exceed that of metals like copper and aluminum, making it a critical material for high-performance electronics, aerospace, and other demanding applications.
The core takeaway is not simply that graphite is a good heat conductor, but that its performance is highly anisotropic—it conducts heat exceptionally well in two dimensions (in-plane) but poorly in the third (through-plane). Understanding this directional property is the key to using it effectively.

Why Graphite Excels at Heat Transfer
Graphite's unique thermal properties are a direct result of its atomic structure. This structure creates a highly efficient pathway for heat energy to travel, but only in specific directions.
The Atomic "Superhighway"
Graphite consists of stacked layers of carbon atoms, with each layer being a one-atom-thick sheet known as graphene. Within each layer, carbon atoms are linked by incredibly strong covalent bonds.
These bonds create a rigid, stable lattice that acts as a "superhighway" for heat energy, which travels in the form of lattice vibrations called phonons. With minimal disruption, phonons move at high speed across the plane.
The Critical Role of Anisotropy
While the atoms within a layer are strongly bonded, the layers themselves are held together by much weaker van der Waals forces. This creates a significant difference in thermal properties.
Imagine a deck of cards. It's very easy to slide the top card across the deck (in-plane), but much harder to push your finger straight through the entire stack (through-plane).
Heat in graphite behaves the same way. It moves with extreme efficiency along the layers (in-plane) but struggles to jump from one layer to the next (through-plane). This directional behavior is known as anisotropy.
Not All Graphite Is Created Equal
The term "graphite" covers a range of materials with vastly different thermal conductivities. The specific form and processing method determine its ultimate performance.
Natural vs. Synthetic Graphite
Natural graphite is mined and processed. While a good conductor, its performance is limited by impurities and the random orientation of its crystalline flakes.
Synthetic graphite is produced by heating carbon precursors to very high temperatures (over 2500°C). This process creates a more ordered, pure structure, leading to significantly better thermal conductivity.
Flexible Graphite Sheets
For electronics, the most common form is a flexible graphite sheet or film. These are made by compressing and rolling exfoliated natural graphite or by graphitizing a polymer film.
These sheets are engineered to maximize in-plane heat spreading. A typical synthetic graphite sheet can have an in-plane thermal conductivity of 700 to 1,900 W/mK (Watts per meter-Kelvin). For comparison, copper is around 400 W/mK.
Pyrolytic Graphite (TPG/APG)
Thermal Pyrolytic Graphite (TPG), also known as Annealed Pyrolytic Graphite (APG), represents the pinnacle of graphite's thermal performance. It is grown through chemical vapor deposition, resulting in a highly ordered layered structure.
TPG exhibits extreme anisotropy. Its in-plane conductivity can reach over 2,000 W/mK—five times that of copper—while its through-plane conductivity is often less than 10 W/mK, making it an excellent insulator in that direction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Graphite is a powerful tool, but its unique properties come with design constraints that are critical to understand.
Anisotropy: A Double-Edged Sword
Graphite's greatest strength is also its main limitation. It is a heat spreader, not a bulk heat sink. It is ideal for moving heat from a small hotspot (like a CPU) to a larger area, but it cannot effectively conduct that heat out of the system on its own.
Mechanical Fragility
Unlike metals, graphite is brittle and lacks structural strength. Graphite sheets are typically very thin and are used as liners or thermal interface materials, often laminated to other substrates for support. They cannot be used as a structural component.
Electrical Conductivity
Graphite is also an electrical conductor. This is a critical consideration in electronics design, as a graphite sheet can cause a short circuit if it comes into contact with exposed electrical components. Careful insulation and placement are required.
Cost and Manufacturing
While standard synthetic graphite is relatively affordable, high-performance materials like TPG are significantly more expensive than aluminum or copper. Their cost limits their use to applications where performance is the absolute priority, such as in satellites or advanced military hardware.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a thermal management material depends entirely on your specific engineering objective.
- If your primary focus is spreading heat away from a hotspot in a thin device: A flexible synthetic graphite sheet is the ideal choice due to its high in-plane conductivity and low profile.
- If your primary focus is maximum in-plane performance at any cost: Thermal Pyrolytic Graphite (TPG) offers unparalleled heat spreading capabilities for mission-critical applications.
- If your primary focus is moving heat through a material with structural strength: A traditional isotropic material like copper or aluminum is the correct solution.
- If your primary focus is reducing weight: Graphite offers a significant advantage, providing superior thermal performance at roughly one-quarter the density of copper.
By understanding the fundamental principles of its performance, you can leverage graphite as a powerful and precise tool for solving complex thermal challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Graphite (In-Plane) | Copper | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | 700 - 2,000+ | ~400 | ~235 |
| Density (g/cm³) | ~2.2 | ~8.9 | ~2.7 |
| Key Characteristic | Anisotropic (directional) | Isotropic (uniform) | Isotropic (uniform) |
Need a precise thermal management solution for your lab or project? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including materials for advanced thermal analysis. Our expertise can help you select the right materials, like specialized graphite, to enhance the efficiency and reliability of your laboratory work. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific thermal challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Can graphite withstand high-temperature? Maximizing Performance in Controlled Atmospheres
- How is synthetic graphite manufactured? A Deep Dive into the High-Temperature Process
- What temperature can graphite handle? Unlocking its extreme heat resistance in inert environments
- Why is the thermal conductivity of graphite so high? Unlock Superior Heat Transfer with Its Unique Structure
- Is graphite affected by heat? Discover Its Remarkable Strength and Stability at High Temperatures



















