The maximum temperature of a heating element is not a single value; it is fundamentally determined by the specific material composition of the element. For example, common Nichrome wire is typically rated for temperatures up to 1200°C (2190°F), while specialized ceramic elements like Molybdenum Disilicide can operate at temperatures exceeding 1800°C (3270°F).
The true "maximum temperature" of a heating element is not its physical melting point, but the highest temperature at which it can operate reliably, safely, and efficiently for its intended lifespan. This practical limit is a careful balance of the element's material, its operating environment, and its physical design.
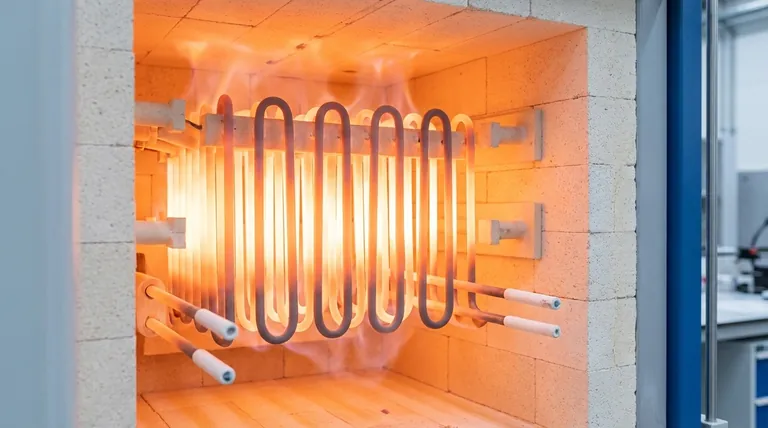
The Core Factor: Element Material
The material used is the primary constraint on an element's maximum temperature. Different materials are chosen based on their ability to resist oxidation and maintain structural integrity at high heat.
Common Metallic Alloys
Most heating elements in consumer and industrial applications use metallic alloys. Their primary advantage is forming a protective oxide layer that prevents further corrosion at high temperatures.
- Nickel-Chromium (Nichrome): The most common choice for applications like toasters and space heaters, typically operating up to 1200°C (2190°F).
- Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl/Kanthal): Capable of higher temperatures, often up to 1400°C (2550°F), making it suitable for industrial furnaces.
High-Temperature Ceramics
For applications requiring extreme heat, such as laboratory furnaces or semiconductor manufacturing, ceramic elements are necessary.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): These rigid elements are self-supporting and can operate up to 1625°C (2957°F).
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2): The choice for the highest temperatures in air, MoSi2 elements can reach 1850°C (3360°F).
Refractory Metals
Metals like Tungsten and Molybdenum have exceptionally high melting points but have a critical weakness.
- Tungsten: While it can operate at temperatures above 2000°C (3632°F), it oxidizes and fails almost instantly in the presence of air. It must be used in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere.
Environmental and Design Constraints
Material choice is only half the story. The element's environment and physical design impose their own strict limitations on its effective maximum temperature.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
The presence of oxygen is the single most significant environmental factor. The protective oxide layer on Nichrome and FeCrAl alloys is what allows them to function in air. Without it, they would burn out quickly. This is why refractory metals like Tungsten are limited to vacuum or inert environments.
Watt Density and "Hot Spots"
Watt density is the measure of heat output per unit of surface area (watts per square inch or cm²). If the watt density is too high, localized "hot spots" can form. These spots can easily exceed the material's maximum temperature rating, leading to premature burnout even if the element's average temperature is within a safe range.
Physical Support and Contamination
At extreme temperatures, heating elements soften and can sag under their own weight, a phenomenon known as creep. Proper ceramic supports are essential to prevent the element from deforming and shorting out. Furthermore, contaminants like oil, grease, or even dust can attack the element's surface, creating weak points that lead to failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a maximum operating temperature is not about pushing a material to its absolute limit. It's an exercise in balancing performance with reliability.
Longevity vs. Temperature
There is an exponential relationship between an element's operating temperature and its lifespan. Running an element at its absolute maximum rated temperature will dramatically shorten its service life. A common engineering practice is to "de-rate" the element.
Operating an element just 50°C to 100°C below its stated maximum can often double or triple its operational lifespan.
Cost vs. Performance
The cost of a heating element scales directly with its temperature capability. Nichrome is inexpensive and perfectly suitable for most common applications. The cost increases significantly for FeCrAl alloys and becomes an order of magnitude higher for specialized ceramic elements like MoSi2.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine the correct temperature limit, you must first define your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is longevity and reliability (e.g., industrial ovens): Choose a material whose maximum temperature is at least 100°C higher than your target operating temperature to build in a significant safety margin.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures (e.g., laboratory furnaces): You must select a specialized ceramic or refractory metal element and strictly control the operating atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is cost for a consumer product (e.g., toasters, hair dryers): A Nickel-Chromium (Nichrome) alloy is the standard, operating well below its theoretical maximum to ensure a safe and long service life.
Ultimately, defining the right temperature limit is about balancing material science with the practical demands of your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Examples | Typical Max Operating Temperature (°C) | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic Alloys | Nichrome, FeCrAl (Kanthal) | 1200°C - 1400°C | Good oxidation resistance, cost-effective |
| Ceramics | Silicon Carbide (SiC), Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | 1625°C - 1850°C+ | High-temp capability, used in lab/industrial furnaces |
| Refractory Metals | Tungsten, Molybdenum | 2000°C+ | Requires vacuum/inert atmosphere, extreme heat |
Need the right heating element for your application? Selecting the correct maximum temperature is critical for performance, safety, and equipment longevity. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance and high-quality heating solutions tailored to your laboratory's specific needs—whether you require standard alloys or high-temperature ceramics.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and ensure optimal, reliable performance for your lab furnaces and ovens.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why are high-performance sealing and refractory materials critical for high-temperature solar thermochemical reactors?
- Is molybdenum a good thermal conductor? Its High-Temperature Performance Explained
- What is the melting point of tungsten? Discover the Metal That Withstands Extreme Heat
- Are there different types of heating elements? Choose the Right Heater for Your Application
- What is the electrical resistivity of molybdenum disilicide? Unlocking its High-Temperature Heating Power
- What is the crystal structure of MoSi2? Unlocking Its High-Temperature Performance
- How do integrated Pt100 temperature sensors assist in the study of dissolution kinetics of materials in liquid tin?
- Why are high-performance resistance heating elements required in pyrolysis? Ensure Precise Biomass Conversion











