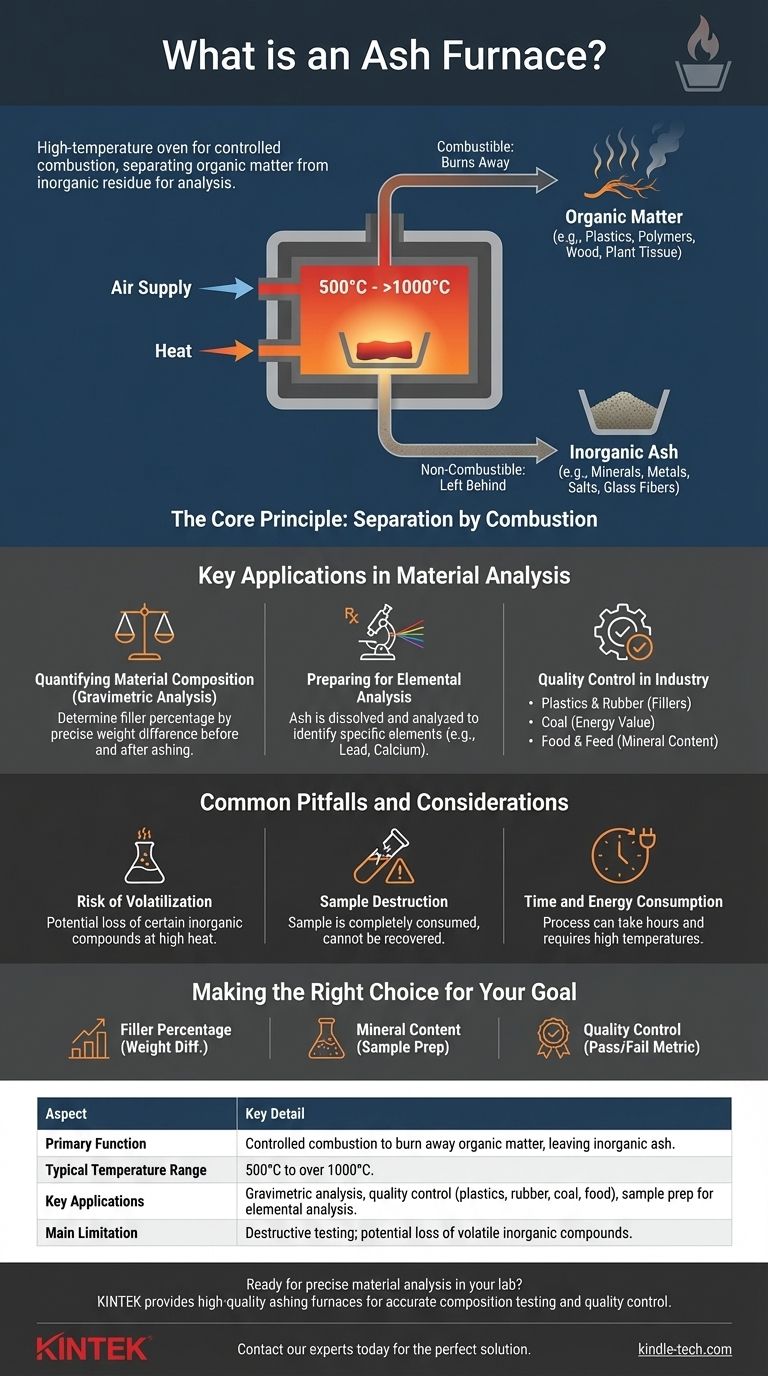
In technical analysis, an ashing furnace is a high-temperature oven designed for the controlled and complete combustion of a sample. Its primary purpose is to burn away all organic matter, leaving behind only the inorganic, non-combustible residue—the "ash"—for subsequent measurement and analysis. This process is a fundamental technique for determining the composition of materials.
An ashing furnace isn't simply for burning things; it's a precision instrument for separating the organic from the inorganic. By reducing a sample to its fundamental mineral components, it allows scientists and engineers to quantify and identify what a material is truly made of.

The Core Principle: Separation by Combustion
An ashing furnace operates on a straightforward yet critical principle: using high heat and oxygen to systematically remove one part of a sample (the combustible portion) to isolate the other (the non-combustible portion).
What is "Ashing"?
Ashing is the process of complete combustion. A sample is placed inside the furnace and heated to temperatures typically ranging from 500°C to over 1000°C in the presence of air. This environment causes all organic compounds—those based on carbon—to oxidize and burn away as gases like carbon dioxide.
The Role of High Temperature and Air
The combination of extreme heat and a controlled air supply ensures that the combustion is complete. Insufficient temperature or oxygen would result in incomplete burning, leaving behind char (carbon) and skewing the final results. The furnace provides the ideal environment for this chemical reaction to run to completion.
Organic vs. Inorganic Components
The key to understanding ashing is the distinction between what burns and what remains.
- Organic Matter: This includes plastics, polymers, rubber, wood, plant tissue, and other carbon-based materials. These components are completely consumed in the furnace.
- Inorganic Matter: This includes minerals, metals, salts, glass fibers, and other fillers. These non-combustible materials are left behind as ash.
Key Applications in Material Analysis
The data gathered from an ashing test is crucial for quality control, research, and regulatory compliance across many industries.
Quantifying Material Composition
The most common use of an ashing furnace is for gravimetric analysis—determining composition by weight. By precisely weighing a sample before and after ashing, one can calculate the percentage of organic and inorganic content. For example, this reveals the amount of mineral filler in a plastic or rubber compound.
Preparing for Elemental Analysis
Ashing is often the first step in a more complex analytical workflow. The resulting ash, free from organic interference, can be dissolved and analyzed using techniques like spectroscopy to identify the specific elements (e.g., lead, calcium, iron) present in the original sample. This is common in food analysis to determine mineral content.
Quality Control in Industry
Industries rely on ashing to ensure their products meet strict specifications.
- Plastics & Rubber: To verify the percentage of reinforcing fillers like glass or talc.
- Coal: To determine the ash content, which is a key indicator of its quality and energy value.
- Food & Feed: To measure the total mineral content, an important nutritional metric.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While powerful, the ashing process is not without limitations. Being aware of them is critical for generating accurate data.
Risk of Volatilization
The primary pitfall is the potential loss of certain inorganic compounds. Some metallic salts or oxides can vaporize or decompose at the high temperatures used for ashing. This leads to an underestimation of the true ash content and requires careful method development for sensitive materials.
Sample Destruction
Ashing is a form of destructive testing. The original sample is completely consumed in the process and cannot be recovered. This must be considered when working with limited or valuable samples.
Time and Energy Consumption
The process of heating, soaking at a high temperature, and cooling can take several hours to complete. This, combined with the high temperatures required, makes ashing a relatively energy-intensive analytical method.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The purpose of an ashing test directly informs how you should interpret its results.
- If your primary focus is determining filler percentage: The critical data points are the precise initial and final weights, as the difference is the key to calculating your percentage.
- If your primary focus is identifying mineral content: View the ashing process as a sample preparation step. The resulting ash is your true starting material for further elemental analysis.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control: The absolute ash value is your pass/fail metric, which you will compare against an established product specification or a known standard.
Ultimately, the ashing furnace serves to uncloud your view by removing organic complexity and revealing a material's inorganic backbone.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Controlled combustion to burn away organic matter, leaving inorganic ash. |
| Typical Temperature Range | 500°C to over 1000°C. |
| Key Applications | Gravimetric analysis, quality control (plastics, rubber, coal, food), sample prep for elemental analysis. |
| Main Limitation | Destructive testing; potential loss of volatile inorganic compounds. |
Ready to achieve precise material analysis in your lab?
An ashing furnace is a cornerstone of accurate composition testing. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, including reliable ashing furnaces, to meet the rigorous demands of quality control and research laboratories.
We provide the tools for you to:
- Accurately determine filler percentages in plastics and rubber.
- Perform essential quality checks on coal and food products.
- Prepare pristine samples for downstream elemental analysis.
Let's discuss your specific application. Contact our experts today to find the perfect ashing solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of a muffle furnace? Understanding the Trade-offs for Your Lab
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and air oven? Choose the Right Tool for Your Thermal Process
- What are the different types of laboratory furnaces? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Application
- What is done by ashing in muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise Inorganic Content Analysis
- How is the ash content determined in a muffle furnace? Master the Gravimetric Analysis Method



















