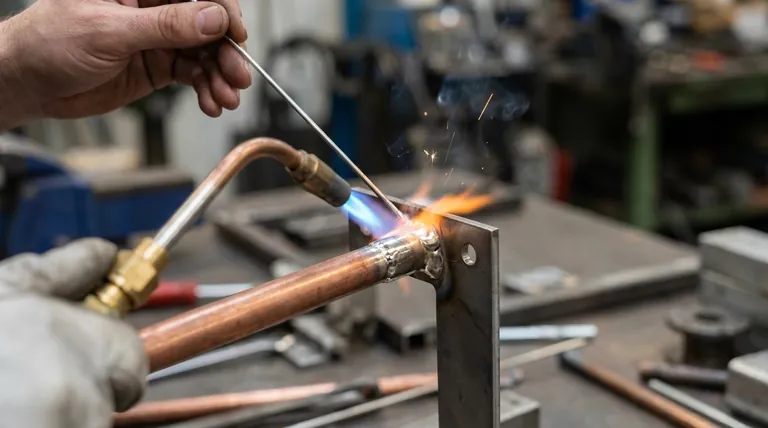
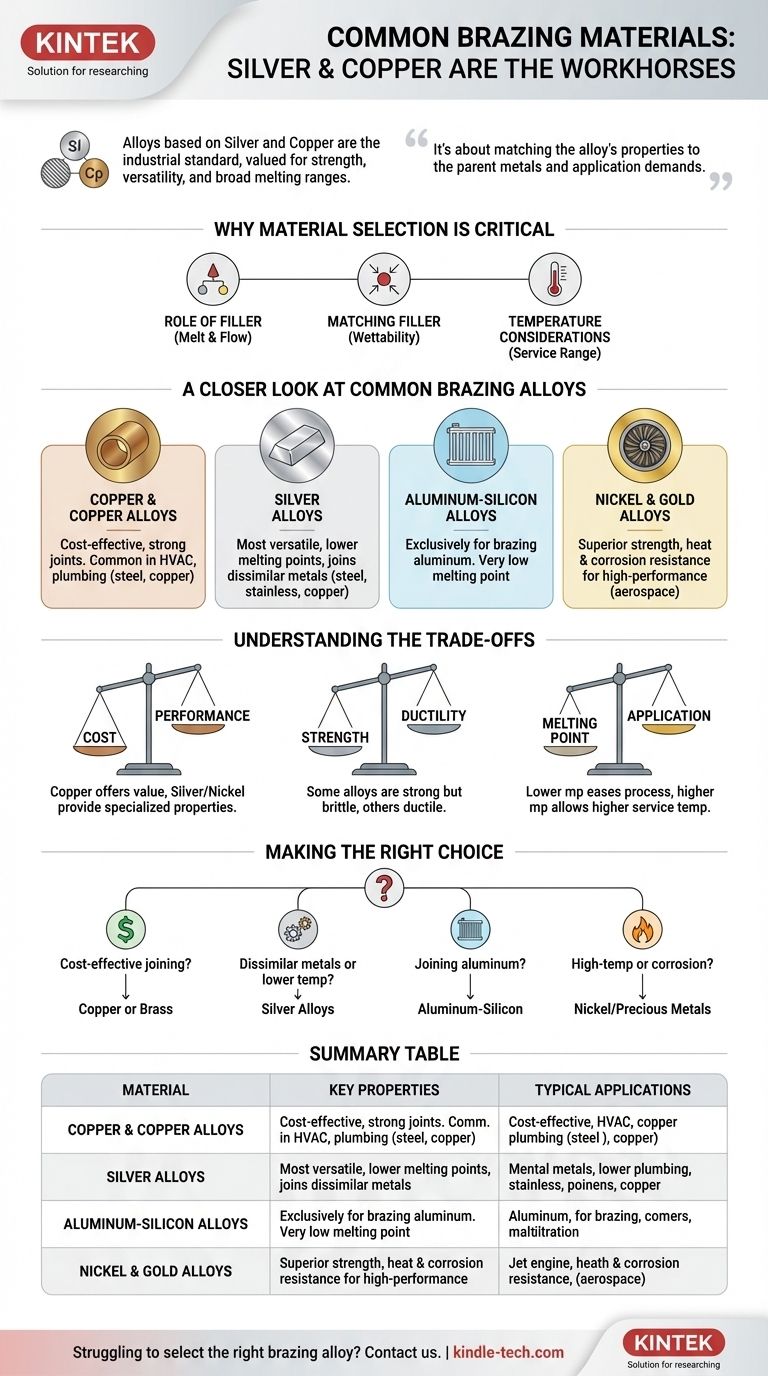
The most common materials used in brazing are alloys based on silver and copper. While a wide variety of filler metals exist for specific applications, copper and silver alloys are the industrial workhorses, valued for their combination of strength, versatility, and broad range of melting temperatures suitable for joining common metals like steel, stainless steel, and copper itself.
The choice of a brazing filler metal is not about finding a single "best" material, but about matching the alloy's properties—primarily its melting point and metallurgical compatibility—to the specific parent metals being joined and the demands of the final application.

Why Material Selection is Critical in Brazing
Brazing creates a permanent metallurgical bond by melting a filler metal that flows between tightly fitted parent materials via capillary action. The success of this entire process hinges on selecting the correct filler metal.
The Role of the Filler Metal
The filler metal must have a melting point lower than that of the parent metals being joined. It is designed to melt and flow freely at the brazing temperature, wetting the surfaces of the joint without melting the parent materials themselves.
Matching Filler to Parent Metal
Proper wettability is crucial. The molten filler must be able to spread smoothly over the parent metal surfaces. This depends on the metallurgical compatibility between the filler and the base materials. An improper match can lead to a weak bond or even damage the parent metals.
Temperature Considerations
The service temperature of the final assembly dictates the choice of filler metal. The filler's melting range must be significantly higher than any temperature the part will experience in operation, otherwise the joint could weaken or fail.
A Closer Look at Common Brazing Alloys
Different base metals and applications require different filler metal characteristics. This has led to the development of several key alloy families.
Copper and Copper Alloys
Alloys like copper-zinc (brass) and copper-phosphorus are extremely common. They are cost-effective and create strong, durable joints, making them a primary choice for brazing steel, cast iron, and copper tubing, especially in the HVAC and plumbing industries.
Silver Alloys
Silver-based alloys are perhaps the most versatile group. They offer lower melting points than copper alloys, which reduces the heat input and potential distortion of the parent parts. They also exhibit excellent flow characteristics and are capable of joining a wide variety of dissimilar metals, including steel, stainless steel, and copper alloys.
Aluminum-Silicon Alloys
These alloys are used exclusively for brazing aluminum. Because aluminum has a very low melting point, a specialized filler metal with an even lower, precisely controlled melting temperature is required. These are essential in the automotive (radiators) and aerospace industries.
Nickel and Gold Alloys
Found in high-performance applications, nickel alloys provide superior strength and resistance to heat and corrosion. Gold-based alloys offer exceptional corrosion resistance and reliability. Both are used in demanding environments like jet engines, aerospace components, and specialized electronics where performance justifies their high cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a brazing material always involves balancing competing factors. Understanding these compromises is key to making an informed decision.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct relationship between cost and performance. Copper alloys offer excellent value for general-purpose applications. Silver and nickel alloys are significantly more expensive but provide essential properties like lower process temperatures or higher service strength that are non-negotiable in demanding applications.
Strength vs. Ductility
The composition of the filler alloy dictates the mechanical properties of the final joint. Some alloys create exceptionally strong but more brittle joints, while others provide more ductility and toughness, allowing the joint to absorb vibration and shock.
Melting Point vs. Application
A lower melting point makes the brazing process easier and safer for heat-sensitive components. However, this directly limits the maximum service temperature of the finished part. High-temperature applications, such as in exhaust systems or engines, demand fillers with high melting points like nickel alloys.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection should be driven by the specific requirements of your project.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective joining of steel or copper: Copper or copper-zinc (brass) alloys are your most reliable and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals or requires a lower brazing temperature: Silver-based alloys provide the necessary versatility and excellent flow characteristics.
- If your primary focus is joining aluminum components: You must use a specialized aluminum-silicon filler metal designed for that purpose.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature or high-corrosion environments: Nickel or precious metal alloys are necessary despite their higher cost.
Selecting the correct brazing alloy is the foundational step to creating a strong, reliable, and permanent joint.
Summary Table:
| Common Brazing Material | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Copper & Copper Alloys | Cost-effective, strong, durable joints | Steel, cast iron, copper tubing (HVAC, plumbing) |
| Silver Alloys | Versatile, lower melting point, excellent flow | Joining dissimilar metals, general-purpose brazing |
| Aluminum-Silicon Alloys | Low melting point, designed for aluminum | Automotive radiators, aerospace aluminum components |
| Nickel & Gold Alloys | High strength, heat/corrosion resistance | Jet engines, aerospace, high-performance electronics |
Struggling to select the right brazing alloy for your specific metals and application requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including brazing materials tailored for your laboratory or production needs. Our experts can help you choose the optimal filler metal to ensure strong, reliable joints for your projects.
Contact us today to discuss your brazing requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your joining process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Conductive Glass Substrate Cleaning Rack
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Corrosion Resistant Cleaning Rack Flower Basket
People Also Ask
- What is the melting point of tungsten? Discover the Metal That Withstands Extreme Heat
- What are the disadvantages of tungsten filament? Key Limitations in Lighting Technology
- Why tungsten is not used in heating devices? The Critical Role of Oxidation Resistance
- Can tungsten be used as a heating element? Unlocking Extreme Heat for High-Temperature Applications
- Why tungsten is not used as heating element? Discover the critical role of oxidation resistance.


















