At its core, muffle furnace analysis refers to any analytical process that uses a high-temperature laboratory furnace to heat a sample in a controlled, isolated environment. These furnaces are not used for a single type of analysis but are a fundamental tool for a range of applications where extreme heat is required to test, change, or determine the composition of a material without contamination from the heating source itself.
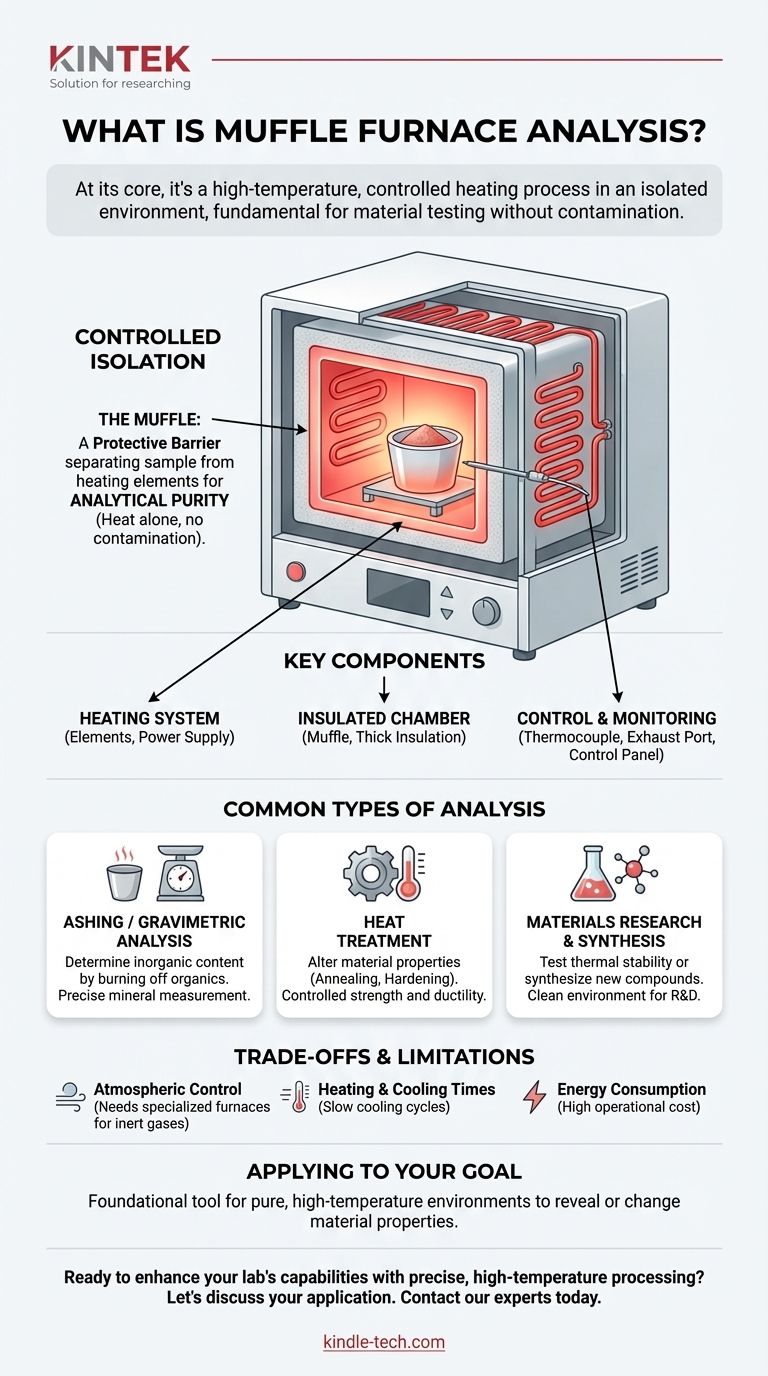
The defining characteristic of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its "muffle"—an insulated inner chamber that isolates the sample from the heating elements. This separation ensures that any changes to the sample are a direct result of heat alone, which is the foundation of accurate, repeatable analysis.

The Principle of the Muffle Furnace: Controlled Isolation
A muffle furnace is essentially a high-performance oven designed for laboratory and industrial settings. Its primary function is to provide a uniform, high-temperature environment that is free from contaminants.
A High-Temperature, Contained Environment
The furnace can achieve rapid heating to temperatures often exceeding 1000°C (and sometimes over 2000°C in specialized models). This capability is essential for processes like melting, ashing, and heat-treating materials.
The "Muffle": A Protective Barrier
The term "muffle" refers to the furnace's inner chamber, which is typically made from high-temperature refractory materials like silica and aluminum ceramics. This chamber acts as a barrier, separating the sample from the actual heating elements.
Ensuring Analytical Purity
In simpler furnaces, byproducts from the combustion or oxidation of the heating elements could interact with and contaminate the sample. The muffle prevents this, ensuring that the results of the analysis are pure and only reflect the impact of temperature on the material.
Key Components and Their Function
A muffle furnace is a system of integrated components working together to provide precise thermal processing.
The Heating System
This includes the heating elements, often made of a durable alloy like iron-chromium-aluminum, which generate the heat. A power supply and temperature controller manage the energy flow, allowing for precise control over heating rates and target temperatures.
The Insulated Chamber
The core of the furnace consists of the muffle chamber where the sample is placed. This is surrounded by thick insulation to maintain high internal temperatures efficiently and keep the outer casing cool and safe to touch.
The Control and Monitoring System
A thermocouple acts as a temperature sensor, feeding real-time data back to the controller. An exhaust port is often included to safely vent any gases or fumes produced by the sample during heating, and a control panel allows the operator to set and monitor the process.
Common Types of Muffle Furnace Analysis
The isolated, high-heat environment of a muffle furnace is critical for several standard analytical and treatment processes.
Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
This is one of the most common applications. A sample (like food, soil, or plastic) is heated to a high temperature to completely burn off all organic matter. By weighing the sample before and after, analysts can precisely determine its inorganic mineral content, known as ash.
Heat Treatment of Materials
Muffle furnaces are used extensively in metallurgy and materials science to alter the physical properties of materials. Processes like annealing (softening), hardening, and tempering of metals and ceramics require exact temperature control to achieve desired strength, ductility, or hardness.
Materials Research and Synthesis
Researchers use muffle furnaces to test the thermal stability of new materials or to synthesize novel compounds that only form at high temperatures. The clean, controlled environment is crucial for experimental research where variables must be minimized.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not the right tool for every thermal application. Understanding its limitations is key to proper use.
Atmospheric Control
A standard muffle furnace operates with a normal air atmosphere. If a process requires an inert (e.g., nitrogen, argon) or reactive gas environment, a more specialized tube furnace or vacuum furnace is necessary.
Heating and Cooling Times
The very insulation that makes a muffle furnace energy-efficient also causes it to retain heat for a long time. While heating can be rapid, the cooling cycle is often slow, which can limit sample throughput in a busy lab.
Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures of 1000°C or more requires a significant amount of electrical energy. This is a primary operational cost to consider.
Applying This to Your Goal
The specific "analysis" you perform depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is determining a sample's inorganic content: You will perform ashing, a type of gravimetric analysis that requires burning the material to a constant weight.
- If your primary focus is altering the properties of a metal or ceramic: You are performing heat treatment, which demands precise control over temperature, soak time, and cooling rates.
- If your primary focus is testing a material's performance at high temperatures: You are conducting thermal stability or degradation testing, where temperature uniformity is paramount.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace is a foundational tool that provides the pure, high-temperature environment essential for revealing or changing the fundamental properties of materials.
Summary Table:
| Analysis Type | Primary Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Ashing / Gravimetric | Determine inorganic content (ash) in samples like food or soil. | Precise measurement of mineral content. |
| Heat Treatment | Alter material properties (e.g., annealing, hardening metals). | Controlled alteration of strength and ductility. |
| Materials Research | Test thermal stability or synthesize new compounds. | Clean, controlled environment for accurate R&D. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precise, high-temperature processing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing reliable lab equipment, including high-performance muffle furnaces designed for accurate ashing, heat treatment, and materials research. Our solutions ensure the contaminant-free environment and precise temperature control your laboratory needs for dependable results.
Let's discuss your specific application. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your analytical goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the use of ashing? Isolate and Quantify Total Mineral Content in Your Samples
- Why is an industrial muffle or tube furnace required for CeTe synthesis? Precision Thermal Management for Rare Earths
- What is a box furnace? A Guide to Batch Thermal Processing for Labs & Industry
- What conditions does a muffle furnace provide for studying (Ti,M)3AlC2 ceramics? Maximize Experimental Accuracy
- What is the temperature of a batch type furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Application
- What is the application of muffle furnace in food industry? Essential for Accurate Food Ash Analysis
- Why is a high-stability furnace essential for 9Cr-1Mo steel tensile testing? Ensure Data Integrity at 600°C
- What is the difference between a chamber furnace and a muffle furnace? Understanding Modern Lab Heating Equipment



















