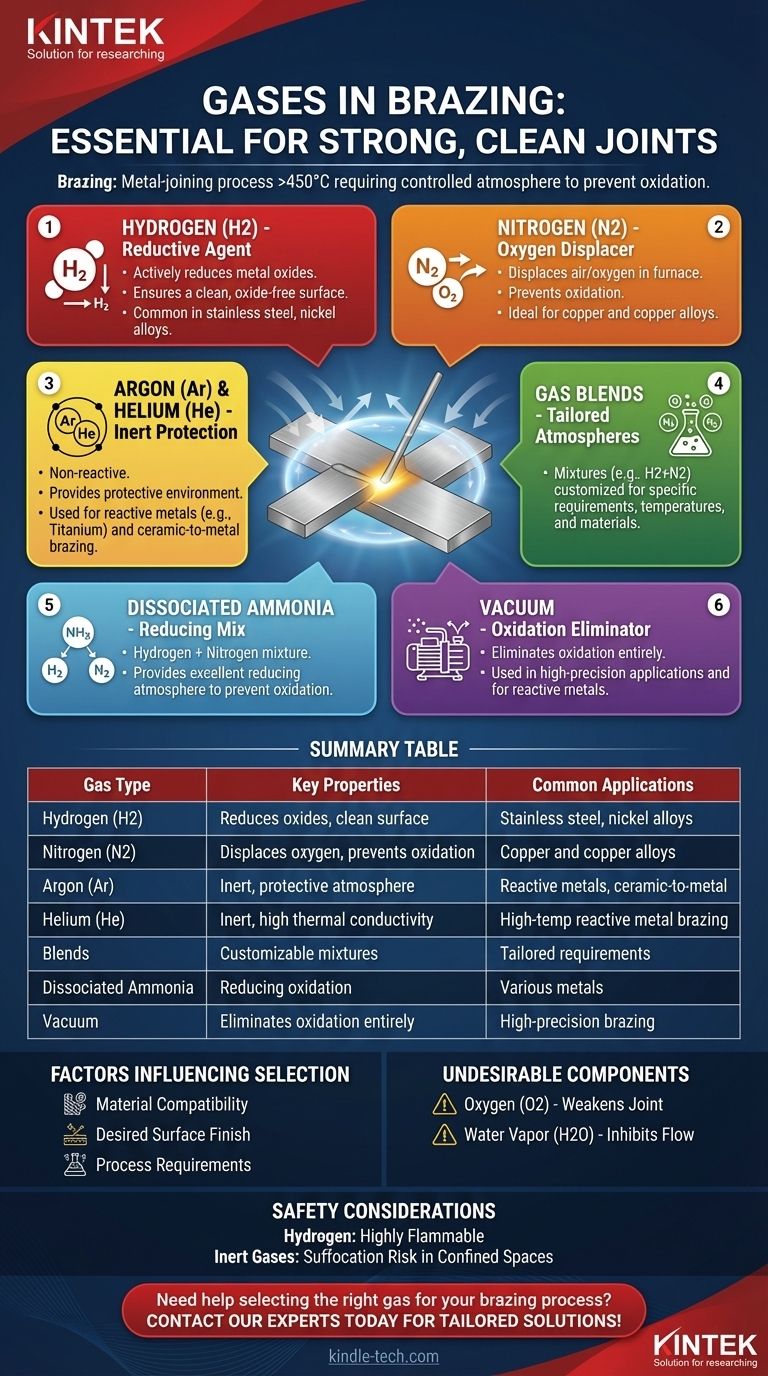
Brazing is a metal-joining process that uses a filler metal with a melting point above 450°C (842°F) but below the melting point of the base metals being joined. The process requires a controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation and ensure a strong, clean joint. The gases used in brazing depend on the materials being joined and the desired outcome. Commonly used gases include hydrogen, nitrogen, argon, helium, and blends of these gases. Hydrogen is particularly effective in reducing metal oxides, while inert gases like argon and helium provide a protective environment. The choice of gas is critical to achieving a high-quality brazed joint.

Key Points Explained:
-
Purpose of Gases in Brazing
- Gases are used in brazing to create a controlled atmosphere that prevents oxidation, scaling, and carbon buildup (soot).
- Oxidation can weaken the joint and reduce the quality of the finished product.
- A clean, bright finished product is achieved by using the appropriate gas or gas mixture.
-
Commonly Used Gases
-
Hydrogen (H2):
- Acts as an active agent for the reduction of metal oxides.
- Commonly used in brazing processes to produce a clean, oxide-free surface.
- Often used in combination with other inert gases.
-
Nitrogen (N2):
- Displaces air/oxygen in the furnace atmosphere, preventing oxidation.
- Particularly effective for brazing copper.
-
Argon (Ar) and Helium (He):
- Inert gases that provide a protective atmosphere, preventing reactions with the base metals.
- Used in brazing metals and ceramics where a non-reactive environment is essential.
-
Blends of Gases:
- Mixtures of hydrogen and nitrogen or other inert gases are often used to tailor the atmosphere to specific brazing requirements.
-
Hydrogen (H2):
-
Specialized Atmospheres
-
Dissociated Ammonia:
- A mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen produced by dissociating ammonia.
- Provides a reducing atmosphere, ideal for preventing oxidation.
-
Exothermic and Endothermic Gases:
- These are generated by burning natural gas or propane with air.
- Used in specific brazing applications where a controlled reactive atmosphere is needed.
-
Vacuum:
- In some cases, a vacuum is used instead of a gas atmosphere to eliminate oxidation entirely.
-
Dissociated Ammonia:
-
Factors Influencing Gas Selection
-
Material Compatibility:
- The type of base metal and filler metal being used determines the appropriate gas. For example, hydrogen is suitable for reducing oxides on steel, while nitrogen is better for copper.
-
Desired Surface Finish:
- A bright, clean finish requires a gas that effectively reduces oxides, such as hydrogen or dissociated ammonia.
-
Process Requirements:
- The brazing temperature, furnace design, and joint configuration influence the choice of gas.
-
Material Compatibility:
-
Undesirable Components in Brazing Atmospheres
-
Oxygen (O2):
- Causes oxidation, which weakens the joint and degrades the surface finish.
-
Water Vapor (H2O):
- Inhibits braze flow and can lead to poor joint quality, except in specific copper brazing applications where it may be beneficial.
-
Oxygen (O2):
-
Applications of Specific Gases
-
Hydrogen:
- Used in brazing stainless steel, nickel alloys, and other metals prone to oxidation.
-
Nitrogen:
- Ideal for brazing copper and copper alloys.
-
Argon and Helium:
- Used in high-temperature brazing of reactive metals like titanium and in ceramic-to-metal brazing.
-
Hydrogen:
-
Safety Considerations
-
Hydrogen:
- Highly flammable and requires careful handling and equipment designed for hydrogen use.
-
Inert Gases:
- While non-reactive, they can displace oxygen in confined spaces, posing a suffocation risk.
-
Hydrogen:
In summary, the gases used in brazing are selected based on their ability to create a controlled atmosphere that prevents oxidation and ensures a strong, clean joint. Hydrogen, nitrogen, argon, helium, and their blends are the most commonly used gases, each offering unique benefits depending on the materials and process requirements. The choice of gas is critical to achieving the desired brazing outcome, and safety considerations must always be taken into account when handling these gases.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H2) | Reduces metal oxides, ensures clean surface | Stainless steel, nickel alloys |
| Nitrogen (N2) | Displaces oxygen, prevents oxidation | Copper and copper alloys |
| Argon (Ar) | Inert, provides protective atmosphere | Reactive metals (e.g., titanium), ceramic-to-metal brazing |
| Helium (He) | Inert, high thermal conductivity | High-temperature brazing of reactive metals |
| Blends | Customizable mixtures (e.g., H2 + N2) | Tailored for specific brazing requirements |
| Dissociated Ammonia | Hydrogen + nitrogen mix, reduces oxidation | Preventing oxidation in various metals |
| Vacuum | Eliminates oxidation entirely | High-precision brazing applications |
Need help selecting the right gas for your brazing process? Contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What are the tubes in a furnace called? Understanding the Role of the Working Tube
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature Uniformity and Control



















