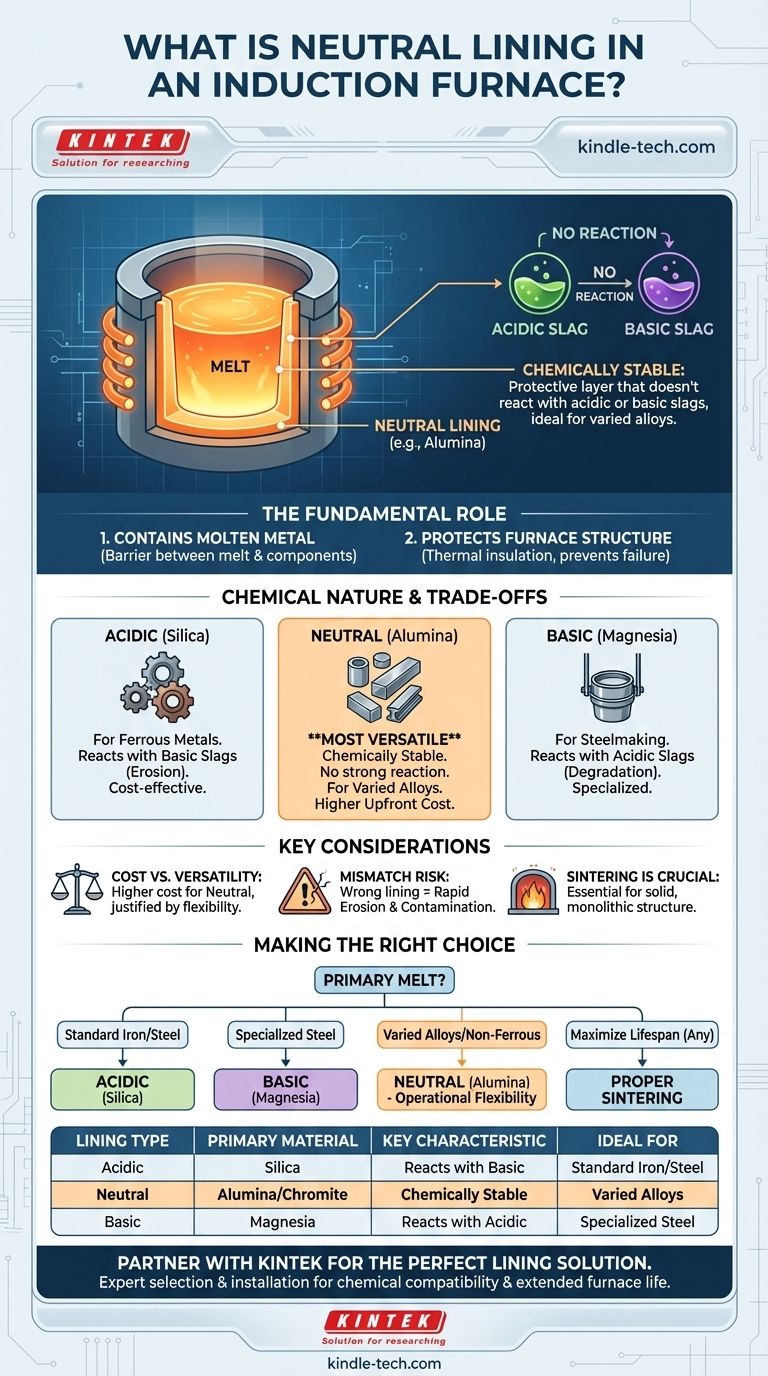
In simple terms, a neutral lining in an induction furnace is a protective layer made from refractory materials that are chemically neutral. Unlike acidic or basic linings, a neutral lining—typically made of materials like alumina—does not react with either acidic or basic slags produced during the melting process. This chemical stability makes it a versatile and robust choice for a wide range of metal alloys.
The core takeaway is that the term "neutral" refers to the chemical property of the lining material. Choosing a neutral lining is a strategic decision to prevent chemical reactions between the furnace wall and the molten metal, which protects the furnace, prevents contamination of the melt, and increases operational flexibility.

The Fundamental Role of a Furnace Lining
Containing the Molten Metal
The most basic function of the furnace lining is to act as a crucible, containing the liquid metal at extremely high temperatures.
It is the only barrier separating the superheated molten charge from the critical furnace components, such as the induction coil.
Protecting the Furnace Structure
The lining provides thermal insulation and protects the furnace's induction coil and steel shell from the intense heat of the melt. A failure of the lining can lead to a catastrophic failure of the entire furnace.
Why Chemical Nature Matters: Acidic, Basic, and Neutral
The interaction between the furnace lining and the molten metal's byproduct, known as slag, dictates the furnace's lifespan and the purity of the final product. Linings are therefore classified by their chemical behavior.
Acidic Linings
Acidic linings, most commonly made of silica (quartzite), are cost-effective and widely used for melting ferrous metals where the slag produced is acidic in nature.
However, they will be rapidly eroded and damaged if they come into contact with basic slags.
Basic Linings
Basic linings are typically made from magnesia (magnesite) and are used in applications like steelmaking where the slag is chemically basic.
These linings are resistant to basic slags but will react and degrade quickly if used with metals that produce an acidic slag.
Neutral Linings
Neutral linings are the most versatile. Made from materials like alumina, chromite, or graphite, they are chemically stable and do not have a strong reaction with either acidic or basic slags.
This makes them ideal for melting a variety of alloys, special steels, and in situations where slag chemistry might vary.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a lining material is not just about chemical compatibility; it's a balance of cost, performance, and operational procedure.
Cost vs. Versatility
Neutral materials like high-purity alumina are generally more expensive than acidic silica linings. This higher upfront cost is often justified by greater flexibility in the types of metals you can melt and potentially longer service life.
The Critical Risk of a Mismatch
Using the wrong lining type is a common and costly mistake. For example, using a silica (acidic) lining to melt a high-manganese steel (which produces a basic slag) will cause the slag to aggressively attack and erode the lining, leading to rapid failure.
This not only shortens furnace life but also contaminates the molten metal with impurities from the lining itself.
The Importance of Sintering
The best lining material is ineffective if not installed correctly. The sintering process—heating the newly installed lining through a controlled cycle—is what transforms the loose refractory powder into a solid, monolithic, and strong structure.
As noted in furnace procedures, a proper sintering schedule that removes moisture and achieves the correct final temperature is essential for maximizing the lining's service life, regardless of its chemical type.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of lining should be dictated by the material you are melting and your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is melting standard cast iron or carbon steels: An acidic (silica) lining is often the most economical and effective choice.
- If your primary focus is specialized steelmaking with basic slags: A basic (magnesia) lining is necessary for chemical compatibility and furnace protection.
- If your primary focus is melting a wide variety of alloys or non-ferrous metals: A neutral (alumina) lining provides the greatest operational flexibility and safety against chemical attack.
- If your primary focus is maximizing furnace lifespan: Ensure that whichever lining you choose is installed and sintered according to the manufacturer's exact specifications to achieve its full performance potential.
Ultimately, understanding the chemistry of your melt is the key to selecting a furnace lining that ensures safety, efficiency, and quality.
Summary Table:
| Lining Type | Primary Material | Key Characteristic | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acidic | Silica (Quartzite) | Reacts with basic slags | Cost-effective melting of standard cast iron, carbon steels |
| Basic | Magnesia (Magnesite) | Reacts with acidic slags | Specialized steelmaking with basic slags |
| Neutral | Alumina, Chromite | Chemically stable; resists both acidic & basic slags | Wide variety of alloys, special steels, non-ferrous metals |
Maximize your melting efficiency and protect your furnace investment with the right lining.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including induction furnaces and the ideal refractory linings for your specific application. Whether you're melting standard steels, specialized alloys, or non-ferrous metals, our experts can help you select and install the perfect neutral, acidic, or basic lining to ensure chemical compatibility, prevent contamination, and extend furnace life.
Contact us today to discuss your needs and let KINTEK be your partner in achieving superior melting results. Get in touch with our specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum arc remelting work? Achieve Ultra-Clean, High-Performance Metal Alloys
- What is the remelting process? Achieve Ultimate Purity and Performance for High-Strength Alloys
- What is the vacuum arc remelting process? Producing Ultra-Pure, High-Performance Metal Alloys
- What is the process of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Ultimate Purity for High-Performance Alloys
- What is var in metals? A Guide to Vacuum Arc Remelting for Superior Alloys



















