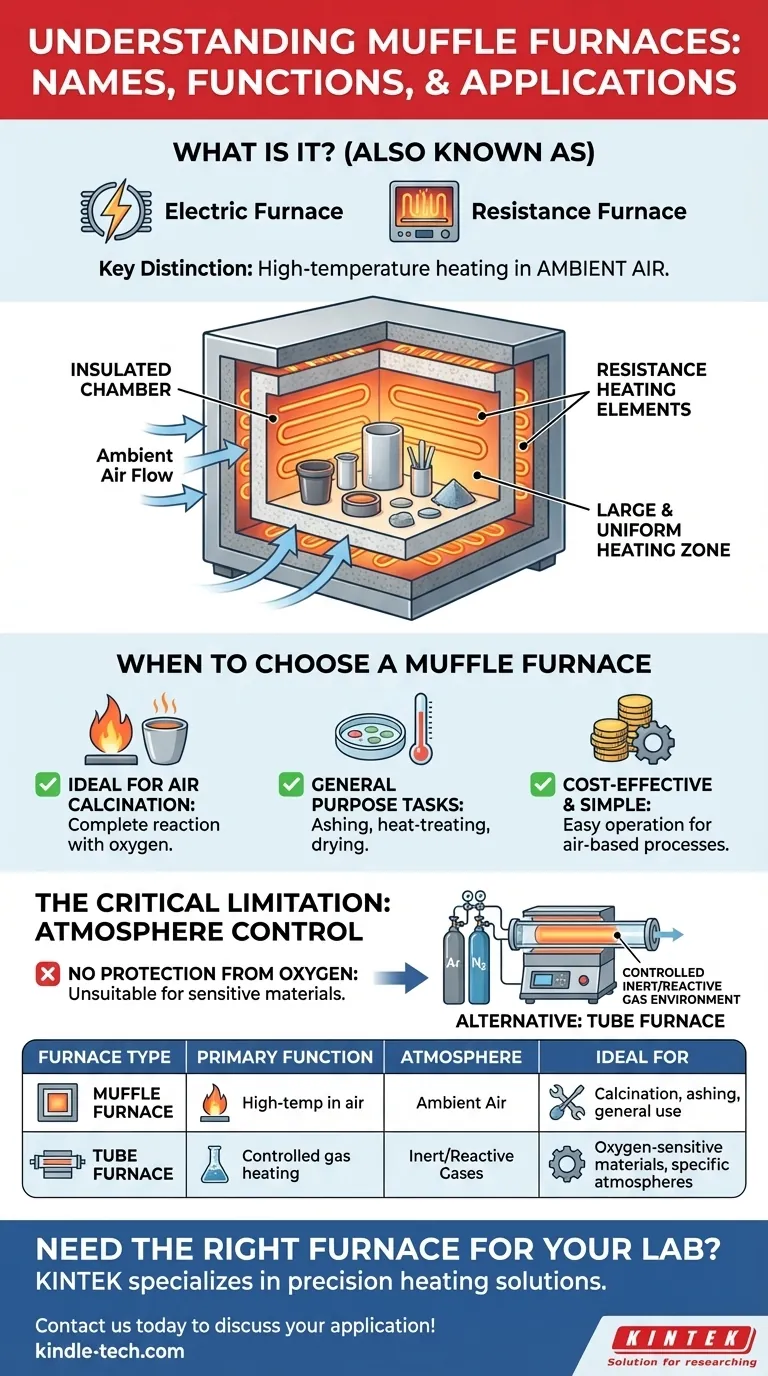
In technical and laboratory settings, a muffle furnace is most commonly known by other names that describe its function, such as an electric furnace or a resistance furnace. These terms highlight the core mechanism it uses to generate extreme heat for various material processing applications.
While it has several names, the key distinction of a muffle furnace is its design for high-temperature heating in ambient air. Understanding this core function is more critical than its name, as it dictates when to use it and when to choose a different tool.
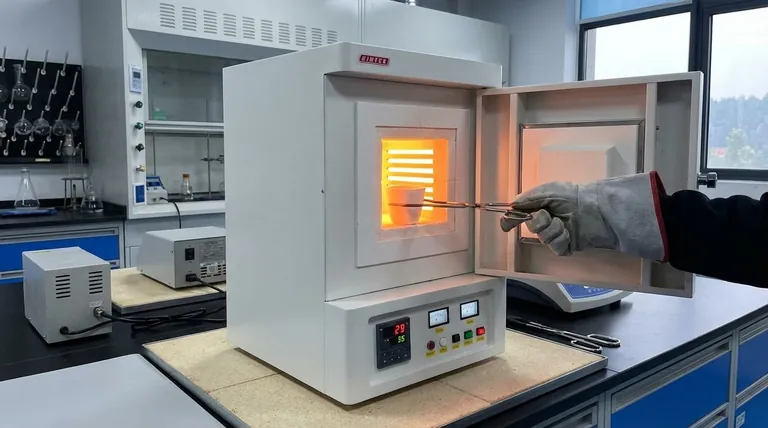

What Defines a Muffle Furnace?
A muffle furnace is a specific type of oven capable of reaching very high temperatures. Its name and function are derived from its core components and operational environment.
The Principle of Resistance Heating
The names electric furnace and resistance furnace point directly to how it works. An electric current is passed through high-resistance heating elements, which generate intense heat inside an insulated chamber, much like the coils on an electric stove.
Designed for Heating in Air
The primary operational feature of a muffle furnace is that it heats samples in ambient air. This design allows the material being heated to have full contact with the surrounding air.
A Large and Uniform Heating Zone
These furnaces are typically built with a larger heating chamber compared to more specialized equipment. This makes them suitable for processing multiple samples at once or for handling bulkier items that require uniform heat exposure.
When to Choose a Muffle Furnace
The choice between a muffle furnace and other high-temperature equipment depends entirely on the requirements of your process, particularly concerning the atmosphere.
Ideal for Air Calcination
A muffle furnace is the preferred instrument for calcination processes that must occur in the presence of oxygen. The open-air environment ensures the material can fully react with the air, leading to complete calcination.
General Purpose High-Temperature Applications
For many straightforward heating tasks—such as ashing, heat-treating, or drying materials at high temperatures without needing a special atmosphere—the muffle furnace is the standard tool.
Cost-Effectiveness and Simplicity
Due to its simpler design, a muffle furnace is often more cost-effective and easier to operate for general heating processes that do not require precise atmospheric control.
The Critical Limitation: Atmosphere Control
The greatest strength of a muffle furnace—its operation in open air—is also its most significant limitation.
The Tube Furnace Alternative
If your process requires heating a sample under a controlled atmosphere, such as with a protective inert gas like argon or nitrogen, a muffle furnace is the wrong tool. In this scenario, a tube furnace is necessary as it is designed to contain and control the gas flowing over the sample.
Why Air Contact Can Be a Problem
Many materials are sensitive to oxygen at high temperatures and will oxidize or react in undesirable ways. A muffle furnace cannot protect samples from this, making it unsuitable for applications involving oxygen-sensitive materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace is fundamental to achieving accurate and repeatable results in a laboratory or industrial setting.
- If your primary focus is complete calcination in air or general-purpose heating of multiple samples: A muffle furnace is the most direct and cost-effective tool.
- If your primary focus is controlling the atmosphere with protective or reactive gases: You must use a tube furnace to prevent unwanted reactions and ensure process integrity.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace begins with a clear understanding of your material's atmospheric requirements.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Function | Atmosphere | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muffle Furnace | High-temperature heating in air | Ambient Air | Calcination, ashing, general-purpose heating |
| Tube Furnace | Heating under controlled gas environments | Inert/Reactive Gases | Oxygen-sensitive materials, controlled atmosphere processes |
Need the right furnace for your lab's specific needs? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories with precision heating solutions. Whether you require a robust muffle furnace for air-based calcination or a controlled atmosphere tube furnace for sensitive materials, our expertise ensures you get the right tool for accurate, repeatable results. Contact us today to discuss your application and find the perfect furnace for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What happens in the muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Uniform High-Temperature Processing
- How do you choose calcination temperature? A Guide to Optimizing Material Properties
- How long is the calcination process? Optimize Your Process Time for Maximum Efficiency
- What is the highest temperature of a furnace? Unlocking the Limits of Extreme Heat
- Is the sintering process hazardous? Identifying Key Risks and Safety Protocols



















