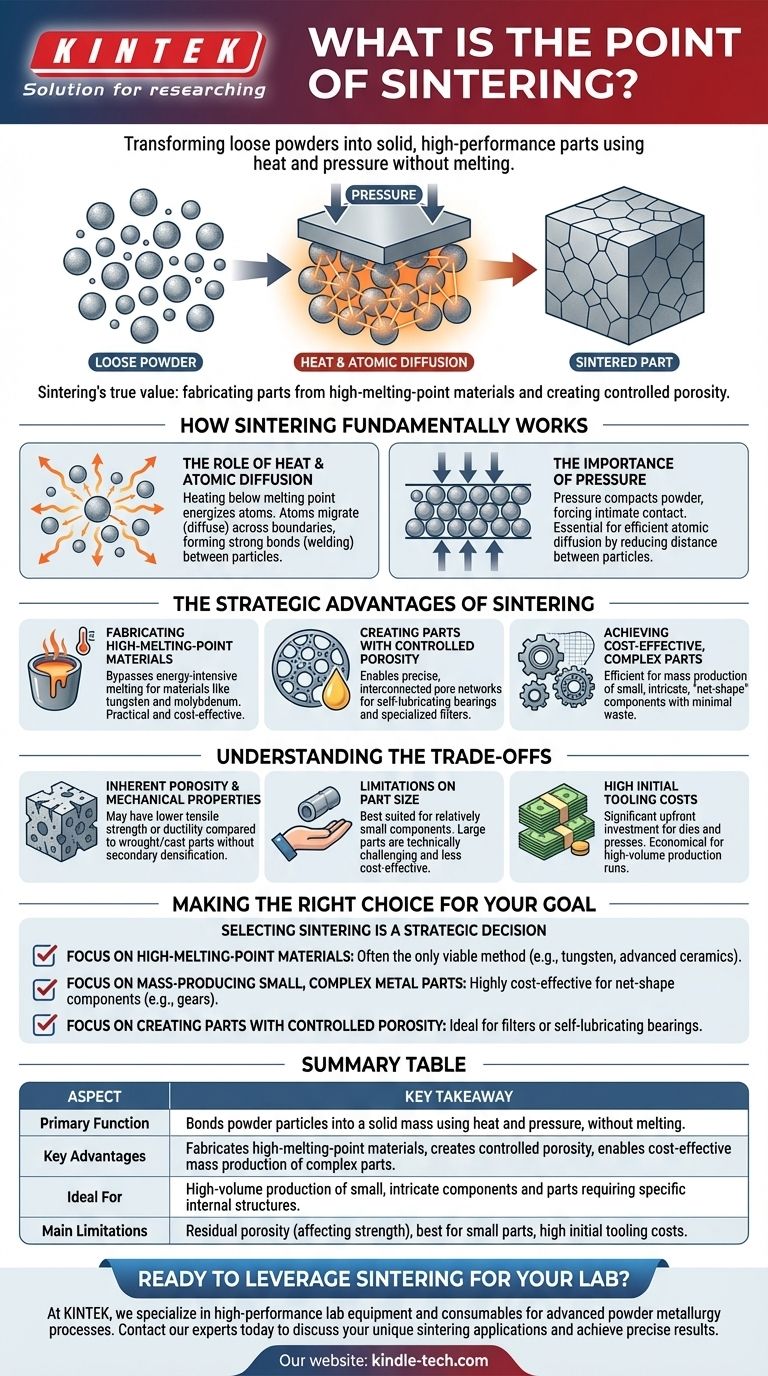
At its core, sintering is a manufacturing process that transforms loose powders into a solid, coherent mass. The key is that it achieves this fusion using heat and pressure without melting the material, allowing engineers to create strong, precise parts from metals, ceramics, and plastics that might otherwise be difficult or inefficient to work with.
Sintering’s true value lies not just in making solid objects, but in its unique ability to fabricate parts from extremely high-melting-point materials and to create components with intentionally controlled properties, like porosity, that are impossible to achieve with conventional melting.
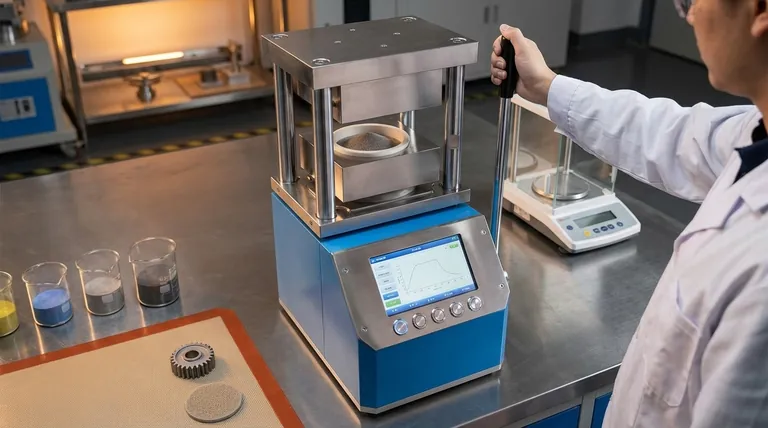

How Sintering Fundamentally Works
Sintering might seem like simply pressing powders together, but the process is driven by a sophisticated atomic-level mechanism. It is a thermal treatment that fundamentally changes the material's internal structure.
The Role of Heat and Atomic Diffusion
The process begins by heating the compacted powder to a temperature below its melting point. This heat doesn't liquefy the material but energizes its atoms.
These energized atoms begin to migrate, or diffuse, across the boundaries of the individual powder particles. As they move, they create strong metallic or chemical bonds, effectively "welding" the particles together at their points of contact.
The Importance of Pressure
Before heating, pressure is typically applied to compact the powder. This serves a critical purpose: it forces the individual particles into intimate contact, reducing the space between them.
This close proximity is essential for atomic diffusion to occur efficiently. Without it, the atoms would have too far to travel to form the bonds needed to create a single, solid piece.
The Strategic Advantages of Sintering
Engineers choose sintering not just as an alternative, but because it unlocks capabilities that other manufacturing methods like casting or machining cannot easily provide.
Fabricating High-Melting-Point Materials
Many advanced applications require materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten and molybdenum. Melting and casting these materials is incredibly energy-intensive and technically challenging.
Sintering bypasses this problem entirely by bonding the material in its solid state, making it a far more practical and cost-effective method for producing parts from these high-performance materials.
Creating Parts with Controlled Porosity
Because sintering starts with individual particles, the final part doesn't have to be 100% dense. By controlling the process parameters, engineers can create components with a precise, interconnected network of pores.
This is leveraged to create self-lubricating bearings (where pores are filled with oil) or specialized metal filters. This level of control over internal structure is unique to powder metallurgy processes.
Achieving Cost-Effective, Complex Parts
For mass production of small, intricate components like gears, sprockets, and cams, sintering is exceptionally efficient.
It can produce "net-shape" or "near-net-shape" parts that require little to no follow-up machining. This drastically reduces material waste and manufacturing time, leading to significant cost savings at high volumes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is not the ideal solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Inherent Porosity and Mechanical Properties
Unless secondary densification steps are taken, sintered parts almost always contain some level of residual porosity.
This porosity can mean that a sintered component may have lower tensile strength or ductility compared to a fully dense part made from wrought metal or through casting. The performance trade-off must be evaluated for the specific application.
Limitations on Part Size
The need to apply uniform pressure and heat throughout the powder mass makes sintering best suited for relatively small components.
Manufacturing very large parts via sintering is technically challenging and often not cost-effective compared to other methods.
High Initial Tooling Costs
The molds (dies) and presses used to compact the powder represent a significant upfront investment.
This makes sintering most economical for high-volume production runs where the cost of the tooling can be amortized over many thousands of parts. It is generally not suitable for one-off prototypes or very small batches.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting sintering is a strategic decision based on your material, geometry, and production volume.
- If your primary focus is working with high-melting-point materials: Sintering is often the most practical and sometimes the only viable method for fabricating parts from materials like tungsten, molybdenum, and advanced ceramics.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing small, complex metal parts: Sintering offers a highly cost-effective path to creating precise, net-shape components like gears and pulleys with minimal material waste and secondary processing.
- If your primary focus is creating parts with controlled porosity: Sintering is the ideal process for manufacturing components like filters or self-lubricating bearings, where a porous internal structure is a design feature.
Ultimately, sintering provides a powerful tool for engineering materials and components that would be difficult, costly, or impossible to create through traditional melting and casting.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Bonds powder particles into a solid mass using heat and pressure, without melting. |
| Key Advantages | Fabricates high-melting-point materials (e.g., tungsten), creates controlled porosity, and enables cost-effective mass production of complex parts. |
| Ideal For | High-volume production of small, intricate components and parts requiring specific internal structures like filters or self-lubricating bearings. |
| Main Limitations | Parts can have residual porosity (affecting strength), and the process is best for small parts with high initial tooling costs. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's unique material or component needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-performance lab equipment and consumables required for advanced powder metallurgy processes. Whether you are developing new materials, optimizing sintering parameters, or scaling up production, our expertise and reliable products are here to support your success.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how we can help you achieve precise, high-quality results with your sintering applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- Why do you need to follow the safety procedure in using hydraulic tools? Prevent Catastrophic Failure and Injury
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- What causes hydraulic pressure spikes? Prevent System Damage from Hydraulic Shock
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More



















