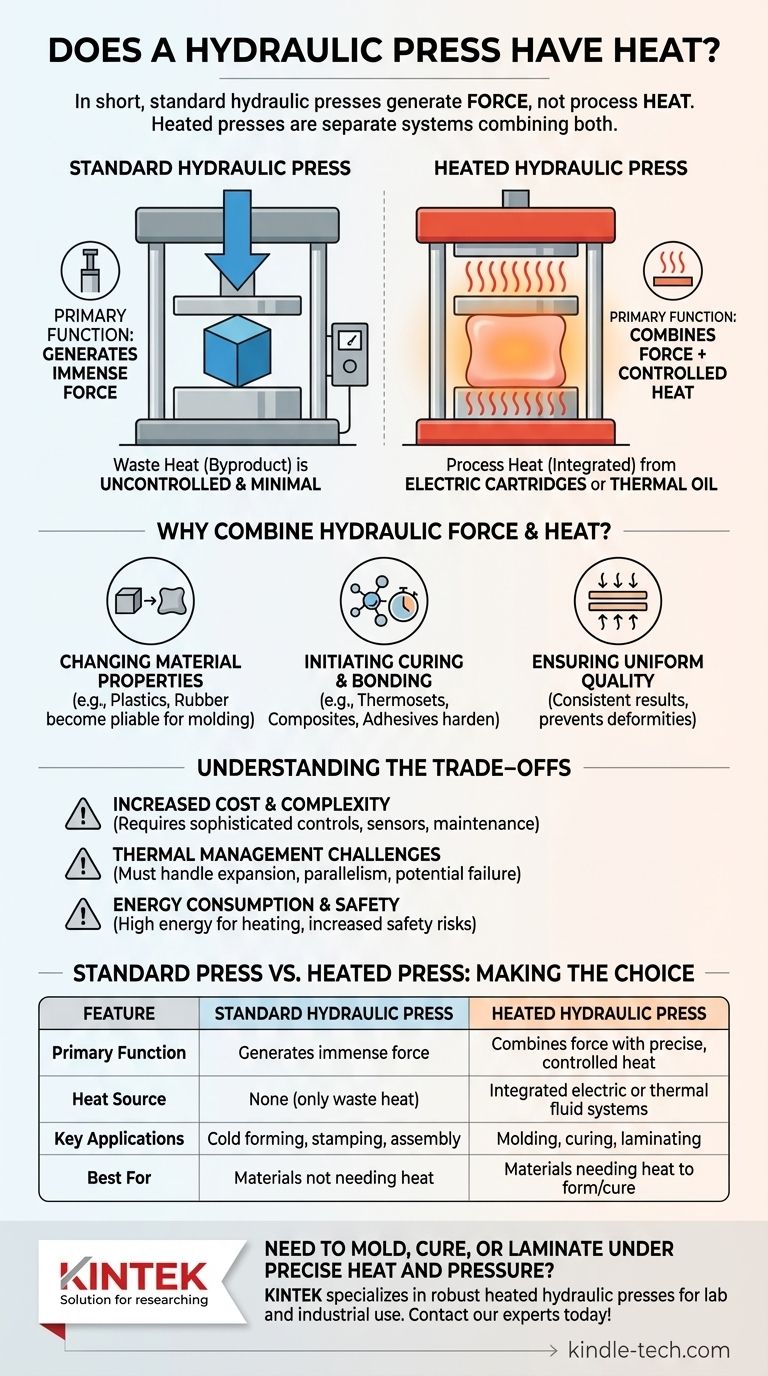
In short, a standard hydraulic press does not inherently create or use heat for its process. Its fundamental purpose is to generate immense force. However, many hydraulic presses are specifically equipped with integrated heating systems, known as heated platens, for applications that require both pressure and high temperatures, such as molding plastics or curing rubber.
The core principle to understand is the separation of functions: the hydraulic system provides force, while a separate, integrated electrical or fluid system provides heat. The two are combined in a "heated press" to perform specific manufacturing tasks that are otherwise impossible.

The Fundamental Roles: Force vs. Heat
To understand a heated press, it's crucial to see it as a combination of two distinct systems working together, not as a single machine where heat is a byproduct of pressure.
The Job of the Hydraulic System
The sole purpose of a hydraulic press's core system is to multiply force. It uses a liquid (typically oil) pressurized by a pump to move a piston, generating compressive forces that can range from a few tons to thousands of tons.
Think of it as a highly advanced and powerful version of a car jack. Its job is simply to push.
Where Process Heat Comes From
In a heated press, the heat is generated by elements embedded within or attached to the press plates (the "platens"). These are almost always separate systems.
The most common methods are electric heating cartridges inserted into the platens or a system that circulates hot thermal oil through channels inside the plates. This provides precise, controllable, and evenly distributed heat.
Waste Heat vs. Process Heat
It is important to distinguish between the intentional, controlled heat used for manufacturing and the unintentional waste heat generated by the machine's operation. The hydraulic power unit will get warm during use, but this heat is low-grade, uncontrolled, and is a byproduct of inefficiency that must be managed, not utilized.
Why Combine Hydraulic Force and Heat?
Adding a controlled heating system to a press unlocks a vast range of industrial capabilities that pressure alone cannot achieve.
Changing Material Properties
Heat makes many materials, especially polymers like plastic and rubber, pliable and soft. Applying immense pressure to a heated, malleable material allows you to form it into a precise and detailed shape inside a mold. Once cooled, it retains this new shape.
Initiating Curing and Bonding
For materials like composites, thermoset plastics, and rubber, heat triggers a chemical reaction known as curing or vulcanization. This process creates strong cross-links between polymer chains, permanently hardening the material.
Similarly, in applications like manufacturing plywood or composite panels, heat and pressure work together to cure the adhesives that bond the layers together.
Ensuring Uniform Quality
The combination of perfectly uniform pressure from the hydraulic system and evenly distributed heat from the platens ensures a consistent result across the entire part. This prevents weak spots, internal stresses, and deformities, leading to a high-quality, reliable product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly capable, heated presses introduce complexities that standard "cold" presses do not have.
Increased Cost and Complexity
A heated press requires a sophisticated control system to manage temperature, including sensors (thermocouples), controllers, and high-power electrical components. This increases the initial purchase price, operational cost, and maintenance requirements.
Thermal Management Challenges
Heat causes metal to expand. The entire press, from the frame to the platens and hydraulic seals, must be engineered to withstand high temperatures and thermal cycling without losing parallelism or dimensional accuracy. Poor thermal management can lead to inconsistent products and premature equipment failure.
Energy Consumption and Safety
Heating large, thick steel platens to several hundred degrees requires a significant amount of energy. Furthermore, the combination of extreme pressure and high heat presents increased safety risks that demand robust guarding, insulation, and operator protocols.
Standard Press vs. Heated Press: Making the Right Choice
Choosing the correct machine depends entirely on the material you are working with and your end goal.
- If your primary focus is cold forming, stamping, or assembly: A standard hydraulic press is the correct, most cost-effective tool for tasks like shaping sheet metal or pressing bearings into a housing.
- If your primary focus is molding, curing, or laminating: A heated press is essential for working with materials like plastics, rubber, composites, or wood panels that require thermal energy to change their state.
Understanding this distinction between applied force and applied heat is the key to selecting the right industrial process for your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Hydraulic Press | Heated Hydraulic Press |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Generates immense force | Combines force with precise, controlled heat |
| Heat Source | None (only waste heat from operation) | Integrated electric cartridges or thermal fluid systems |
| Key Applications | Cold forming, stamping, assembly | Molding plastics, curing rubber, laminating composites |
| Best For | Materials that don't require heat to form | Materials needing heat to become pliable or cure (thermoplastics, rubber) |
Need to mold, cure, or laminate materials under precise heat and pressure? KINTEK specializes in industrial lab equipment, including robust heated hydraulic presses designed for reliable performance in plastics, rubber, and composite applications. Our experts can help you select the right press to ensure uniform quality and efficiency in your manufacturing process. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and get a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How does a heated laboratory hydraulic press facilitate densification in CSP? Optimize Mg-doped NASICON Sintering
- How does a vacuum furnace environment influence sintered Ruthenium powder? Achieve High Purity and Theoretical Density
- What technical conditions does a heated hydraulic press provide for PEO batteries? Optimize Solid-State Interfaces
- How much force can a hydraulic press exert? Understanding its immense power and design limits.
- What is the role of a laboratory-grade heated hydraulic press in MEA fabrication? Optimize Fuel Cell Performance



















