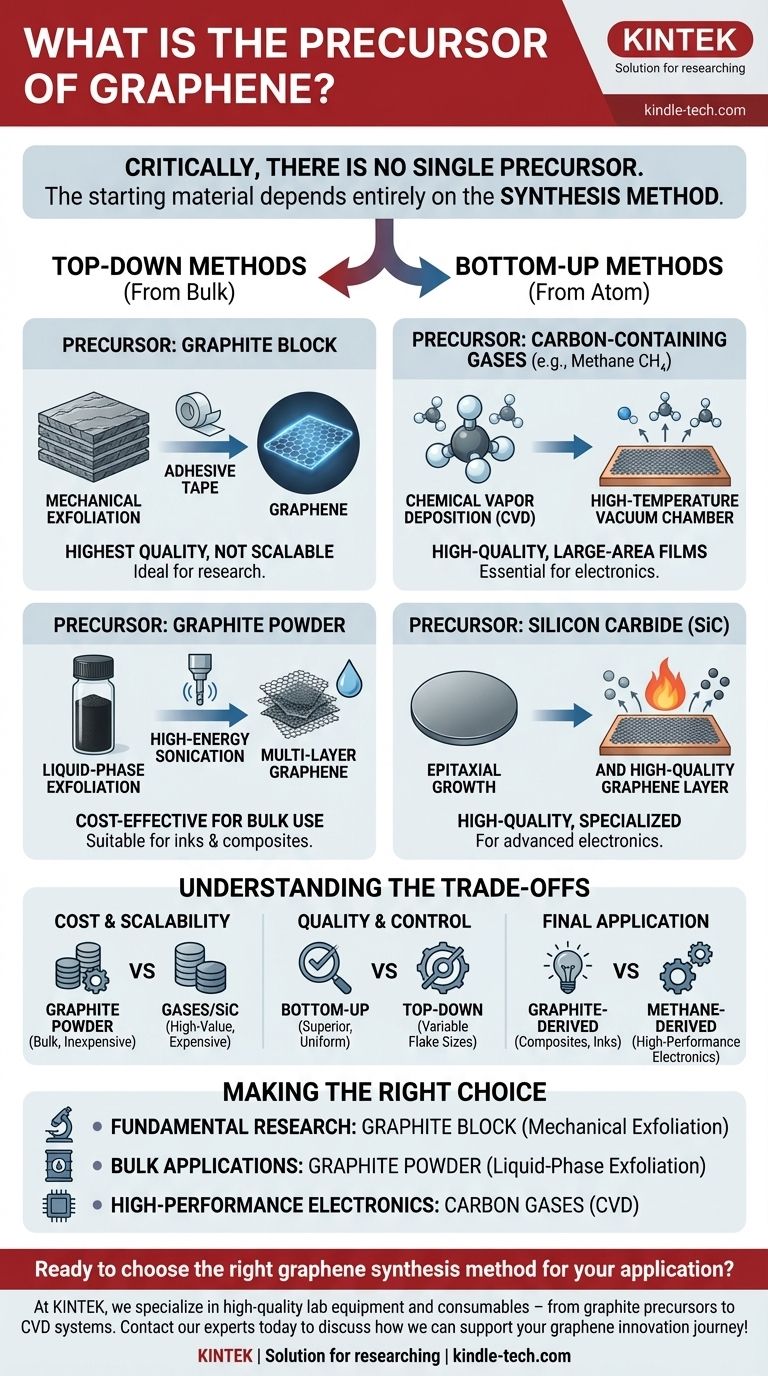
Critically, there is no single precursor to graphene. The starting material, or "precursor," is entirely dependent on the synthesis method used to create it. The two most common classes of precursors are graphite, used in exfoliation methods, and carbon-containing gases like methane, used in deposition methods.
The question of graphene's precursor is fundamental because graphene is not a naturally occurring material you can mine; it must be manufactured. The choice of precursor directly dictates the final product's quality, scalability, and cost, determining its suitability for applications ranging from basic research to industrial electronics.
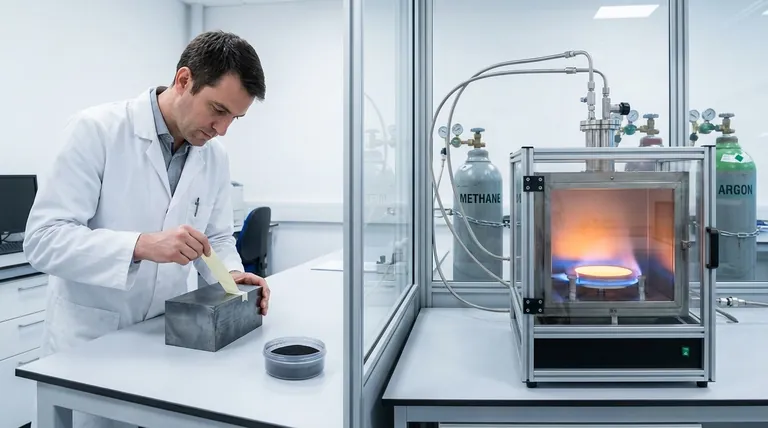

From Bulk Material to a Single Layer: Top-Down Methods
Top-down methods start with a bulk carbon source and isolate the single-atom-thick layers of graphene. The precursor here is almost always graphite.
Precursor: Graphite Block
Mechanical exfoliation, famously known as the "Scotch tape method," uses a block of high-purity graphite as its precursor.
Layers of graphite are repeatedly peeled off using adhesive tape until a single layer of graphene is isolated. This produces exceptionally high-quality graphene but is not scalable for industrial production.
Precursor: Graphite Powder
Liquid-phase exfoliation begins with graphite powder suspended in a liquid solvent.
High-energy processes, such as sonication, are used to overcome the forces holding the graphite layers together, dispersing them into the liquid as graphene flakes. This method is suitable for producing graphene inks and composites but often results in lower electrical quality and thicker, multi-layer flakes.
Building from the Atom Up: Bottom-Up Methods
Bottom-up methods construct the graphene lattice atom by atom on a substrate. These methods use more fundamental precursors.
Precursor: Carbon-Containing Gases
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the most prominent bottom-up technique for creating large, high-quality graphene sheets.
The precursors are carbon-containing gases, most commonly methane (CH₄), but also ethylene (C₂H₄) or acetylene (C₂H₂). These gases are introduced into a high-temperature vacuum chamber, where they decompose on a metallic catalyst substrate (like copper), allowing the carbon atoms to arrange themselves into the honeycomb lattice of graphene.
Precursor: Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Epitaxial growth on silicon carbide uses a solid wafer of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as both the substrate and the carbon precursor.
When the SiC wafer is heated to very high temperatures (above 1,100°C) in a vacuum, the silicon atoms sublimate (turn directly into a gas), leaving the carbon atoms behind. These remaining carbon atoms then restructure on the surface to form a high-quality graphene layer.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why the Precursor Matters
The choice of precursor and its associated method involves critical trade-offs between cost, quality, and the final application.
Cost and Scalability
Graphite powder is an inexpensive and abundant precursor, making liquid-phase exfoliation economically viable for bulk applications. In contrast, the high-purity gases for CVD and, especially, the single-crystal SiC wafers are significantly more expensive, making these methods better suited for high-value applications.
Quality and Control
Bottom-up methods using gaseous or SiC precursors offer superior control over layer thickness and uniformity. CVD, in particular, is the leading method for producing the large, single-layer, and highly conductive sheets required for electronics. Top-down methods from graphite often yield a wider distribution of flake sizes and thicknesses.
Final Application
The precursor directly informs the end-use. Graphite-derived graphene is ideal for adding mechanical strength to composites or conductivity to inks and coatings. Graphene from methane (via CVD) is destined for high-performance applications like transparent electrodes, sensors, and next-generation semiconductors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is fundamental research or device prototyping: Using a block of graphite as a precursor for mechanical exfoliation provides the highest-quality flakes for analysis.
- If your primary focus is large-scale use in composites, batteries, or conductive inks: Using graphite powder as the precursor for liquid-phase exfoliation is the most cost-effective and scalable approach.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics or photonics: Using carbon-containing gases like methane as the precursor for CVD synthesis is the essential path to achieving large-area, high-quality films.
Ultimately, understanding the precursor is the first step toward mastering the synthesis and application of this revolutionary material.
Summary Table:
| Synthesis Method | Primary Precursor | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Exfoliation | Graphite Block | Highest quality, not scalable, ideal for research. |
| Liquid-Phase Exfoliation | Graphite Powder | Cost-effective for bulk use (inks, composites). |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Methane (CH₄) Gas | High-quality, large-area films for electronics. |
| Epitaxial Growth | Silicon Carbide (SiC) Wafer | High-quality, suitable for specialized electronics. |
Ready to choose the right graphene synthesis method for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables—from graphite precursors to CVD systems—that your laboratory needs to successfully produce and utilize graphene. Our expertise ensures you have the right tools for your specific research or production goals, whether you're focused on fundamental research or scaling up for industrial applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your graphene innovation journey!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of graphite? Mastering High-Temperature Performance vs. Contamination Risk
- Why is graphite melting point high? Unlocking the Power of Strong Covalent Bonds
- What is special about graphite? Unlocking Its Unique Properties for Extreme Applications
- What is the thermal conductivity of graphite at high temperatures? A Guide to Thermal Management in Extreme Heat
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab

















