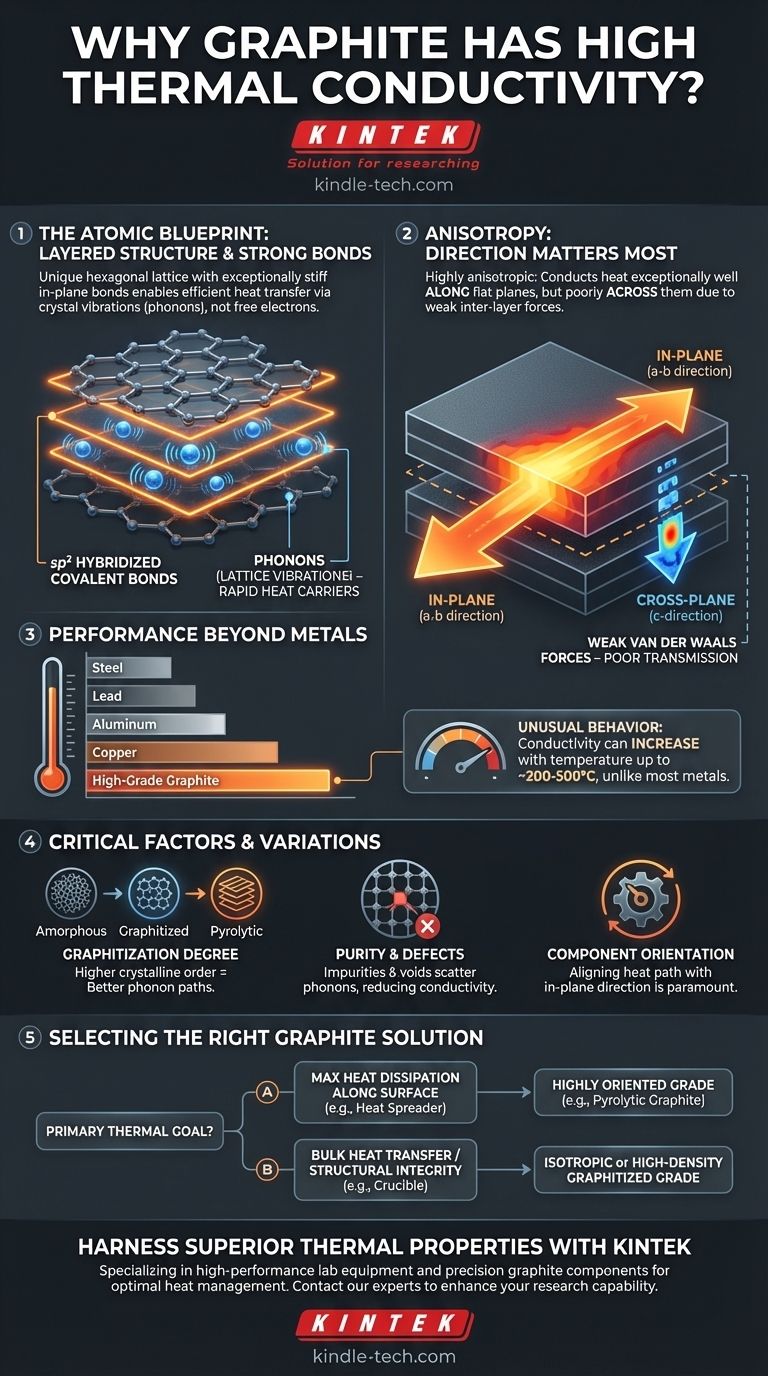
At its core, graphite's high thermal conductivity stems from its unique, layered atomic structure. Strong covalent bonds within these layers allow heat energy, in the form of lattice vibrations, to travel with exceptional speed and minimal resistance, much like sound through a tautly stretched drumhead.
The key is understanding that graphite is not uniformly conductive. It is a highly anisotropic material, meaning it conducts heat exceptionally well along its flat planes but poorly across them. This directional property is the single most important factor in its practical application.
The Atomic Blueprint for Heat Transfer
The reason graphite outperforms many metals, including steel and lead, is not due to free electrons as in metals, but rather the efficiency of physical vibrations within its crystal lattice.
The Role of sp² Hybridized Bonds
Each carbon atom in a graphite layer is bonded to three other carbon atoms in a hexagonal lattice. These are sp² hybridized bonds—the same strong type of bond found in other carbon allotropes like graphene. These bonds are incredibly stiff and strong, forming a rigid, flat sheet.
Lattice Vibrations as Heat Carriers (Phonons)
In a non-metallic solid like graphite, heat is transferred primarily by phonons, which are quantized packets of vibrational energy. Think of striking a bell; the sound you hear is the energy traveling through the material as vibrations.
When one part of the graphite lattice is heated, its atoms vibrate more intensely. Because the in-plane bonds are so strong and the structure is so orderly, these vibrations are transferred efficiently to neighboring atoms with very little energy loss.
Anisotropy: A Tale of Two Directions
The secret to graphite's properties lies in its two distinct structural characteristics:
- In-Plane (a-b direction): The flat hexagonal layers have extremely high thermal conductivity. Heat travels rapidly along these planes.
- Cross-Plane (c-direction): The layers themselves are stacked and held together by very weak van der Waals forces. These weak bonds are poor at transmitting vibrations, resulting in significantly lower thermal conductivity between the layers.
This difference can be dramatic, with in-plane conductivity sometimes being hundreds of times greater than cross-plane conductivity.
Performance Compared to Other Materials
Graphite's thermal performance is often counter-intuitive, especially when compared to the metals we typically associate with good conductivity.
Surpassing Common Metals
As noted, the thermal conductivity of specific graphite grades is greater than that of iron, steel, and lead. High-quality graphite can even rival the conductivity of copper and aluminum, especially on a per-weight basis, making it a superior choice for lightweight thermal management. Its electrical conductivity is also high, often correlating with its thermal performance.
The Temperature Factor
Unlike metals, whose thermal conductivity typically decreases as temperature rises, many grades of graphite exhibit an unusual behavior. Their thermal conductivity can increase with temperature up to a certain point (typically around 200-500°C) before beginning to decrease. This makes graphite exceptionally useful for high-temperature applications where metals would become less effective.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
Choosing graphite is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Its effectiveness is entirely dependent on the grade of the material and how it is oriented in the final application.
The Critical Impact of Anisotropy
The most common mistake is failing to account for graphite's directional conductivity. If a component is designed for heat to flow across the graphite layers (c-direction) instead of along them, performance will be drastically lower than expected. Proper orientation is paramount.
Not All Graphite Is Created Equal
The term "graphite" covers a wide range of materials.
- Amorphous Carbon: A disordered structure with very low thermal conductivity.
- Graphitized Carbon: Material that has been heat-treated at very high temperatures (over 2500°C) to create a more ordered, crystalline structure. The higher the degree of graphitization, the higher the thermal conductivity.
- Pyrolytic Graphite: A highly ordered form with extreme anisotropy, offering some of the highest in-plane thermal conductivity available.
The Role of Purity and Defects
Impurities, voids, and defects in the crystal lattice disrupt the clean path for phonons to travel. They act as "scattering sites" that impede heat flow. Therefore, purer and more perfect crystalline structures, like those found in high-grade synthetic graphite, will always have superior thermal conductivity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct graphite grade and orientation is essential for success. Your decision should be guided by the primary thermal challenge you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat dissipation along a surface (e.g., a heat spreader): Use a highly oriented grade like pyrolytic graphite, ensuring the material's planes are aligned with the desired heat path.
- If your primary focus is bulk heat transfer in multiple directions (e.g., a crucible): An isotropic graphite, which has more uniform properties in all directions, or a metal-impregnated composite grade may be the better choice.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature structural integrity with good thermal management: A high-purity, high-density graphitized grade will provide a balance of mechanical strength and thermal conductivity.
By understanding the link between graphite's atomic structure and its thermal properties, you can select the precise material to meet your engineering goals.
Summary Table:
| Property | In-Plane (a-b direction) | Cross-Plane (c-direction) |
|---|---|---|
| Bond Type | Strong sp² covalent bonds | Weak van der Waals forces |
| Thermal Conductivity | Exceptionally High | Significantly Lower |
| Primary Heat Carrier | Phonons (Lattice Vibrations) | Phonons (Inefficiently transferred) |
Ready to harness the superior thermal properties of graphite in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including precision graphite components designed for optimal heat management. Whether you need a heat spreader, crucible, or a custom high-temperature solution, our expertise ensures you get the right grade and orientation for maximum efficiency.
Let KINTEK be your partner in innovation. Contact our experts today to discuss how our graphite solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your research forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is physical vapor phase deposition? Achieve Superior Thin-Film Coatings for Your Components
- What are the drawbacks of sputtering? Balancing High Film Quality with Cost and Speed
- Does heat treatment change hardness? A Guide to Controlling Material Properties
- How do you measure thin film SEM thickness? A Direct Visual Guide for Accurate Analysis
- What is the feedstock for bio-oil production? Choosing the Right Biomass for Optimal Yield and Quality
- What is biomass conversion efficiency? Maximize Your Bioenergy Output and ROI
- What is the bias of sputtering RF? How a Negative DC Self-Bias Enables Insulator Sputtering
- Why is a high-precision constant temperature stirring reaction device necessary for functionalized BNNS grafting?



















