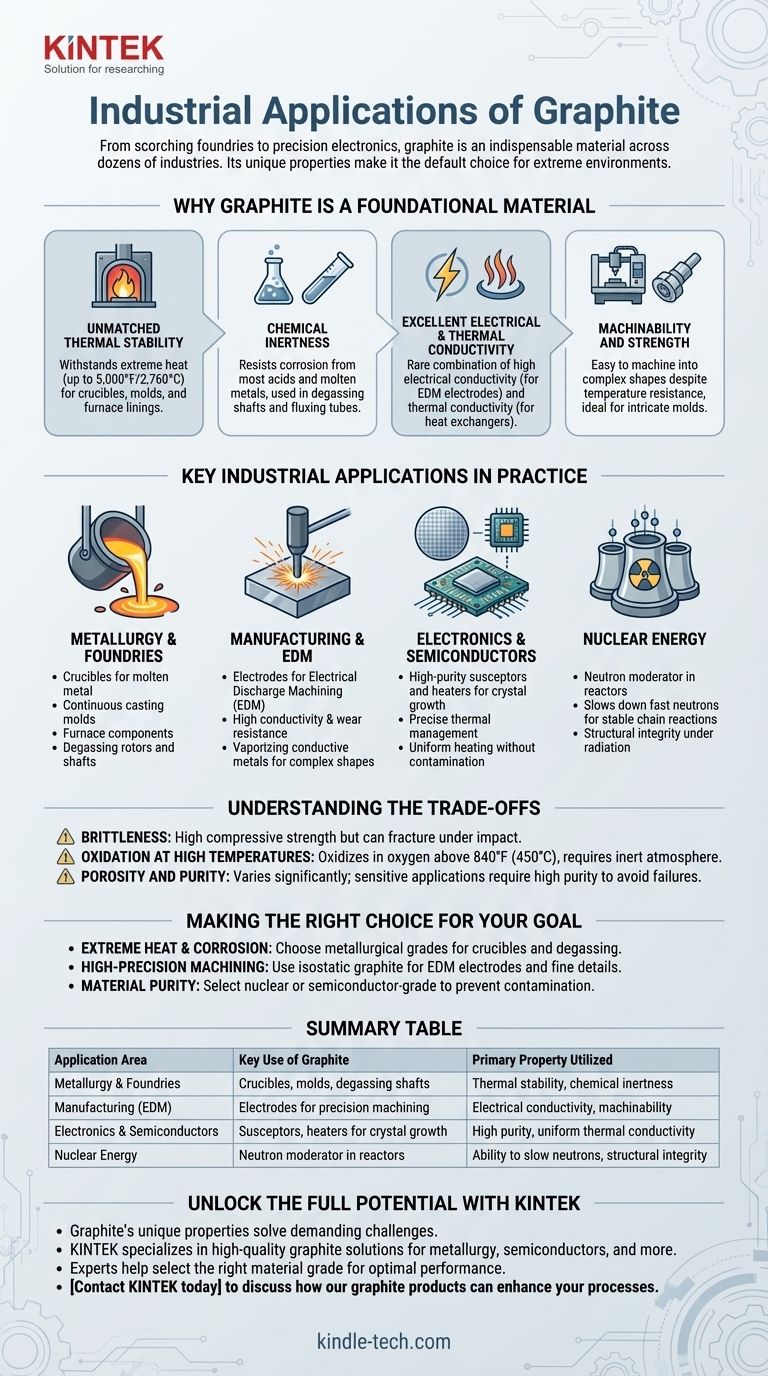
From scorching foundries to precision electronics, graphite is an indispensable material across dozens of industries. Its primary industrial applications are found in metallurgy for processes like continuous casting and degassing, high-temperature manufacturing, and advanced sectors like semiconductor production, solar energy, and nuclear power.
Graphite's industrial versatility is not accidental; it stems directly from its remarkable ability to withstand extreme heat and chemical corrosion while maintaining structural integrity, making it the default choice for processes where other materials would simply fail.

Why Graphite is a Foundational Industrial Material
To understand graphite's applications, you must first understand its core properties. It is not one single attribute but the unique combination of several that makes it so valuable.
Unmatched Thermal Stability
Graphite has an extremely high melting point and maintains its strength and dimensional integrity at temperatures up to 5,000°F (2,760°C).
This makes it essential for creating components like crucibles, molds, and furnace linings that must contain molten metals without degrading.
Chemical Inertness
Graphite resists corrosion and does not react with most acids, bases, or molten metals.
This property is why it's used for fluxing tubes, degassing shafts, and impellers, which are submerged directly into corrosive molten materials to remove impurities.
Excellent Electrical & Thermal Conductivity
Graphite is an excellent conductor of both heat and electricity, a rare combination in a non-metal.
Its electrical conductivity is the basis for its use in Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), where graphite electrodes are used to precisely erode and shape hard metals. Its thermal conductivity is critical in heat exchangers and semiconductor manufacturing.
Machinability and Strength
Despite its extreme temperature resistance, graphite is relatively easy to machine into complex and precise shapes.
Specialized types like isostatic graphite, which has a very fine and uniform grain structure, are used to create intricate molds and electrodes for the semiconductor and solar industries.
Key Industrial Applications in Practice
These fundamental properties translate directly into critical roles across a wide range of industries.
Metallurgy and Foundries
This is one of graphite's largest markets. It is used to make crucibles for holding molten metal, molds for continuous casting, and furnace components.
Its chemical inertness also makes it ideal for degassing rotors and shafts that purify molten aluminum by bubbling inert gas through it.
Manufacturing and EDM
In Electrical Discharge Machining, a graphite electrode is used to vaporize conductive metals with high-frequency electrical sparks, creating complex shapes that are impossible to achieve with traditional cutting tools.
Graphite is the preferred material for these electrodes due to its high conductivity, wear resistance, and ease of machining.
Electronics and Semiconductors
The production of semiconductors and solar cells requires exceptionally pure environments and precise thermal management.
High-purity graphite is used to make "susceptors" and "heaters" inside reactors that grow silicon crystals, as it can be heated uniformly and does not contaminate the delicate process.
Nuclear Energy
Graphite plays a critical role in nuclear reactors as a neutron moderator.
Its atomic structure is effective at slowing down fast neutrons produced during fission, which is necessary to sustain a stable nuclear chain reaction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, graphite is not a perfect material. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Brittleness
Graphite has high compressive strength but can be brittle. It does not deform like metal and can fracture under sharp impact or high tensile stress.
Oxidation at High Temperatures
Although it is stable at extreme temperatures, graphite will begin to oxidize (burn) in the presence of oxygen above approximately 840°F (450°C).
For this reason, many high-temperature applications require the graphite to be used in a vacuum or an inert (non-oxygen) atmosphere.
Porosity and Purity
Graphite grades vary significantly in their porosity and purity. For general foundry work, some porosity is acceptable.
However, for sensitive applications like semiconductor or nuclear use, any impurity or porosity can cause catastrophic failures, requiring much more expensive, high-purity grades.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" graphite is entirely dependent on the specific industrial problem you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is extreme heat and corrosion resistance: Focus on graphite grades designed for metallurgical applications, such as crucibles, casting molds, and degassing shafts.
- If your primary focus is high-precision machining: Isostatic graphite is essential for applications like EDM electrodes and semiconductor components where fine detail and material uniformity are critical.
- If your primary focus is material purity for sensitive processes: Seek out nuclear-grade or semiconductor-grade graphite to avoid contamination in nuclear moderation or silicon crystal growth.
By matching the material's core properties to your application's demands, you can leverage graphite to solve unique and difficult engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Use of Graphite | Primary Property Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Metallurgy & Foundries | Crucibles, molds, degassing shafts | Thermal stability, chemical inertness |
| Manufacturing (EDM) | Electrodes for precision machining | Electrical conductivity, machinability |
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Susceptors, heaters for crystal growth | High purity, uniform thermal conductivity |
| Nuclear Energy | Neutron moderator in reactors | Ability to slow neutrons, structural integrity |
Unlock the full potential of graphite for your specific industrial challenge.
Graphite's unique properties can solve your most demanding high-temperature and precision manufacturing needs. The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including advanced graphite solutions for metallurgy, semiconductor production, and more. We help laboratories and industrial facilities select the right material grade—from standard to high-purity isostatic graphite—to ensure optimal performance, longevity, and cost-efficiency.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our graphite products can enhance your processes and deliver reliable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab
- What is the density of graphite? A Key Indicator for Performance and Quality
- What are the properties of graphite at high temperatures? Unlock Its Strength and Stability in Extreme Heat
- How well does graphite transfer heat? Unlock Superior Thermal Management for Your Electronics
- What is the graphite furnace used for? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C in a Controlled Environment



















