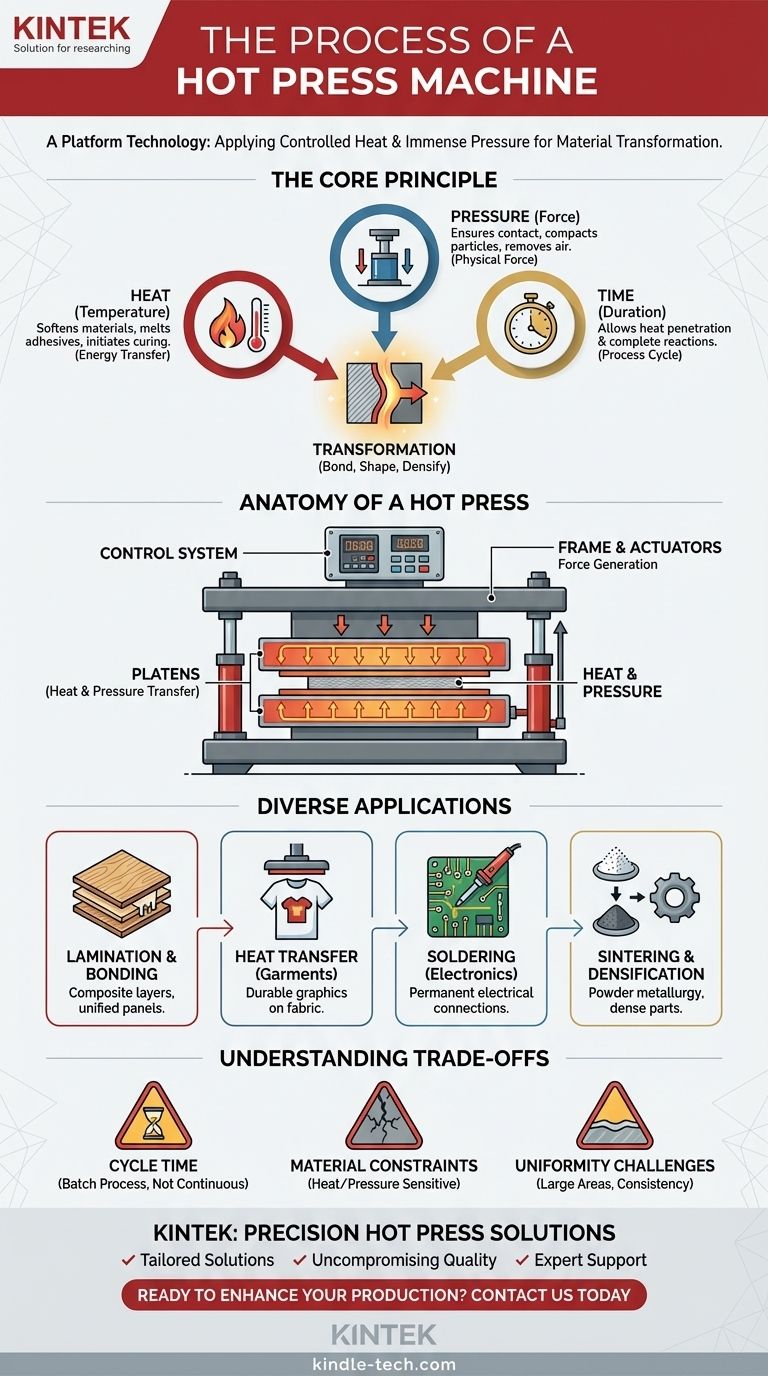
The fundamental process of a hot press machine involves applying precisely controlled heat and immense pressure to a material for a specific duration. This combination forces a physical or chemical change, allowing the machine to bond, shape, or densify materials for a vast range of industrial, electronic, and commercial applications.
A hot press is not a single-use tool but a platform technology. Its core function is to leverage the laws of thermodynamics and mechanics—using controlled heat and pressure—to permanently alter materials, whether for bonding electronic components, applying graphics to textiles, or creating dense industrial parts.

The Core Principle: A Union of Heat and Pressure
The effectiveness of a hot press comes from the deliberate and controlled combination of three critical variables: temperature, pressure, and time. Each plays a distinct role in the final outcome.
The Role of Heat
Heat provides the energy necessary to change the material's state. It might be used to soften a material to make it pliable, melt an adhesive or solder, or initiate a chemical reaction like curing a resin. This application of thermal energy is a direct expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics, transferring energy into the material to change its internal properties.
The Role of Pressure
Pressure, typically generated by a hydraulic system, ensures intimate contact between surfaces and provides the physical force for transformation. In lamination, it squeezes out air and locks layers together. In powder metallurgy, it compacts loose particles. This force is what guarantees the bond, shape, or density is achieved uniformly.
The Importance of Time
The duration of the press cycle is the final critical element. It allows heat to penetrate the material fully and ensures that chemical reactions like curing have enough time to complete. A cycle that is too short may result in a weak bond, while one that is too long could damage the material.
Anatomy of a Hot Press Machine
While designs vary by application, most hot press machines share a common set of core components that work together to deliver precise results.
The Frame and Actuators
The machine is built on a heavy base that houses one or more hydraulic cylinders. These actuators, driven by oil pressure and compressed air, generate the immense force required for pressing. The head of the press is connected to the base by solid columns or frames, creating a rigid structure that can withstand the operational forces.
The Platens
The platens are the thick, flat plates that transfer both heat and pressure directly to the workpiece. They are typically machined from solid steel and contain drilled channels for a heating medium, such as hot oil or steam, to circulate. The surfaces are often ground smooth and plated with chromium to ensure a fine surface finish, prevent corrosion, and stop materials like glue from sticking.
The Control System
Modern hot press operations are managed by advanced electronic systems. These controls allow operators to precisely set and automate the entire process, including temperature stages, pressure application, and cycle time. Features like a digital pressure gauge and adjustable heating speeds give users fine control to achieve ideal and repeatable results.
Diverse Applications Define the Process
The term "hot pressing" describes a category of processes, each tailored to a specific industry and outcome. The core principle remains the same, but the application dictates the machine's specific features.
Lamination and Bonding
In woodworking and composite manufacturing, large multi-platen presses are used to bond layers of material together with a heat-activated adhesive. The press ensures consistent heat and pressure over a large surface area to create strong, unified panels.
Heat Transfer for Garments
This is one of the most common applications. A heat press applies a pre-printed design or transfer onto fabric. The heat activates the adhesive on the transfer, while the pressure permanently fuses it to the garment's fibers for a durable, long-lasting finish.
Soldering for Electronics
In electronics assembly, a specialized hot press heats two parts coated with flux and solder. The machine's head, or indenter, heats to a precise temperature, melting the solder. After curing, this forms a permanent electrical and mechanical connection between the components.
Sintering and Densification
In powder metallurgy and ceramics, hot pressing is a manufacturing process that simultaneously presses and heats a powder. This action, known as sintering, compacts the powder into a solid, highly dense part, which is often impossible to achieve through pressure or heat alone.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the hot pressing process has inherent limitations that are important to understand for proper application.
Cycle Time
Hot pressing is a batch process, not a continuous one. The need to heat the material, apply pressure for a set duration, and often cool it down means that cycle times can be a limiting factor in high-volume production.
Material Constraints
The process is inherently destructive to materials that cannot withstand high temperatures and pressures. Its use is limited to materials like thermoset and thermoplastic polymers, specific metals, wood composites, and ceramics.
Uniformity Challenges
Achieving perfectly uniform temperature and pressure across very large platens is a significant engineering challenge. Any inconsistencies can lead to defects, such as weak bonds or variations in density across the part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right hot press process depends entirely on the material you are working with and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is surface decoration (e.g., t-shirts): You need a standard heat press focused on even temperature distribution and moderate pressure for applying transfers.
- If your primary focus is electronics manufacturing: You require a hot bar soldering press with exceptionally precise temperature control and a specialized pressure head.
- If your primary focus is creating dense, structural parts from powder: You need an industrial hot press or a specialized Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) capable of extreme temperatures and pressures.
- If your primary focus is laminating large sheets (e.g., plywood): You need a large-format hydraulic press, often with multiple platens, designed for consistency over wide surface areas.
Ultimately, understanding that "hot pressing" is a category of processes, not a single action, is the key to leveraging its power for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Variable | Role in Hot Pressing | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Softens materials, melts adhesives, initiates curing | Heat transfer printing, soldering, resin curing |
| Pressure | Ensures intimate contact, compacts materials, removes air | Lamination, powder metallurgy, composite bonding |
| Time | Allows heat penetration and complete chemical reactions | All processes requiring curing or sintering cycles |
| Platen Design | Transfers heat and pressure uniformly across the workpiece | Large-scale panel lamination, uniform part creation |
Ready to enhance your production with precision hot pressing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're in electronics manufacturing, textiles, or materials science, our hot press machines deliver the exact temperature, pressure, and control required for flawless results.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Tailored Solutions: From heat transfer presses to industrial sintering systems, we match the machine to your application.
- Uncompromising Quality: Built for durability and repeatable performance in demanding environments.
- Expert Support: Our team helps you optimize cycles for efficiency and material integrity.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK’s hot press technology can drive your success. Get in touch now →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum environment system contribute to the hot pressing sintering of B4C-CeB6? Unlock Peak Ceramic Density
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play for nanocopper? Achieve Maximum Densification Today
- What are the key functions of a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Produce High-Density UN Ceramic Pellets



















