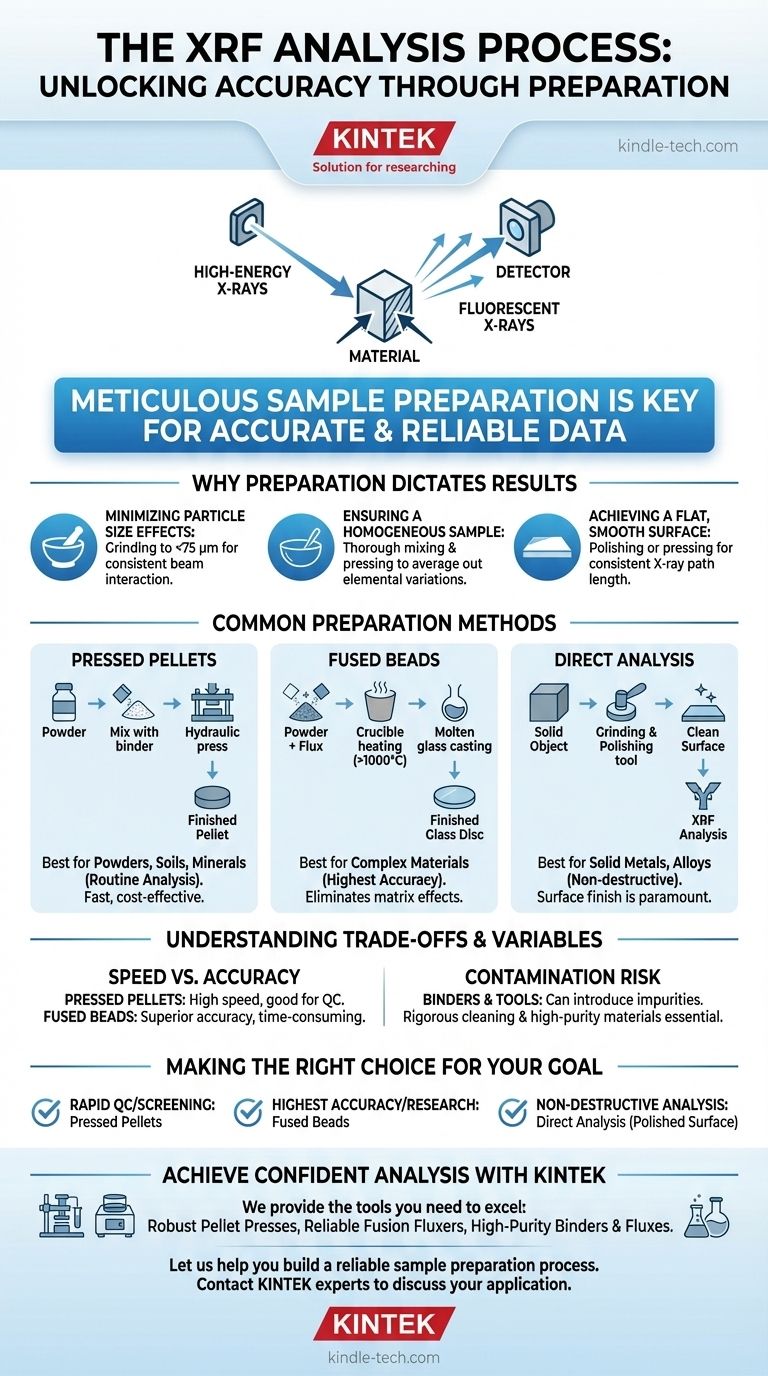
The core process of X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) analysis involves bombarding a material with high-energy X-rays and measuring the characteristic "fluorescent" X-rays emitted back from the sample. However, the true determinant of a successful analysis lies not in the machine, but in the meticulous sample preparation that precedes the measurement. Proper preparation is essential for generating accurate and reliable data.
The accuracy of XRF analysis is fundamentally dependent on how the sample is prepared. The primary goal is to create a sample that is perfectly homogeneous, has a smooth and flat surface, and is truly representative of the bulk material being tested.

The Principle: Why Preparation Dictates Results
XRF is a surface-sensitive analytical technique. The primary X-rays only penetrate a shallow depth into the sample, meaning the spectrometer only "sees" the top layer. This makes the physical state of that surface paramount.
Minimizing Particle Size Effects
In powdered samples, large or inconsistent particle sizes can cause significant errors. X-rays can scatter in unpredictable ways from coarse grains, creating background noise that obscures the signals from the elements you are trying to measure.
Grinding the sample to a very fine, uniform particle size (typically less than 75 µm) is critical. This ensures the X-ray beam interacts with the material in a consistent and repeatable manner.
Ensuring a Homogeneous Sample
The X-ray beam analyzes a relatively small spot on the sample's surface. If the sample is not homogeneous—meaning its elemental composition is not uniform throughout—the analysis will only reflect the small area being measured, not the bulk material.
Proper grinding, mixing, and pressing or fusing ensures that any elemental variations are averaged out, making the analyzed surface representative of the entire sample.
Achieving a Flat, Smooth Surface
An irregular or rough surface deflects the emitted fluorescent X-rays, altering the signal that reaches the detector. A perfectly flat and smooth surface ensures a consistent path length for both the incoming and outgoing X-rays.
For solid metal samples, this means polishing the surface. For powdered samples, it involves compressing them into dense, smooth pellets.
Common Preparation Methods for Solid Materials
The specific preparation method depends on the sample type, the elements of interest, and the required level of accuracy.
Direct Analysis of Solid Objects
This is the simplest method, often used for quality control of metals and alloys. The primary requirement is creating a clean, flat measurement surface.
Preparation involves using tools like grinders or lathes to produce a smooth face. The surface must then be cleaned, often with a file, to remove any contamination from the preparation process.
Pressed Pellets
This is the most common method for powders, soils, minerals, and cements due to its speed and low cost. The sample is ground to a fine powder and then compressed under high pressure in a die set to form a solid, stable pellet.
If the powdered material does not bind well on its own, a small amount of a wax binder is mixed in before pressing to help the particles cohere.
Fused Beads
For the highest level of accuracy, especially with complex geological materials, the fused bead method is used. This process eliminates errors from both particle size and mineralogical structure.
The powdered sample is mixed with a flux (like a lithium borate salt) and heated in a crucible to over 1000°C until it melts into a homogeneous molten glass. This glass is then cast into a perfectly smooth, flat disc for analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variables
Choosing the right method requires balancing speed, cost, and accuracy. Each approach has potential pitfalls that must be managed.
Method Selection: Speed vs. Accuracy
Pressed pellets are fast and produce high-quality results for many applications. They are excellent for routine process control and screening.
Fused beads are more time-consuming and expensive but provide superior accuracy by removing physical matrix effects. However, the dilution with flux can make it harder to detect trace elements at very low concentrations.
The Role and Risk of Binders
Binders are necessary for non-cohesive powders but introduce a potential source of error. The binder dilutes the sample and may contain contaminating elements.
It is critical to choose a binder that is free of the elements you are analyzing and to use the exact same amount consistently across all samples and standards.
Controlling Pressure and Thickness
When making pressed pellets, the amount of pressure applied and the final thickness of the pellet are important variables. These factors must be kept consistent to ensure repeatable density and results.
The Ever-Present Risk of Contamination
Contamination can occur at any stage. Using grinding tools for different sample types can cross-contaminate materials. Even the choice of binder or thin film used to support the sample can introduce elemental impurities.
A rigorous protocol, including thorough cleaning of all equipment between samples, is essential for maintaining data integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your analytical objective should guide your preparation strategy.
- If your primary focus is rapid quality control or screening: Pressed pellets offer the best balance of speed, cost, and reliable results.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible accuracy for certification or research: The fused bead method is the gold standard for eliminating matrix effects.
- If your primary focus is non-destructive analysis of a metal part: Direct analysis after proper surface polishing and cleaning is the correct approach.
Ultimately, your confidence in your XRF data is built upon the foundation of a deliberate, consistent, and well-executed sample preparation plan.
Summary Table:
| Preparation Method | Best For | Key Steps | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressed Pellets | Powders, soils, minerals (Routine analysis) | Grind to <75 µm, mix with binder, press under high pressure | Fast and cost-effective; binder choice is critical to avoid contamination |
| Fused Beads | Complex materials, highest accuracy requirements | Mix with flux, melt at >1000°C, cast into glass disc | Eliminates matrix effects; dilutes trace elements |
| Direct Analysis | Solid metals, alloys (Non-destructive) | Polish to a flat, smooth surface, clean thoroughly | Surface finish is paramount for accurate readings |
Achieve Confident and Accurate XRF Analysis with KINTEK
Unreliable sample preparation can compromise your entire analytical workflow. At KINTEK, we specialize in the lab equipment and consumables that form the foundation of precise XRF analysis.
We provide the tools you need to excel:
- Robust Pellet Presses for creating consistent, high-quality pressed pellets.
- Reliable Fusion Fluxers for producing perfectly homogeneous fused beads.
- High-Purity Binders and Fluxes to minimize contamination and ensure data integrity.
Let us help you build a sample preparation process that guarantees reliable results, whether you're in mining, manufacturing, or research.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and ensure your next XRF analysis is a success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- How much psi can a hydraulic press make? From 2,000 PSI to over 50,000 PSI Explained
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing
- What causes hydraulic pressure spikes? Prevent System Damage from Hydraulic Shock



















