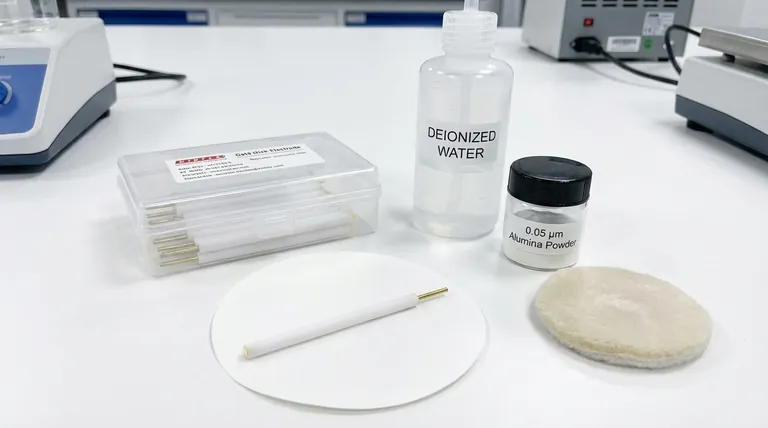
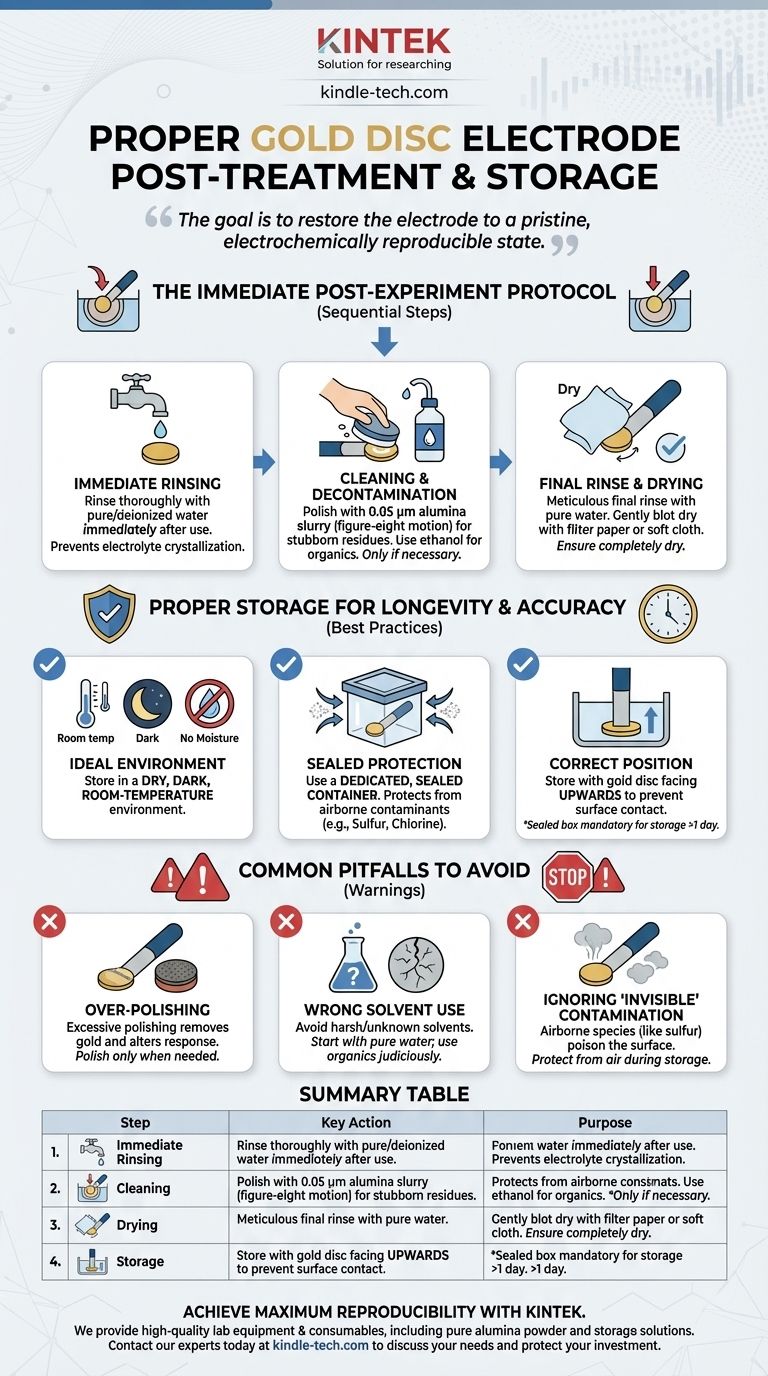
Proper post-experiment procedure for a gold disc electrode involves immediately rinsing it with pure water, polishing it with 0.05 µm alumina powder only if necessary to remove stubborn contaminants, and thoroughly drying it with filter paper or a soft cloth. Once clean and dry, the electrode must be stored in a dedicated, dry container, protected from air, moisture, and corrosive atmospheric contaminants like sulfur.
The goal of post-experiment care is not just to clean the electrode, but to restore it to a pristine, electrochemically reproducible state. Improper handling or storage is one of the most common sources of experimental error, leading to unreliable and invalid data.

The Immediate Post-Experiment Protocol
A consistent protocol performed immediately after each experiment is the first line of defense against electrode degradation and data drift. Time is of the essence; do not let electrolyte dry on the surface.
Step 1: Immediate Rinsing
As soon as the experiment concludes, remove the electrode from the electrochemical cell.
Rinse the surface thoroughly with high-purity or deionized water. This prevents residual electrolyte salts from crystallizing on the surface, which can be difficult to remove later and can cause corrosion.
Step 2: Cleaning and Decontamination
If the surface is free of visible residue after rinsing, you may proceed to the drying step. However, for most applications, a more thorough cleaning is required.
If stubborn residues or films are present, you must polish the surface. Create a slurry by adding a small amount of 0.05 µm alumina polishing powder to a polishing pad moistened with distilled water.
Hold the electrode perpendicular to the pad and polish the gold surface using a gentle, figure-eight motion. This action mechanically removes contaminants and exposes a fresh gold surface.
For organic contaminants, a gentle wipe with a solvent like ethanol or acetone can be effective. Always follow any solvent use with a thorough rinse with pure water to remove any residual solvent film.
Step 3: Final Rinse and Drying
After any cleaning or polishing, a final, meticulous rinse with pure water is critical to wash away all polishing media and cleaning agents.
Gently blot the electrode surface dry using a soft, lint-free cloth or filter paper. Avoid rubbing the surface, as this can cause scratches and introduce new contaminants. Ensure the entire electrode body is completely dry.
Proper Storage for Longevity and Accuracy
How you store the electrode between uses is as important as how you clean it. The goal is to protect the pristine surface from both physical damage and atmospheric contamination.
The Ideal Storage Environment
The electrode must be kept in a dry, dark, room-temperature environment. High temperatures can cause materials to deform, and strong light can potentially catalyze reactions on the surface.
Protecting Against Contamination
Store the electrode in a dedicated, sealed container. This protects it from dust and, more importantly, from corrosive elements often present in a lab's atmosphere, such as compounds containing sulfur, chlorine, and bromine.
Storing the electrode with the gold disc facing upwards is a simple but effective practice to prevent accidental contact with the container surface.
Long-Term vs. Short-Term Storage
For short periods between frequent experiments, placing the clean, dry electrode in a covered beaker may suffice. For any storage longer than a day, a sealed, dedicated electrode box is mandatory to prevent invisible electrochemical contamination from the air.
Understanding the Common Pitfalls
Avoiding common mistakes is key to preserving the function and extending the life of your electrode.
The Danger of Over-Polishing
Polishing is an abrasive process that physically removes a microscopic layer of gold. While necessary for decontamination, excessive or unnecessary polishing will wear down the electrode, potentially recessing the disc into its insulating shroud and altering its electrochemical response. Polish only when necessary.
Choosing the Right Cleaning Solvent
Always start with pure water. It is the safest and most universal cleaning agent. Organic solvents like ethanol are useful for specific contaminants but must be used judiciously and rinsed away completely. Avoid harsh or unknown solvents that could permanently damage the electrode surface or its insulating body.
Ignoring "Invisible" Contamination
An electrode can appear visually clean but be electrochemically "dirty." Airborne species, particularly sulfur compounds, can readily adsorb onto a gold surface, poisoning it for future experiments. This is why protecting the electrode from the air during storage is not optional—it is a critical step for data reproducibility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your maintenance strategy should align with your experimental needs. Use this checklist to guide your actions.
- If your primary focus is maximum reproducibility: Implement and document a strict, consistent polishing and cleaning protocol that is performed before every single experiment, not just after.
- If your primary focus is extending the electrode's lifespan: Prioritize gentle handling, polish only when absolutely necessary, and be fanatical about proper storage in a sealed container away from corrosive fumes.
- If you are troubleshooting inconsistent data: Your first step should be to review and overhaul your cleaning and storage procedures, as this is the most frequent cause of unreliable results.
Treating your electrode with meticulous care is the foundation of reliable and trustworthy electrochemical data.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Immediate Rinsing | Rinse with pure water immediately after use. | Prevents electrolyte crystallization and corrosion. |
| 2. Cleaning | Polish with 0.05 µm alumina slurry if needed; use ethanol for organics. | Removes stubborn contaminants to restore a fresh surface. |
| 3. Drying | Blot dry gently with a lint-free cloth or filter paper. | Prevents water spots and avoids surface scratches. |
| 4. Storage | Store in a sealed, dry container, disc facing upwards. | Protects from air, moisture, and corrosive atmospheric contaminants. |
Achieve Maximum Reproducibility in Your Lab
Inconsistent electrochemical data is often a result of improper electrode care. The meticulous cleaning and storage procedures outlined above are fundamental to obtaining reliable results.
At KINTEK, we understand that your research depends on precision. We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including the pure alumina polishing powders and dedicated storage containers essential for proper electrode maintenance. Our products are designed to support laboratories in achieving the highest standards of data integrity and experimental reproducibility.
Let us help you protect your investment and your data.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your workflow and ensure the longevity of your critical equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Gold Electrochemical Sheet Electrode Gold Electrode
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
People Also Ask
- What are the necessary pretreatment steps before using a gold disc electrode? A Guide to Reliable Electrochemical Data
- What are the key aspects of maintaining and caring for a gold plate electrode? Preserve Performance and Extend Lifespan
- What is the typical role of a gold disc electrode in an electrochemical setup? Your Guide to a Precise Working Electrode
- What are the key precautions for a gold disc electrode? Ensure Accurate Results & Long Lifespan
- What are the performance characteristics of a gold plate electrode? Unmatched Stability for Reliable Data



















