In essence, a crucible is a high-performance container engineered to hold substances, most often metals, while they are melted at extreme temperatures. It is a fundamental tool in metallurgy, chemistry, and material science, designed to withstand conditions that would destroy ordinary vessels.
A crucible's true purpose extends beyond simple containment. Its core function is to provide a chemically stable and thermally resistant environment, ensuring the material being melted remains pure and uncontaminated throughout the heating process.

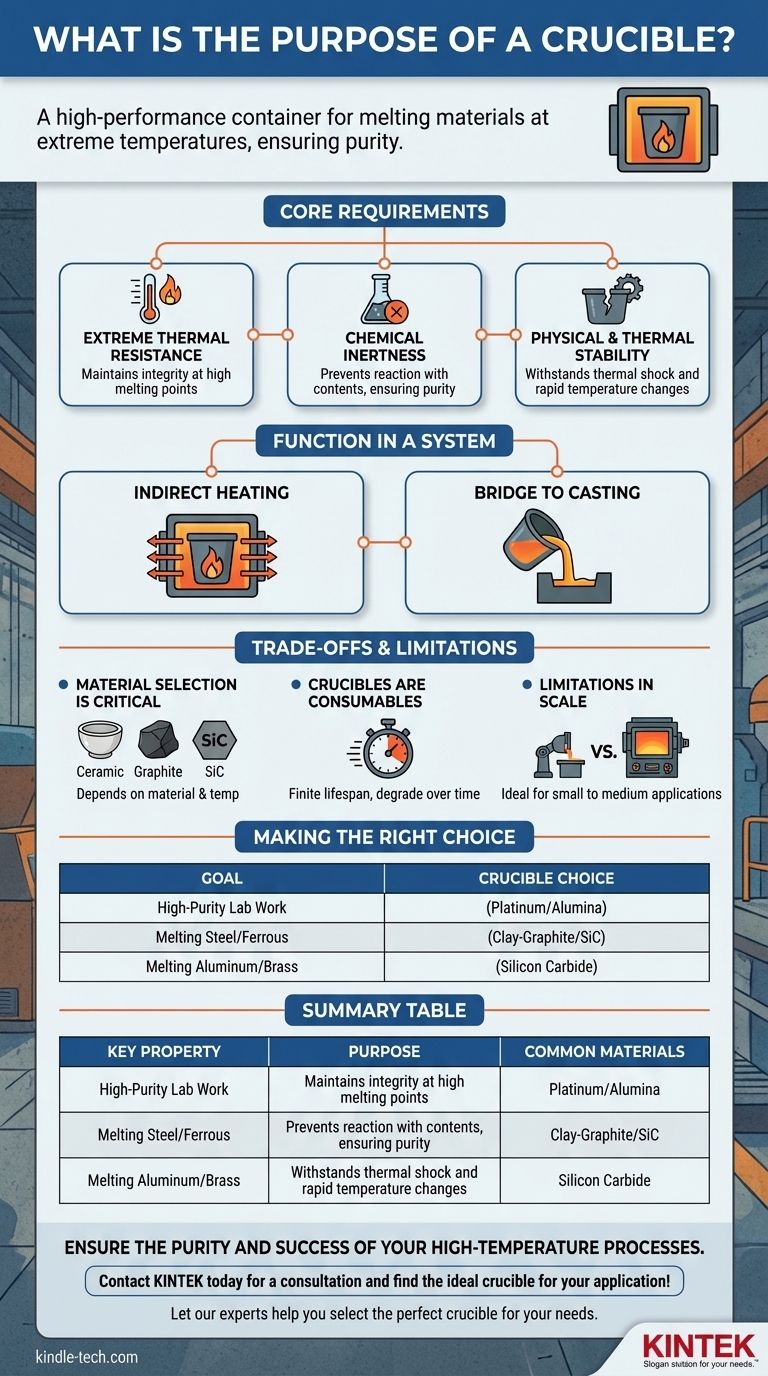
The Core Requirements of a Functional Crucible
A vessel can only be called a crucible if it meets a strict set of non-negotiable criteria. These properties are what separate it from any other type of container.
Extreme Thermal Resistance
The most fundamental requirement is that a crucible must have a melting point significantly higher than the substance it contains. This allows it to maintain its structural integrity without melting, deforming, or failing under intense heat.
Chemical Inertness
A crucible must be chemically compatible with the molten material inside it. Any reaction between the crucible wall and its contents can lead to two critical failures: contamination of the melt and rapid deterioration of the crucible itself.
This property is vital for maintaining the purity and intended properties of the final cast material.
Physical and Thermal Stability
The crucible must be able to withstand thermal shock—the stress created by rapid changes in temperature. It cannot crack or fracture when heated quickly or when the molten material is poured out.
How a Crucible Functions in a System
A crucible does not generate heat itself; it is a passive but critical component within a larger heating system, typically a furnace.
The Role in Indirect Heating
In a traditional crucible furnace, the crucible containing the raw material is placed inside. Heat is then applied to the outside of the crucible by gas burners or electric heating elements.
The crucible's material must efficiently transfer this thermal energy to its contents to achieve a uniform melt.
The Bridge to Casting
The crucible's function is to hold the metal or other substance through its transition from a solid to a liquid state. Once the material is fully molten, the crucible is used to safely transport and pour it into a mold for casting.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While essential, crucibles are not universal or permanent tools. Their selection and use involve important considerations.
Material Selection Is Critical
There is no single crucible material suitable for all applications. The choice of ceramic, graphite, silicon carbide, or a specific metal alloy depends entirely on the material being melted and the peak temperature required.
Using the wrong crucible can lead to catastrophic failure or costly contamination of the melt.
Crucibles Are Consumables
Even when used correctly, crucibles have a finite lifespan. The repeated stress of extreme temperature cycles and potential minor chemical reactions cause them to degrade over time. They are considered a consumable component in metallurgical operations.
Limitations in Scale
Crucible furnaces are ideal for small-scale foundries, laboratories, and artisan work. For massive industrial applications, other technologies like large induction furnaces are often more efficient, though the principles of containment and non-reactivity remain.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The material you are melting dictates the type of crucible you must use. Your goal determines your selection.
- If your primary focus is high-purity laboratory work: You need a highly inert material like platinum or pure alumina to eliminate any risk of sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is melting steel or other ferrous alloys: You require a robust crucible, often made of clay-graphite or silicon carbide, that can withstand exceptionally high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum or brass: A silicon carbide crucible is often the standard choice, offering a good balance of durability and performance.
Ultimately, selecting the correct crucible is the foundational step for ensuring the success and integrity of any high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Purpose | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Withstands extreme melting temperatures | Graphite, Silicon Carbide, Alumina |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents contamination of the melt | Platinum, Alumina, Clay-Graphite |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Prevents cracking from rapid temperature changes | Silicon Carbide, Ceramics |
Ensure the Purity and Success of Your High-Temperature Processes
Choosing the right crucible is the first critical step to achieving a pure, uncontaminated melt and protecting your equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a wide range of crucibles designed for specific materials and applications—from delicate laboratory work to robust metal melting.
Let our experts help you select the perfect crucible for your needs. We provide solutions that ensure durability, performance, and the integrity of your materials.
Contact KINTEL today for a consultation and find the ideal crucible for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-purity alumina crucible preferred for high-temperature oxidation? Ensure Unmatched Data Integrity
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for LATP? Preserve Purity and Conductivity in Sintering
- Why is the use of high-purity alumina crucibles necessary for NMC powders? Ensure Purity in Cathode Synthesis
- What are the functional advantages of using high-purity alumina crucibles? Achieve Precise Oxidation Data
- What role do high-purity alumina crucibles play in high-temperature steam oxidation? Ensure Data Integrity up to 1350°C



















