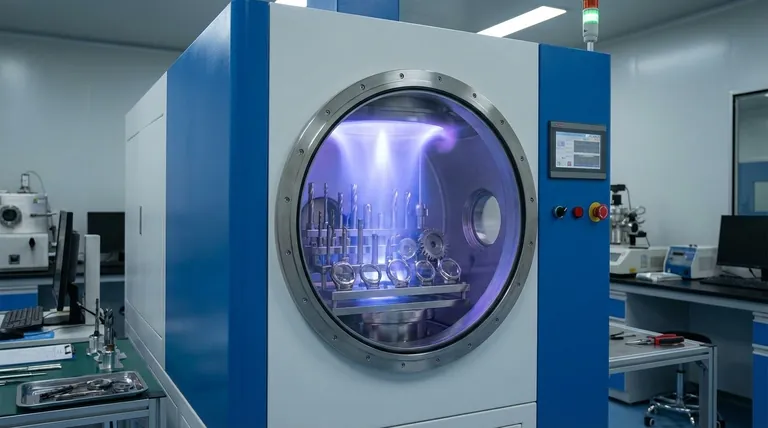
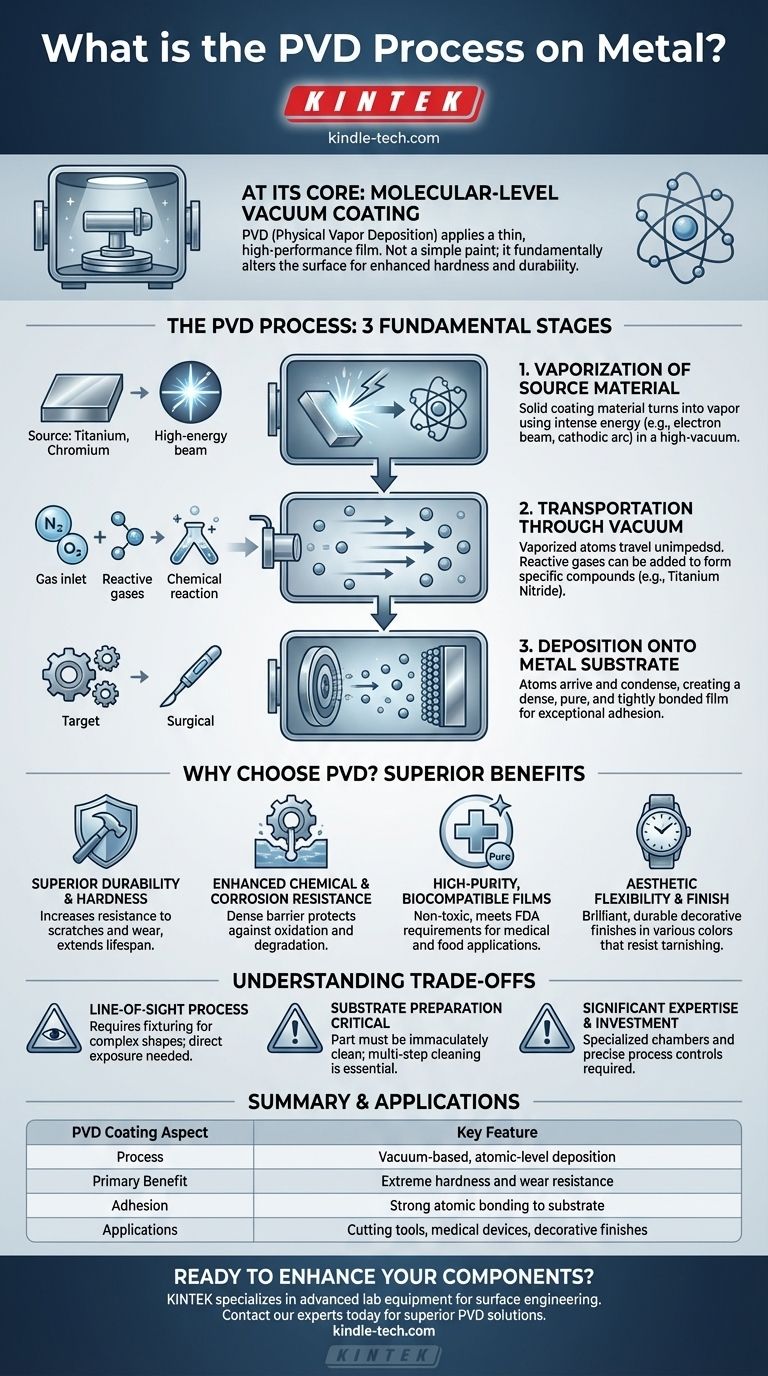
At its core, the Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) process is a sophisticated vacuum coating technique used to apply an extremely thin, high-performance film onto a metal surface. A solid coating material is vaporized in a high-vacuum chamber, and its atoms are then precisely deposited, layer by layer, onto the target object, forming a strong, bonded surface.
The central concept to grasp is that PVD is not a simple paint or plating; it is a molecular-level process that fundamentally alters the surface of a metal to make it significantly harder, more durable, and more resistant to wear and corrosion.

How Does the PVD Process Actually Work?
To understand PVD, it's best to break it down into its fundamental stages, all of which occur within a specialized vacuum chamber. The vacuum is critical as it prevents the vaporized coating material from reacting with any contaminants in the air.
Step 1: Vaporization of the Source Material
The process begins by turning a solid, high-purity coating material (often a metal or ceramic like titanium or chromium) into a vapor. This is not achieved through simple melting but by bombarding the material with intense energy.
Common methods include using a high-energy electron beam to vaporize the source material or using a powerful cathodic arc to create a plasma that releases atoms.
Step 2: Transportation Through the Vacuum
Once the atoms of the coating material are vaporized, they travel through the vacuum chamber. Because the pressure is so low, these atoms can move in a straight line without colliding with air molecules or other particles.
In some processes, reactive gases like nitrogen or oxygen are intentionally introduced into the chamber. These gases combine with the metal atoms mid-flight to create specific ceramic compounds, such as titanium nitride, which modifies the final coating's properties.
Step 3: Deposition onto the Metal Substrate
The vaporized atoms arrive at the target object—the metal part being coated—and condense on its surface. This deposition happens atom by atom, creating a very dense, pure, and tightly bonded film.
This atomic bonding is what gives PVD coatings their exceptional adhesion and durability compared to traditional plating methods.
Why Choose PVD Over Other Coatings?
The benefits of the PVD process are directly tied to the atomic-level precision of its application, resulting in a surface that is superior in both function and form.
Superior Durability and Hardness
PVD coatings significantly increase the surface hardness of a component. This makes the product far more resistant to scratches and wear, reduces friction, and can dramatically extend its operational lifespan.
Enhanced Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
The deposited film is extremely dense and non-porous, creating a robust barrier against environmental factors. This provides excellent protection against oxidation (rusting) and degradation from chemical exposure.
High-Purity, Biocompatible Films
Because the process is conducted in a vacuum, the resulting coatings are exceptionally pure and free of contaminants. This makes PVD an ideal choice for medical and food-grade applications, as the coatings are often non-toxic and meet strict FDA requirements.
Aesthetic Flexibility and Finish
Beyond its functional benefits, PVD provides a brilliant, durable decorative finish that is superior to many traditional methods. The process allows for a wide range of colors and finishes that resist tarnishing and fading.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PVD is a technical process with specific requirements and limitations that must be considered.
It Is a Line-of-Sight Process
The vaporized coating material travels in a straight line. This means that surfaces not directly exposed to the source material will not be coated effectively. Coating complex internal geometries or deep crevices requires sophisticated fixturing and part rotation to ensure even coverage.
Substrate Preparation is Critical
The final quality of the PVD coating is entirely dependent on the condition of the substrate. The metal part must be immaculately clean and free of any oils, oxides, or other contaminants. This often involves an intensive multi-step pre-treatment and cleaning process.
It Requires Significant Expertise and Investment
PVD is not a simple workshop procedure. It requires specialized vacuum chambers, high-energy sources, and precise process controls. Achieving consistent, high-quality results demands significant technical expertise and capital investment.
Is PVD the Right Choice for Your Application?
Choosing a coating technology depends entirely on your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear resistance and hardness: PVD is an industry-leading choice for cutting tools, engine components, and other high-friction applications.
- If your primary focus is a decorative, yet highly durable finish: PVD offers a superior alternative to traditional plating for items like watches, architectural hardware, and high-end fixtures.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility and chemical inertness: PVD is a trusted process for coating medical implants, surgical tools, and food processing equipment.
- If you are coating complex internal shapes or working with a limited budget: You must carefully evaluate the costs of advanced fixturing or consider alternative coating technologies.
Ultimately, PVD is a strategic choice for enhancing a product's value by creating a surface that is engineered to perform.
Summary Table:
| PVD Coating Aspect | Key Feature |
|---|---|
| Process | Vacuum-based, atomic-level deposition |
| Primary Benefit | Extreme hardness and wear resistance |
| Adhesion | Strong atomic bonding to the substrate |
| Applications | Cutting tools, medical devices, decorative finishes |
Ready to enhance your metal components with a high-performance PVD coating?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface engineering. Our expertise can help you select the right PVD technology to achieve superior durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic finishes for your laboratory or manufacturing needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your project with reliable, high-quality solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















