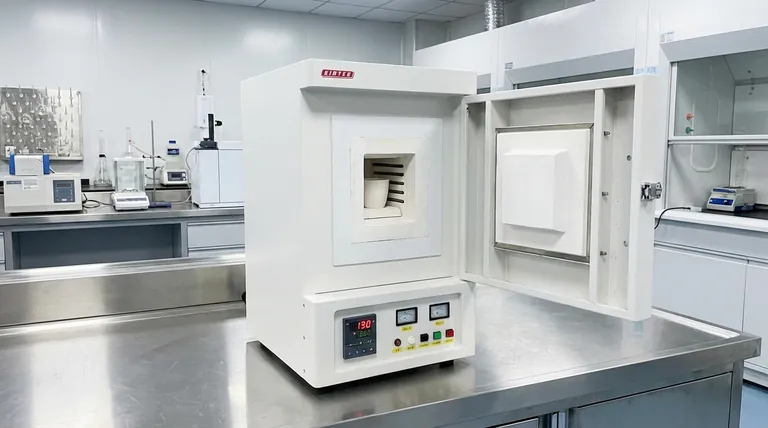
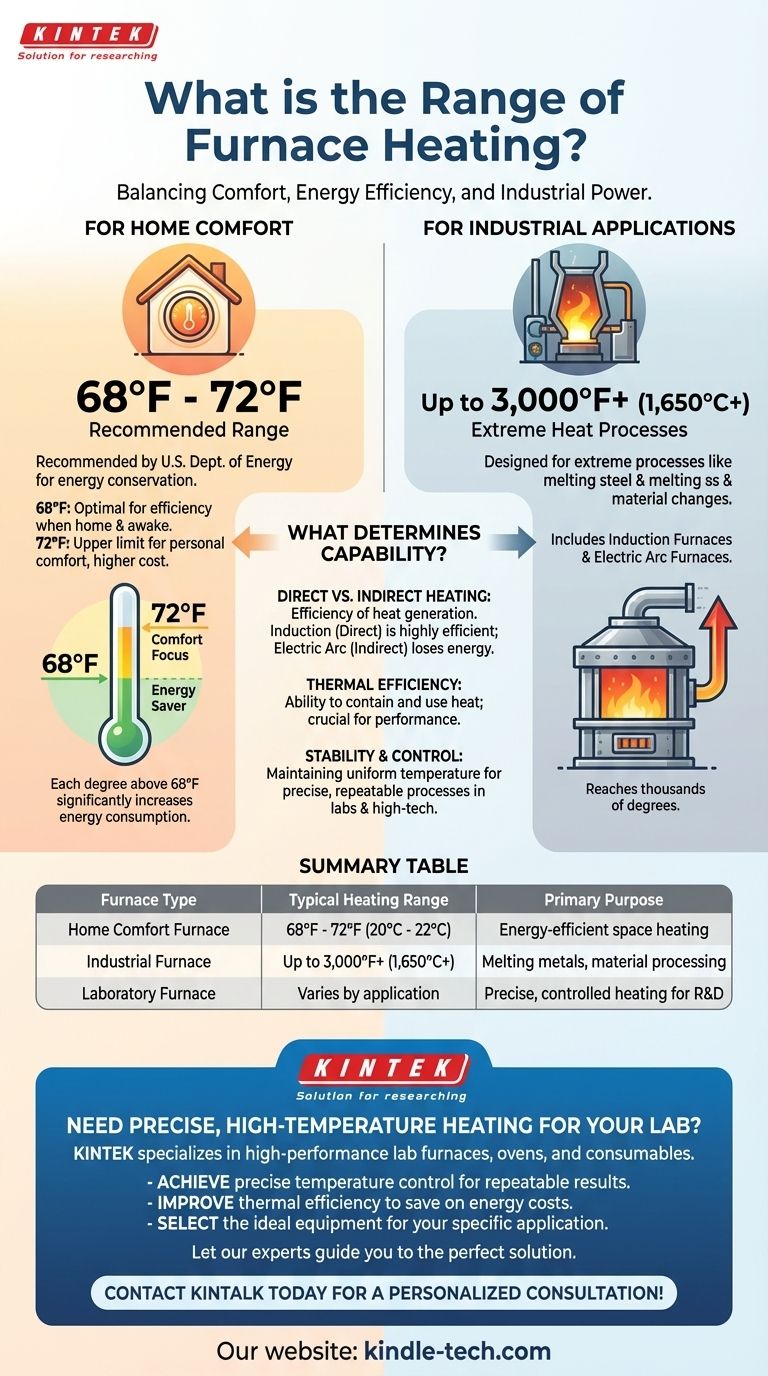
For a typical home, the recommended furnace heating range is between 68°F and 72°F. This specific range, advised by the U.S. Department of Energy, represents the ideal balance between personal comfort and energy efficiency, ensuring you stay warm without incurring excessive utility costs.
The term "furnace" is incredibly broad. While a home furnace operates in a narrow comfort-focused range, industrial and scientific furnaces are designed for extreme processes like melting steel and operate at temperatures thousands of degrees higher.

The Two Worlds of Furnaces: Comfort vs. Process
The core reason there isn't a single answer for a furnace's range is that furnaces are built for vastly different purposes. Understanding the distinction between home comfort and industrial processes is key.
For Home Comfort: The 68°F Guideline
The Department of Energy's recommendation is centered on energy conservation. Setting your thermostat to 68°F while you are home and awake is considered the most efficient starting point for heating.
Each degree above this mark can significantly increase your energy consumption. The 72°F upper limit is a nod to personal comfort, but it comes at a higher operational cost.
For Industrial Applications: Reaching Extreme Temperatures
In manufacturing and scientific research, furnaces perform tasks that require immense heat. These are not about gentle warmth but about fundamentally changing materials.
Industrial units like induction furnaces or electric arc furnaces are designed to melt steel and other metals. Their operational range is not measured in tens of degrees, but thousands.
What Determines a Furnace's Heating Capability?
The vast difference in heating ranges comes down to fundamental design, purpose, and the principles of heat transfer. A furnace's capability is defined by more than just its maximum temperature.
The Principle of Direct vs. Indirect Heating
The efficiency of heat generation is critical. An induction furnace heats material directly by generating heat within the substance itself (like liquid steel), leading to high thermal efficiency.
In contrast, an electric arc furnace uses indirect heating. The arc's heat must be transferred to the material, a less efficient process that loses a significant amount of energy to the furnace walls and cover.
The Importance of Thermal Efficiency
A furnace's effectiveness isn't just about the heat it can produce, but the heat it can contain and use. Poor insulation or design can lead to massive heat loss, wasting energy and limiting the furnace's practical capabilities.
Stability and Control
For scientific or high-tech manufacturing, raw power is not enough. These furnaces are characterized by their ability to maintain a uniform temperature and provide stable control, ensuring a precise and repeatable process, which is far more critical than simply getting "hot."
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing or evaluating a furnace involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" furnace, only the right furnace for a specific job.
Efficiency vs. Maximum Heat
The energy required to achieve higher temperatures increases exponentially. A home furnace is engineered for high efficiency within a very low and specific temperature band. An industrial furnace sacrifices some of this low-temperature efficiency for the ability to reach extreme heat levels.
Purpose-Built Design
You cannot use one type of furnace for the other's job. A home furnace lacks the power and materials to melt anything, while an industrial furnace would be an extraordinarily inefficient and unsafe way to heat a living room. The design is always tailored to the task.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your definition of a furnace's "range" should be guided by your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is saving money on your home heating bill: Set your thermostat to 68°F as the standard, and consider lowering it further when you are away or asleep.
- If your primary focus is maximizing home comfort: Use 72°F as a reasonable upper limit, but be aware that every degree above 68°F comes with a notable increase in cost.
- If your interest is technical or professional: Acknowledge that a furnace's range is dictated entirely by its application, from residential air heating to industrial metallurgy.
Ultimately, a furnace's heating range is a direct reflection of its intended purpose.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Heating Range | Primary Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Home Comfort Furnace | 68°F - 72°F (20°C - 22°C) | Energy-efficient space heating |
| Industrial Furnace | Up to 3,000°F+ (1,650°C+) | Melting metals, material processing |
| Laboratory Furnace | Varies by application | Precise, controlled heating for R&D |
Need Precise, High-Temperature Heating for Your Lab?
Whether your research requires uniform low-temperature stability or extreme heat for material testing, the right laboratory furnace is critical. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces, ovens, and consumables designed for accuracy, efficiency, and durability.
We help you:
- Achieve precise temperature control for repeatable results.
- Improve thermal efficiency to save on energy costs.
- Select the ideal equipment for your specific application, from basic heating to advanced material synthesis.
Let our experts guide you to the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Contact KINTALK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What affects the melting point of a substance? Uncover the Key Factors & Forces
- Do different liquids melt at different rates? Unlock the Science of Melting Points and Material Properties
- What is brazing vs soldering? Choose the Right Joining Method for Strength vs. Precision
- Why do we need to use properly some of the laboratory apparatus in the laboratory? The Foundation of Safe and Accurate Science
- What is the debinding process? A Guide to Critical Binder Removal for MIM & 3D Printing



















