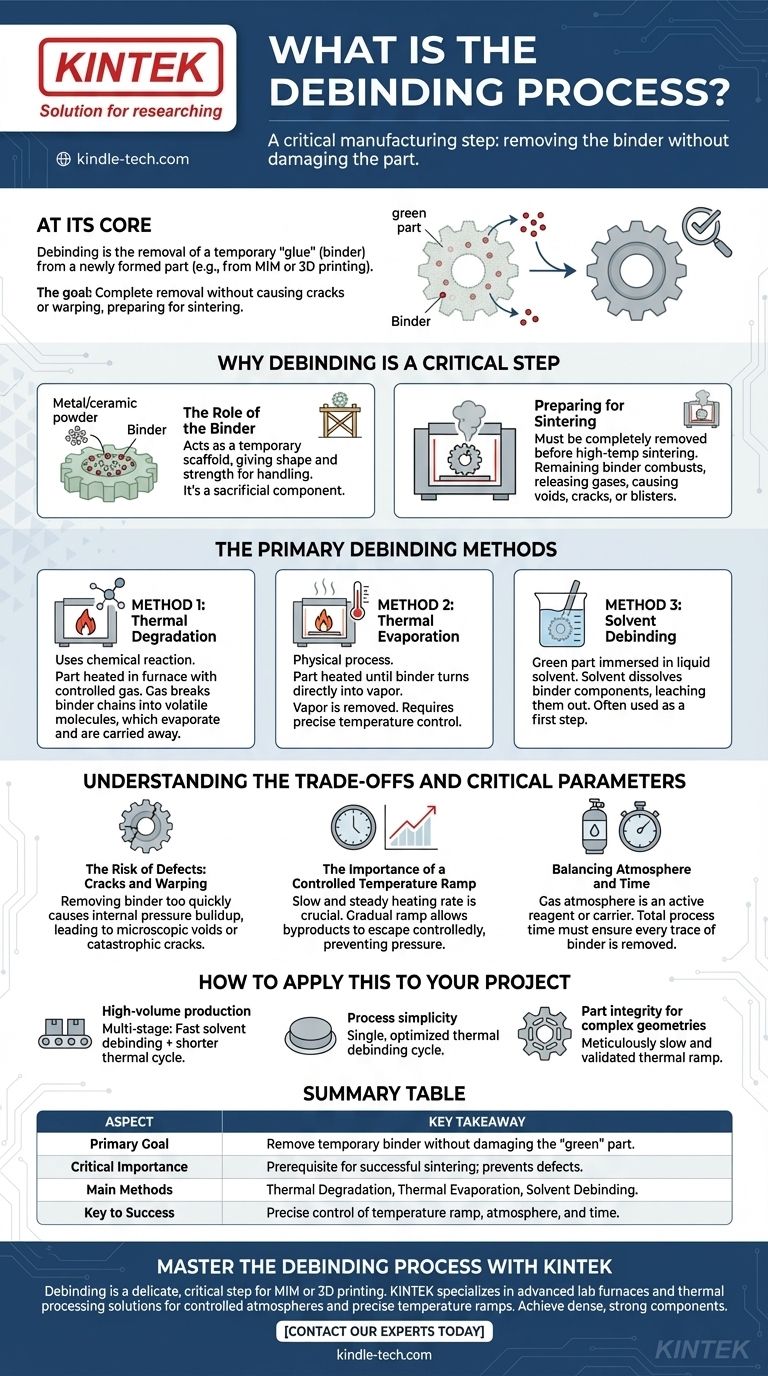
At its core, debinding is the critical manufacturing step where a temporary "glue," known as a binder, is removed from a newly formed part. This process is essential for parts made through methods like metal injection molding (MIM) or certain types of 3D printing, clearing the way for the final strengthening phase known as sintering. The goal is to remove this binder completely without causing any damage, such as cracks or warping, to the fragile part.
Debinding is not simply about removing a material; it is a precisely controlled process of deconstruction. The method and parameters—temperature, atmosphere, and time—must be carefully balanced to preserve the part's integrity before it gains its final strength.

Why Debinding is a Critical Step
The Role of the Binder
In processes like MIM, a fine metal or ceramic powder is mixed with a polymer binder. This mixture is then molded into the desired shape, creating what is called a "green part."
The binder acts as a temporary scaffold, giving the green part its shape and enough strength to be handled. However, it is a sacrificial component that serves no purpose in the final product.
Preparing for Sintering
Before the part can be heated to a high temperature to fuse the powder particles together (sintering), the binder must be completely removed.
If any binder remains, it can combust or decompose uncontrollably during sintering, releasing gases that create voids, cracks, or blisters in the final part. A successful debind is a prerequisite for a dense, strong, and dimensionally accurate component.
The Primary Debinding Methods
There are three main strategies for removing a binder, which can be used alone or in combination. The choice depends on the binder material, part geometry, and production requirements.
Method 1: Thermal Degradation
This method uses a chemical reaction to break down the binder. The part is heated in a furnace with a controlled gas atmosphere.
The gas reacts with the binder's polymer chains, breaking them into smaller, more volatile molecules. These smaller molecules then evaporate and are carried away by the furnace's gas flow.
Method 2: Thermal Evaporation
This is a physical process rather than a chemical one. The part is heated to a temperature where the binder itself turns directly into a vapor.
This vapor is then removed from the furnace. This method is simpler but requires extremely precise temperature control to avoid happening too quickly.
Method 3: Solvent Debinding
In this approach, the green part is immersed in a liquid solvent. The solvent is specifically chosen to dissolve one or more components of the binder system.
This process leaches the binder out of the part. Solvent debinding is often used as a first step to remove the bulk of the binder, followed by a thermal debinding step to remove the rest.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Parameters
Debinding is a delicate balance. Improper execution is one of the most common sources of part failure.
The Risk of Defects: Cracks and Warping
The greatest danger during debinding is removing the binder too quickly. If the binder evaporates or degrades faster on the surface than in the core, immense internal pressure can build up.
This pressure differential can easily lead to defects, from microscopic internal voids to catastrophic cracks and part-distorting warps.
The Importance of a Controlled Temperature Ramp
To prevent defects, a slow and steady heating rate is crucial, especially at the beginning of the thermal cycle.
A gradual temperature ramp allows the binder byproducts to escape the part at a controlled rate, preventing pressure buildup. The exact profile of temperature, pressure, and gas flow must be carefully engineered for the specific part and binder system.
Balancing Atmosphere and Time
The gas atmosphere in the furnace is not just a passive element; it can be an active reagent in degradation or a carrier to transport vapor away.
The total process time, or anneal time, must be long enough to ensure every trace of the binder has been removed from the deepest sections of the part. Rushing this step will compromise the final product.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing a debinding strategy requires aligning the method with your primary manufacturing goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: A multi-stage process, starting with fast solvent debinding to remove most of the binder, followed by a shorter thermal cycle, is often most efficient.
- If your primary focus is process simplicity: A single, carefully optimized thermal debinding cycle can be effective, eliminating the need for chemical solvents and extra handling steps.
- If your primary focus is part integrity for complex geometries: Your non-negotiable priority must be a meticulously slow and validated thermal ramp to ensure binder escapes evenly without causing stress.
Mastering the debinding process is fundamental to unlocking the full potential of advanced powder-based manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Remove temporary binder without damaging the fragile 'green' part. |
| Critical Importance | A prerequisite for successful sintering; prevents voids, cracks, and blisters. |
| Main Methods | Thermal Degradation, Thermal Evaporation, and Solvent Debinding. |
| Key to Success | Precise control of temperature ramp, atmosphere, and time to avoid defects. |
Master the Debinding Process with KINTEK
Debinding is a delicate, critical step that can make or break your Metal Injection Molding (MIM) or 3D printing project. Ensuring complete binder removal without causing cracks or warping requires precise thermal control and the right equipment.
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab furnaces and thermal processing solutions designed for the exacting demands of debinding and sintering. Our equipment provides the controlled atmospheres and precise temperature ramps necessary to preserve part integrity and achieve dense, strong final components.
Let us help you optimize your process for superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the high temperature of a muffle furnace? From 1100°C to 1700°C+ for Your Lab Needs
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and an electric furnace? A Guide to Precision Heating
- What type of furnace is a muffle furnace? A Guide to High-Purity, Contamination-Free Heating
- What is the working temperature of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise Heat Control for Your Lab
- What is the working principle of muffle furnace? Achieving Pure, Uniform High-Temperature Processing



















