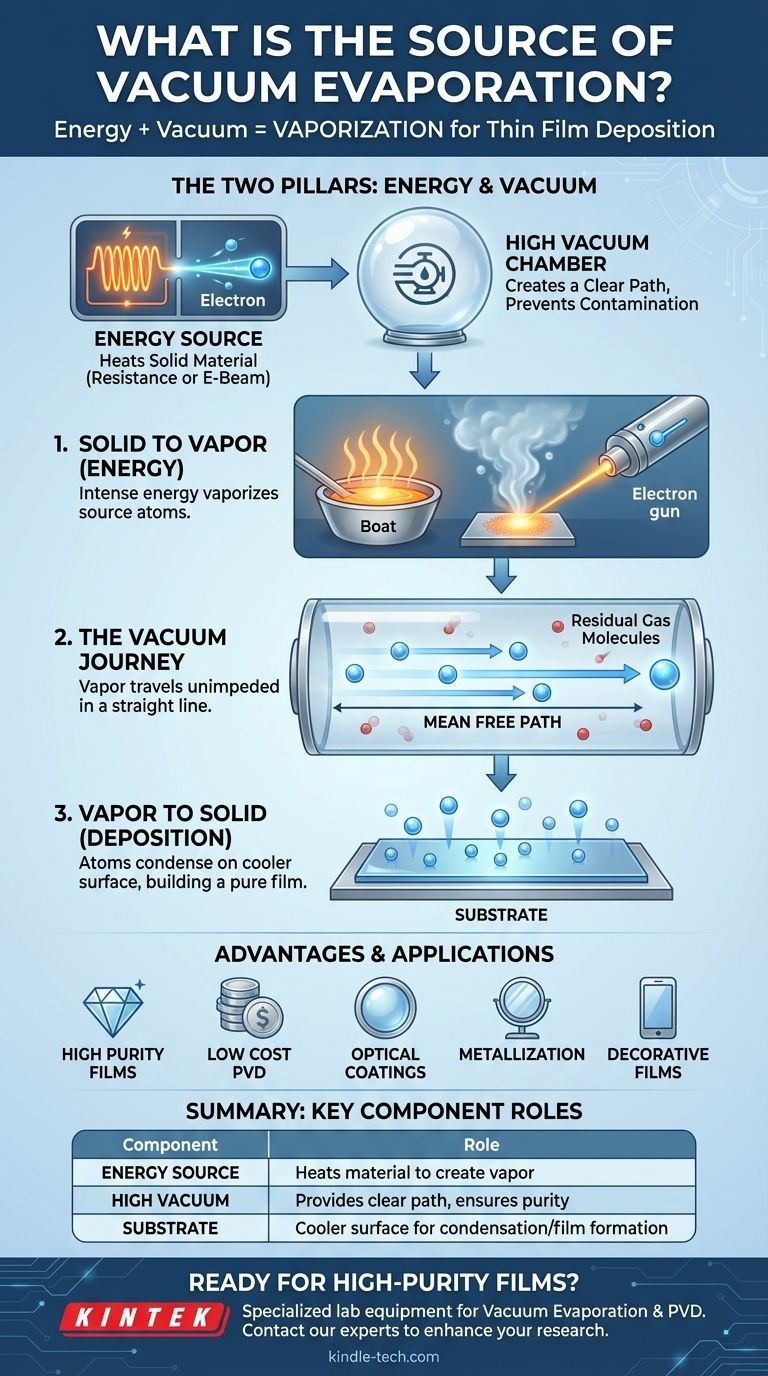
The source of vacuum evaporation is the energy applied to a material within a high-vacuum chamber. This energy, typically from electrical resistance heating or a high-energy electron beam, heats the source material until its atoms vaporize. These vaporized atoms then travel through the vacuum and condense onto a cooler surface, forming a thin, uniform film.
The core principle is simple: use intense energy to create a vapor from a solid material. The critical component, however, is the vacuum itself, which clears the path for this vapor to travel unimpeded and form an exceptionally pure coating on a target.

The Two Pillars of the Process: Energy and Vacuum
To truly understand vacuum evaporation, you must see it as a system built on two fundamental pillars. One provides the material vapor, and the other ensures that vapor can do its job correctly.
The Energy Source: Turning Solid to Vapor
The process begins by applying a significant amount of focused energy to a solid "source" material.
This is most often accomplished in one of two ways. Electrical heating involves passing a large current through a high-resistance holder, often called a "boat," which contains the material. The boat heats up intensely, causing the material within it to melt and evaporate.
Alternatively, electron beam heating uses a focused beam of high-energy electrons to directly strike the source material. The kinetic energy of the electrons is transferred to the material, causing localized boiling and evaporation from its surface.
The Vacuum: Why It's Non-Negotiable
A high vacuum is not an optional component; it is essential for the process to succeed.
The primary reason is to increase the mean free path of the evaporated atoms. This is the average distance an atom can travel before colliding with another particle. Removing nearly all the air molecules ensures this path is much longer than the distance to the target.
This long, clear path ensures the evaporated atoms travel in a straight line, a principle known as line-of-sight trajectory. It also prevents the hot vapor from reacting with or being scattered by residual gas molecules like oxygen, which would contaminate the final film.
Finally, the vacuum helps prepare and maintain clean surfaces on the target substrate, which is critical for ensuring the deposited atoms adhere properly and form a stable layer.
From Vapor to Solid: The Deposition Stage
Once the vapor is generated in the vacuum, the second half of the process begins: forming the film.
The Journey to the Substrate
Because of the vacuum, the atoms travel directly from the source to the target substrate without interference. This allows for precise and predictable deposition on surfaces that are directly in the line of sight of the source.
Condensation and Film Formation
The substrate is kept at a much lower temperature than the vapor source. When the hot, energetic atoms of vapor strike this cooler surface, they rapidly lose their energy and condense back into a solid state.
This condensation builds up atom by atom, creating a highly pure and uniform thin film across the substrate's surface. The rate of deposition can be easily monitored and controlled by adjusting the power of the energy source.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Applications
Like any technical process, vacuum evaporation has distinct advantages and is suited for specific applications.
Key Advantages of This Method
The primary benefit is the ability to create high-purity films, as the process starts with a pure source material and is conducted in a clean vacuum environment.
It is also the least expensive Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) process, making it highly economical. The use of a direct line-of-sight trajectory allows for precise deposition and straightforward rate control.
Common Applications
This technique is widely used to create a variety of functional and decorative coatings.
Common uses include optical interference coatings on lenses, reflective mirror coatings, and decorative films. It is also used for creating electrically conducting films, permeation barrier films on flexible packaging, and protective anti-corrosion layers. When used to deposit metals, it is often called vacuum metallization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a coating technology depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for purity, cost, and geometry.
- If your primary focus is high purity and low cost: Vacuum evaporation is an excellent choice, as it uses high-purity source materials and is the least expensive PVD process.
- If your primary focus is coating simple, flat surfaces: The line-of-sight deposition makes it ideal for creating uniform optical, metallic, or decorative coatings on substrates like lenses or wafers.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D objects: You may need to consider alternative methods, as the direct trajectory of evaporated atoms makes uniform coverage on intricate shapes challenging.
Understanding that the "source" is a combination of targeted energy and a pristine vacuum environment is the key to leveraging this powerful coating technology effectively.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Role in Vacuum Evaporation |
|---|---|
| Energy Source | Heats the material (e.g., via electron beam) to create a vapor. |
| High Vacuum | Provides a clear path for vapor travel, ensuring purity and adhesion. |
| Substrate | The cooler surface where the vapor condenses to form a thin film. |
Ready to achieve high-purity, cost-effective thin films for your laboratory?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for vacuum evaporation and other Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) processes. Whether you are creating optical coatings, conductive films, or protective layers, our expertise ensures you get the right solution for your application.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our reliable equipment can enhance your research and production quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
People Also Ask
- What is the evaporation process of semiconductors? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is low temperature evaporation technology? A Guide to Coating Heat-Sensitive Materials
- What are the applications of evaporation in industries? From Wastewater to Electronics
- What is the thermal evaporation method of thin film? A Guide to PVD Coating
- What is vacuum deposition of metals? A Guide to High-Purity, Durable Metal Coatings
- What is the process of thin film evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity PVD Coating
- What is the mechanism of evaporation? Unlock High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is the electron beam evaporation technique? Achieve High-Purity Thin Film Deposition



















