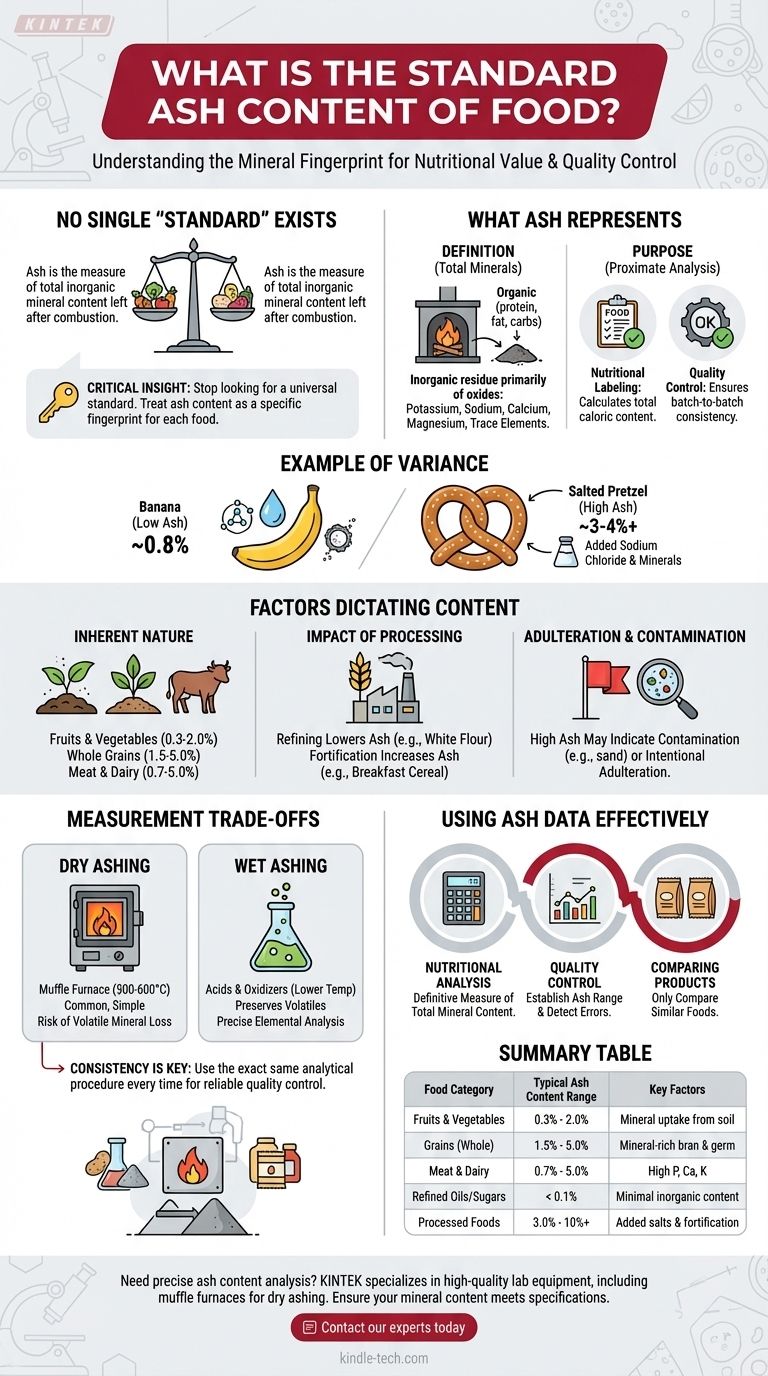
There is no single "standard" ash content for all food. This is because ash is the measure of a food's total mineral content—the inorganic, non-combustible portion left after complete combustion. Since different foods have vastly different mineral compositions, their ash content varies dramatically, from less than 0.1% in pure oils or sugars to over 10% in certain processed products or additives.
The critical insight is to stop looking for a universal standard. Instead, you must treat ash content as a specific fingerprint for a given food, using it to verify nutritional value, ensure batch-to-batch consistency, and detect potential adulteration or processing deviations.

What Ash Content Actually Represents
The Definition: A Measure of Total Minerals
Ash is the inorganic residue that remains after a food sample is heated at very high temperatures, effectively burning off all the organic matter like protein, fat, and carbohydrates.
This residue consists primarily of the oxides of essential minerals such as potassium, sodium, calcium, and magnesium, along with trace elements. It is, in essence, a proxy for the total mineral content of the food.
The Purpose: Why This Is Measured
Ash analysis is a fundamental part of proximate analysis in food science. It serves two main purposes.
First, it is crucial for nutritional labeling. By subtracting the percentages of moisture, protein, fat, carbohydrate, and ash from 100%, manufacturers can calculate the total caloric content more accurately.
Second, it is a vital tool for quality control. A consistent ash value indicates that the product composition and mineral content are uniform from one batch to the next.
An Example: A Banana vs. A Salted Pretzel
To understand the variance, consider two different foods. A banana, primarily composed of water and carbohydrates, might have an ash content of around 0.8%.
In contrast, a salted pretzel will have a much higher ash content, potentially 3-4% or more. This is due not only to the minerals in the flour but also the significant amount of added sodium chloride (salt).
Factors That Dictate a Food's Ash Content
The Inherent Nature of the Food
The single biggest factor is the food itself. Foods are biologically diverse and have naturally different mineral levels.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Generally have low to moderate ash (0.3% to 2.0%), reflecting their mineral uptake from the soil.
- Grains: Whole grains have more ash than refined grains because the mineral-rich bran and germ layers are intact.
- Meat and Dairy: These tend to have higher ash content due to naturally high levels of minerals like phosphorus, calcium, and potassium.
The Impact of Processing
How a food is processed has a profound effect on its final ash content.
Refining wheat to produce white flour, for example, removes the bran and germ, drastically lowering the ash content. Conversely, fortifying a breakfast cereal with iron, calcium, and zinc will intentionally increase its ash content.
Adulteration and Contamination
An unusually high ash content in a product that should have a low value can be a red flag. It may indicate contamination with inorganic material like sand or soil, or even intentional adulteration with cheap mineral fillers.
Understanding the Trade-offs in Measurement
Dry Ashing vs. Wet Ashing
The reference methods for determining ash content come with their own considerations. Dry ashing, where a sample is incinerated in a muffle furnace at 500-600°C, is the most common method due to its simplicity.
However, this high heat can cause certain volatile minerals, like chlorides and sulfates, to be lost. For precise elemental analysis, wet ashing is used. This method uses acids and oxidizing agents at lower temperatures to dissolve the sample, preserving those volatile elements.
The Critical Role of Consistency
The choice of method is less important than the consistency of its application. To use ash content as a reliable quality control metric, the exact same analytical procedure must be used every single time.
Comparing an ash value derived from dry ashing to one derived from wet ashing is invalid, as the results can differ significantly for the same sample.
How to Use Ash Content Data Effectively
Interpreting an ash value requires understanding your specific goal. Use these guidelines to apply the data correctly.
- If your primary focus is nutritional analysis: Use ash content as the definitive measure of total mineral content and a key variable for calculating a food's total energy value.
- If your primary focus is quality control: Establish a specific ash content range for your product and use it as a benchmark to ensure consistency and detect formulation errors or contamination.
- If your primary focus is comparing products: Only compare ash values between very similar foods (e.g., two brands of whole wheat flour) to make a meaningful judgment about relative mineral content.
Ultimately, viewing ash content not as a generic score but as a specific signature of a food's composition is the key to its proper application.
Summary Table:
| Food Category | Typical Ash Content Range | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Fruits & Vegetables | 0.3% - 2.0% | Mineral uptake from soil |
| Grains (Whole) | 1.5% - 5.0% | Mineral-rich bran and germ |
| Meat & Dairy | 0.7% - 5.0% | High phosphorus, calcium, potassium |
| Refined Oils/Sugars | < 0.1% | Minimal inorganic content |
| Processed Foods (e.g., salted pretzels) | 3.0% - 10%+ | Added salts and mineral fortification |
Need precise ash content analysis for your food products? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including muffle furnaces for dry ashing, to help you achieve accurate nutritional labeling and consistent batch quality. Ensure your product's mineral content meets specifications—contact our experts today to find the right solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of a muffle furnace? Achieve Uncontaminated, High-Purity Heating
- What does a lab muffle furnace do? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free Heating for Your Lab
- How do you use a muffle furnace in a lab? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe & Precise Operation
- How do you take care of a muffle furnace? Extend Equipment Life and Ensure Accurate Results
- What is a muffle furnace and how does it work? Achieve Clean, High-Temperature Heating for Your Lab



















