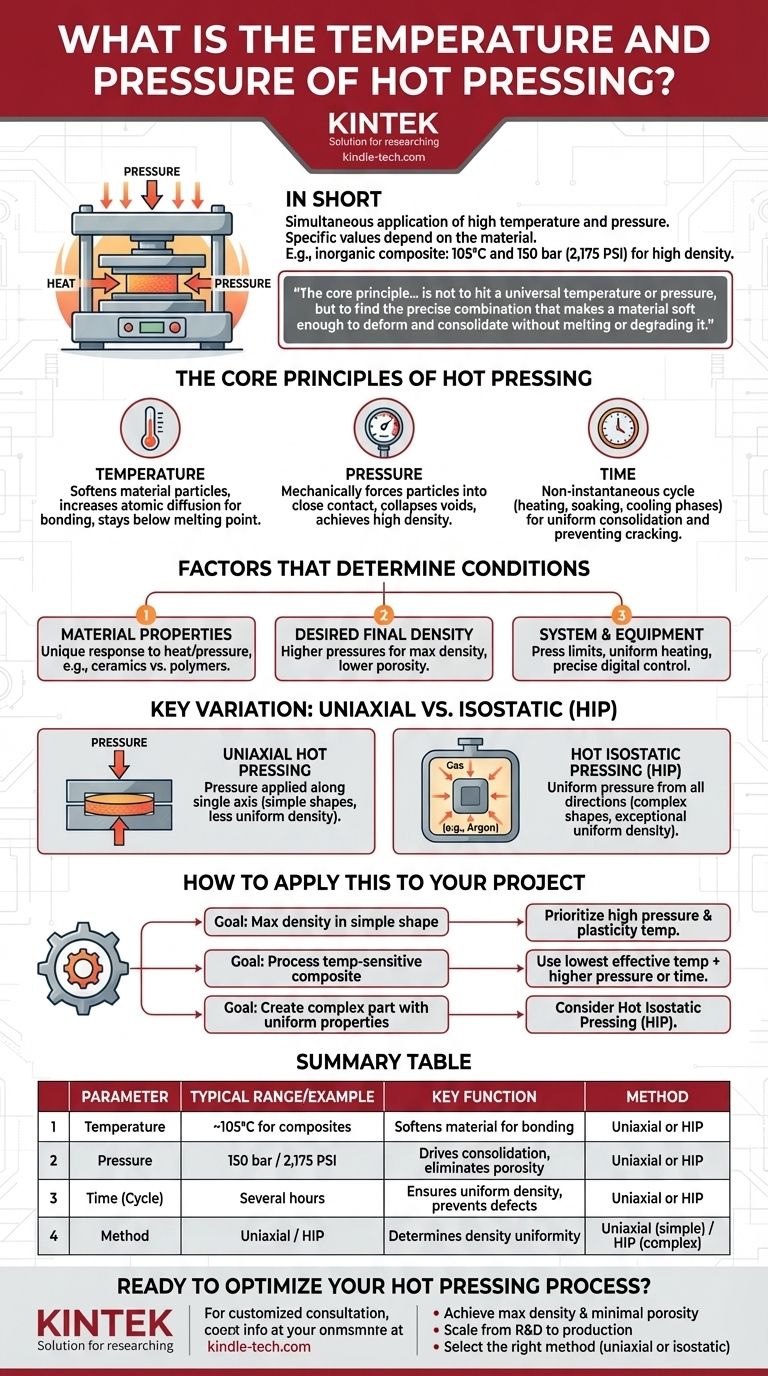
In short, hot pressing operates by simultaneously applying high temperature and pressure, but the specific values depend entirely on the material. As a concrete example for an inorganic composite, a temperature of 105°C and a pressure of 150 bar (approximately 2,175 PSI) can be used to achieve high density.
The core principle of hot pressing is not to hit a universal temperature or pressure, but to find the precise combination that makes a material soft enough to deform and consolidate without melting or degrading it.

The Core Principles of Hot Pressing
Hot pressing is a manufacturing process that consolidates powders or composite materials into a dense, solid part. It achieves this by applying both heat and pressure at the same time, often within a rigid die.
The Role of Temperature
The primary purpose of heat is to soften the material particles. This increases atomic diffusion and makes the material plastic, allowing the particles to deform and bond together much more effectively than at room temperature. The temperature must be high enough to enable this flow but remain safely below the material's melting or decomposition point.
The Role of Pressure
Pressure is the driving force for consolidation. It mechanically forces the particles into close contact, collapsing the voids (porosity) between them. This action is critical for achieving a final part with high density and minimal internal defects.
The Time Factor
Hot pressing is not an instantaneous process. A typical cycle can last for several hours, including the time required for uniform heating, the "soaking" period where temperature and pressure are held constant, and a controlled cooling phase to prevent thermal shock and cracking.
Factors That Determine the Right Conditions
The ideal temperature and pressure are not fixed values; they are carefully selected based on several key factors.
Material Properties
Every material has a unique response to heat and pressure. A ceramic powder will require vastly different conditions than a polymer composite or a metal alloy to achieve proper consolidation.
Desired Final Density
The end goal heavily influences the parameters. For applications requiring a perfect barrier, like the inorganic composite mentioned in studies, higher pressures are used to eliminate nearly all porosity and achieve maximum density.
System and Equipment
The equipment itself sets practical limits. Modern hot presses often feature specialized components, like a titanium alloy head, to ensure uniform temperature distribution and rapid heating. Digital pressure gauges allow for precise control over the applied force.
Understanding the Key Variation: Isostatic Pressing
While standard hot pressing is highly effective, it's important to distinguish it from a common variation.
Uniaxial Hot Pressing
Most conventional hot pressing is uniaxial, meaning pressure is applied along a single axis (e.g., from top to bottom). This is efficient for simple shapes like discs or blocks but can result in less uniform density in complex geometries.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is a more advanced technique where the part is heated in a high-pressure vessel. An inert gas, such as argon or nitrogen, is used to apply uniform, or isostatic, pressure from all directions simultaneously. This produces exceptionally uniform density, even in parts with highly complex shapes.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The correct parameters are determined by your specific goal and material.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density in a simple shape: Prioritize high pressure and a temperature that allows for material plasticity without degradation.
- If your primary focus is processing a temperature-sensitive composite: Use the lowest effective temperature and compensate with higher pressure or longer pressing times to achieve consolidation.
- If your primary focus is creating a complex part with perfectly uniform properties: Standard hot pressing may be insufficient; consider using Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) to ensure even consolidation.
Ultimately, hot pressing is a balancing act between temperature, pressure, and time, tailored precisely to the material and the desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Typical Range / Example | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Varies by material (e.g., ~105°C for composites) | Softens material for particle bonding and diffusion |
| Pressure | Varies by material (e.g., 150 bar / 2,175 PSI) | Drives consolidation to eliminate porosity |
| Time (Cycle) | Several hours (heating, soaking, cooling) | Ensures uniform density and prevents defects |
| Method | Uniaxial (simple shapes) or Isostatic (HIP, complex shapes) | Determines density uniformity in the final part |
Ready to optimize your hot pressing process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processing. Whether you are consolidating advanced ceramics, composites, or metal powders, our expertise ensures you achieve the perfect balance of temperature, pressure, and time for superior results.
Let’s discuss your project requirements and how our solutions can help you:
- Achieve maximum density and minimal porosity
- Scale from R&D to production with reliable equipment
- Select the right method (uniaxial or isostatic) for your application
Contact our experts today for a customized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- How does the uniaxial pressing function of a vacuum hot press furnace influence the microstructure of ZrC-SiC ceramics?
- Why is precise temperature control necessary for SiC/Cu Vacuum Hot Pressing? Mastering the Cu9Si Interface Phase
- What role does a high-temperature hot press play in the sintering of NITE-SiC? Optimize Your Densification Process
- What conditions does a Vacuum Hot Pressing Furnace provide for Copper-MoS2-Mo composites? Achieve Peak Densification
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press for CuCr50? Achieve Superior Density & Purity in Alloy Production



















