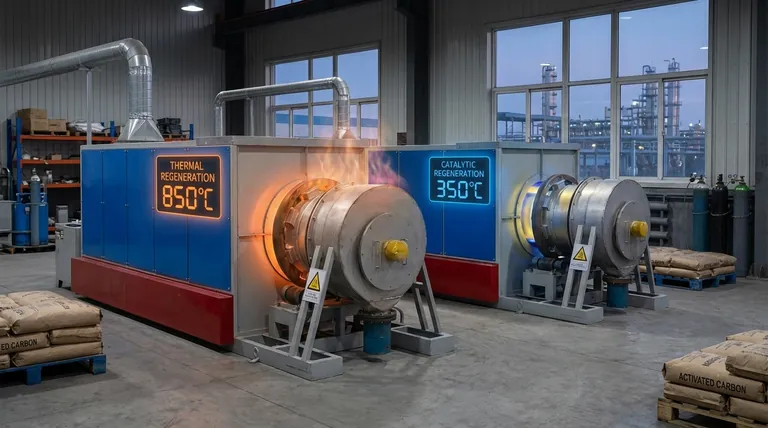
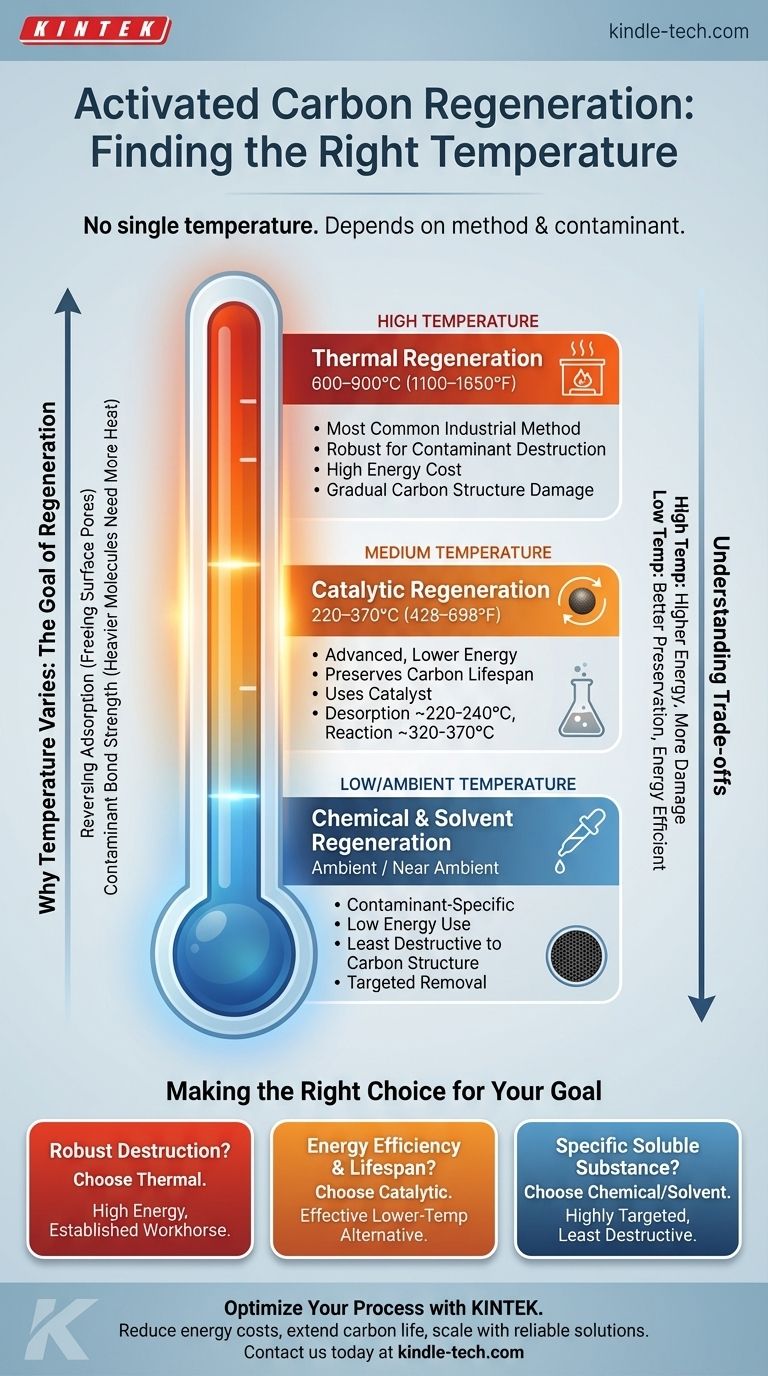
For activated carbon regeneration, the required temperature depends entirely on the method used. While advanced methods like catalytic regeneration work in a lower range of 220–370°C (428–698°F), the most common industrial method, thermal regeneration, requires much higher temperatures, often exceeding 800°C (1472°F).
The critical takeaway is that there is no single regeneration temperature. The correct temperature is determined by the regeneration technology chosen, the specific contaminants being removed, and the balance between operational cost and preserving the carbon's long-term effectiveness.

Why Temperature Varies: The Goal of Regeneration
Reversing Adsorption
Activated carbon works by adsorption, where contaminant molecules stick to its vast internal surface area. Regeneration is the process of using energy—typically heat—to break these bonds and drive the contaminants off, freeing up the surface pores for reuse.
The Role of the Contaminant
Different substances are held onto the carbon with different bond strengths. Light, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can often be released with less energy, while heavier, more complex molecules require significantly more heat to break down and remove.
Key Regeneration Methods and Their Temperatures
Thermal Regeneration
This is the most common and robust method used in large-scale industrial applications. It involves heating the carbon in a low-oxygen environment, often with steam.
The process typically occurs in a multi-step furnace at very high temperatures, usually between 600–900°C (1100–1650°F). This intense heat is necessary to pyrolyze (thermally decompose) the adsorbed organic contaminants.
Catalytic Regeneration
This is a more advanced technique designed to reduce the high energy costs of thermal regeneration. It uses a catalyst to lower the temperature required to break down contaminants.
As noted in technical studies, this process operates in a much lower range. Desorption of the contaminant occurs around 220–240°C (428–464°F), and the subsequent catalytic reaction to destroy it happens between 320–370°C (608–698°F).
Chemical and Solvent Regeneration
For certain applications, regeneration can be done by washing the carbon with a solvent or a chemical that dissolves the adsorbed contaminant. These methods often operate at or near ambient temperatures but are highly specific to the contaminant being targeted.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Impact of High Temperatures
While effective, the high heat of thermal regeneration gradually damages the carbon's internal pore structure. With each cycle, a small amount of the carbon is burned off, reducing its overall capacity and mechanical strength over time.
The Benefit of Lower Temperatures
Methods like catalytic regeneration are gentler on the activated carbon. By operating at lower temperatures, they better preserve the pore structure, leading to less material loss and a potentially longer service life for the carbon.
Energy and Operational Costs
The difference in energy consumption is significant. The high temperatures of thermal regeneration translate directly to higher fuel costs, which is a major factor in its operational expense. Lower-temperature methods are inherently more energy-efficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal regeneration strategy depends entirely on your operational priorities and the nature of your application.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, robust contaminant destruction: Standard thermal regeneration is the established industry workhorse, despite its high energy use.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and maximizing carbon lifespan: Catalytic regeneration provides an effective lower-temperature alternative for compatible contaminants.
- If your primary focus is removing a specific, soluble substance: Chemical or solvent regeneration may be the most targeted and least destructive method.
Ultimately, selecting the right temperature means first selecting the right regeneration technology for your specific process.
Summary Table:
| Regeneration Method | Typical Temperature Range (°C) | Typical Temperature Range (°F) | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Regeneration | 600–900°C | 1100–1650°F | High energy, robust for industrial scale |
| Catalytic Regeneration | 220–370°C | 428–698°F | Lower energy, preserves carbon lifespan |
| Chemical/Solvent Regeneration | Ambient/Near Ambient | Ambient/Near Ambient | Contaminant-specific, low-temperature |
Optimize Your Activated Carbon Regeneration Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right regeneration temperature and method is critical for balancing operational costs, energy efficiency, and the long-term effectiveness of your activated carbon. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific regeneration needs—whether you require high-temperature thermal solutions or energy-efficient catalytic systems.
Our expertise helps you:
- Reduce energy costs with efficient regeneration technologies
- Extend carbon service life by selecting the right temperature profile
- Scale your process with reliable, industrial-grade equipment
Let’s enhance your regeneration strategy together. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK’s solutions can drive efficiency and performance in your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a carbon regeneration kiln? Mastering the 750-800°C Reactivation Process
- What are the principles of a rotary kiln? Master the Mechanics of High-Temperature Processing
- How to regenerate activated carbon? Master the 3-Stage Thermal Process for Cost Savings
- Can you restore activated carbon? Understanding the Industrial Reactivation Process
- What temperature is a carbon regeneration kiln? Master the 650°C-800°C Range for Optimal Results



















