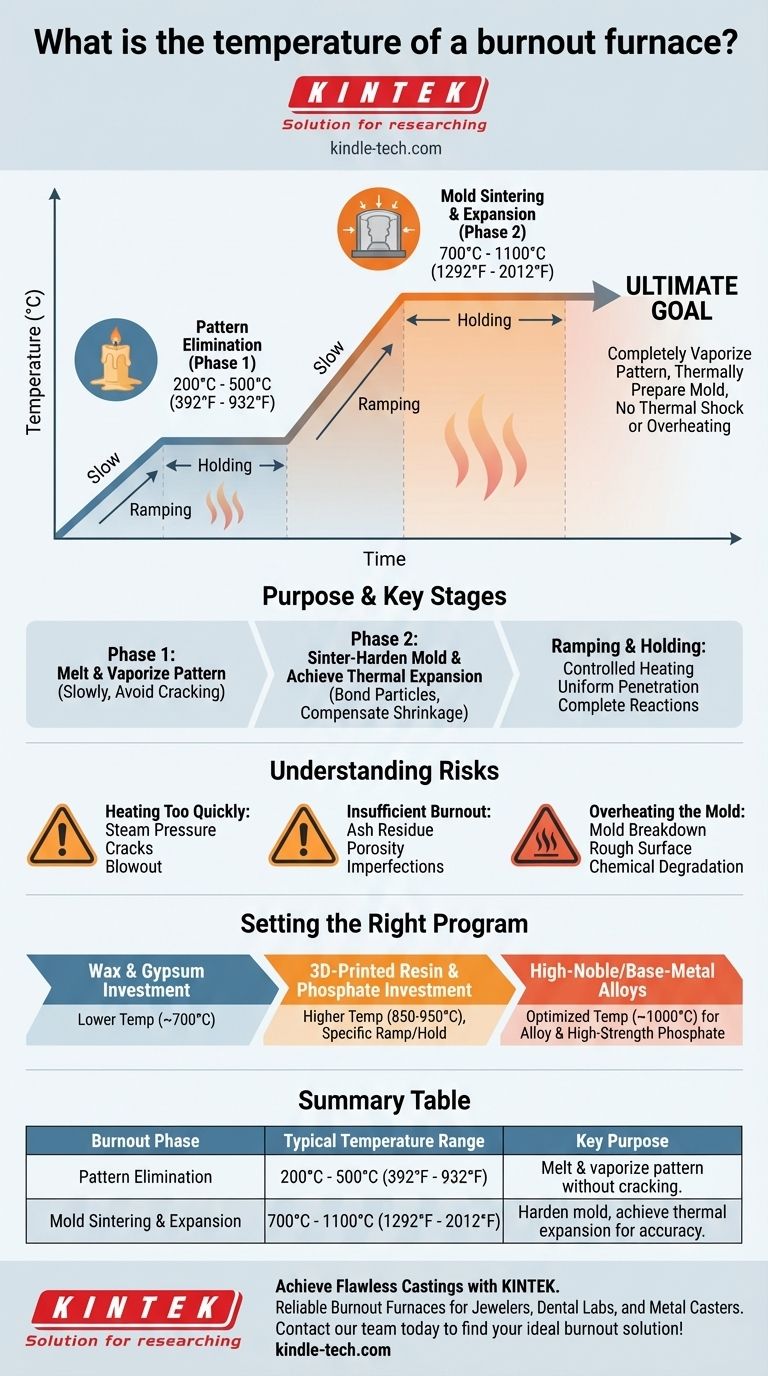
The operational temperature of a burnout furnace is not a single value but a carefully controlled cycle with multiple stages. While some high-temperature furnaces can reach 1800°C, a typical burnout process for casting ranges from a low of 200°C (392°F) to a high of 1100°C (2012°F). The precise temperatures are dictated entirely by the pattern material and the investment mold being used.
A burnout furnace's temperature profile is a means to an end. The ultimate goal is to completely vaporize a pattern (like wax or resin) and thermally prepare the investment mold for casting, all without causing damage from thermal shock or overheating.

The Purpose of a Burnout Cycle
A burnout is not a simple heating process but a multi-stage thermal program. Each stage has a distinct purpose in preparing the mold for the introduction of molten metal.
Phase 1: Pattern Elimination
The initial, low-temperature stage is designed to melt and vaporize the pattern. For traditional wax patterns, this occurs at a relatively low temperature, often between 200°C and 500°C.
This phase must be slow enough to allow the material to liquefy and run or vaporize out of the mold without creating pressure that could crack the investment.
Phase 2: Mold Sintering and Expansion
After the pattern is gone, the temperature is increased to the final, higher setpoint, typically between 700°C and 1100°C. This phase has two critical functions.
First, it sinter-hardens the investment mold. This process heats the refractory particles in the investment, causing them to bond and significantly increasing the mold's strength to withstand the pressures of casting.
Second, it brings the mold to a specific, calculated thermal expansion. This expansion is engineered to compensate for the shrinkage of the metal alloy as it cools, ensuring the final cast piece is dimensionally accurate.
The Critical Role of Ramping and Holding
The furnace does not jump to its final temperature. The rate of temperature increase, or "ramping," is carefully controlled.
Different stages are also held at a specific temperature for a set duration, known as "holding" or "heat soaking." This ensures the heat penetrates the entire mold uniformly and that all chemical and physical reactions (like vaporizing residual carbon) are complete.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Achieving a perfect casting requires balancing temperature, time, and material properties. Deviating from the ideal burnout cycle introduces significant risks.
Heating Too Quickly
Ramping the temperature too fast is a common cause of failure. It can generate steam from residual moisture inside the investment, creating internal pressure that leads to cracks or a complete mold blowout.
Insufficient Burnout
If the peak temperature is too low or the hold time is too short, the pattern material will not be completely eliminated. This leaves behind ash or carbon residue, which will cause porosity, surface imperfections, and an incomplete casting.
Overheating the Mold
Exceeding the recommended temperature for your investment material is just as damaging. Overheating can cause the investment to break down, resulting in a rough, unusable surface on the final casting. As a core principle, you must heat the material without causing it to chemically degrade or melt.
Setting the Right Burnout Program
To determine your furnace settings, you must start with your materials. The manufacturer's instructions for your specific investment powder and pattern material are your primary guide.
- If your primary focus is casting standard wax with a gypsum investment: Your final burnout temperature will be on the lower end, typically around 700°C (1292°F), as gypsum-based investments cannot tolerate higher heat.
- If your primary focus is casting 3D-printed resins with a phosphate investment: You will need a cycle with a higher top temperature, often 850-950°C (1562-1742°F), and a specific ramp/hold schedule to ensure complete, ash-free burnout of the resin.
- If your primary focus is casting high-noble or base-metal alloys: The mold temperature must be optimized for the alloy's characteristics, often requiring a high-strength phosphate investment and a final temperature approaching 1000°C (1832°F).
Always consult the manufacturer's technical data sheets for your specific materials to build the correct, successful burnout program.
Summary Table:
| Burnout Phase | Typical Temperature Range | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Pattern Elimination | 200°C - 500°C (392°F - 932°F) | Melt and vaporize wax/resin pattern without cracking the mold. |
| Mold Sintering & Expansion | 700°C - 1100°C (1292°F - 2012°F) | Harden the mold and achieve thermal expansion for dimensional accuracy. |
Achieve flawless castings with the right burnout furnace. The precise temperature cycle is critical for eliminating pattern residue and preparing your investment mold. At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment, including reliable burnout furnaces designed for the exacting needs of jewelers, dental labs, and metal casters. Our experts can help you select the perfect furnace for your specific materials—whether you're working with wax, 3D-printed resins, gypsum, or phosphate investments.
Let KINTEK provide the reliable equipment and support you need for perfect results every time. Contact our team today to discuss your application and find your ideal burnout solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the use of furnace in laboratory? Unlock Material Transformation for Your Research
- What is the difference between a furnace and an oven in a laboratory? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Heat Needs
- What is the thermal debinding process? A Guide to Safe Binder Removal for MIM & Ceramics
- What is the use of a digital muffle furnace? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the use of electric muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing



















