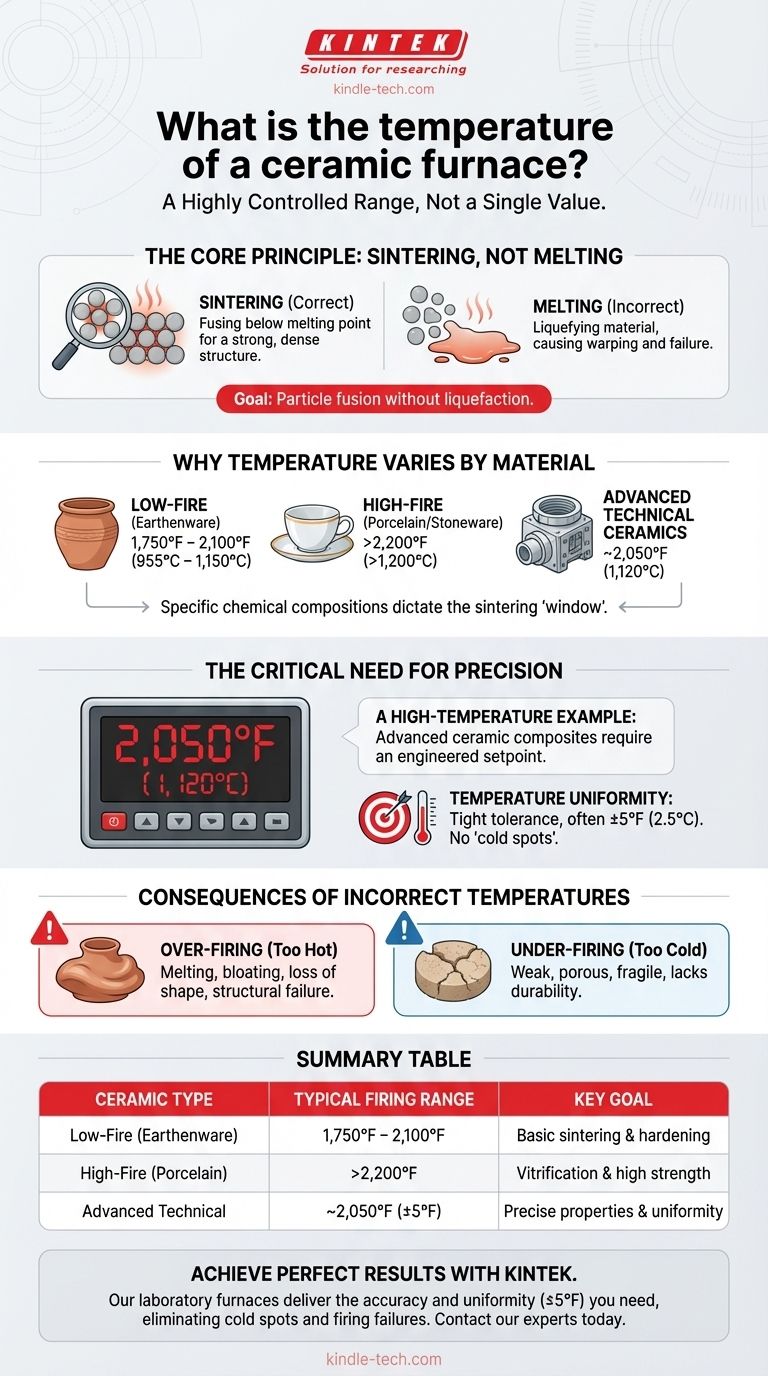
The temperature of a ceramic furnace is not one specific value but a highly controlled range determined by the exact material being fired. For example, some advanced ceramic composites are processed at 2,050°F (1,120°C). The key principle is that the temperature must be high enough to fuse the material's particles together but must remain below its actual melting point.
The correct temperature for a ceramic furnace is dictated entirely by the material being fired. The goal is always to heat the ceramic to a point where particles fuse together—a process called sintering—without reaching the material's melting point.

The Core Principle: Sintering, Not Melting
The fundamental process inside a ceramic furnace is not about melting. It's about a physical transformation that happens at a solid state.
What is Sintering?
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat without liquefying it.
The intense heat causes the individual grains or particles of the ceramic to fuse at their contact points, creating a strong, dense, and rigid structure.
Why Temperature Varies by Material
Different ceramic materials have vastly different chemical compositions. Earthenware clays sinter at much lower temperatures than high-performance porcelain or advanced technical ceramics.
Each type of ceramic has a specific temperature "window" where it will properly sinter to achieve its desired properties, such as strength, density, and porosity.
The Critical Need for Precision
Simply reaching a target temperature is not enough; maintaining it with extreme accuracy is essential for producing high-quality ceramics.
A High-Temperature Example
For certain advanced ceramic composites, the furnace is heated to a precise 2,050°F (1,120°C).
This temperature is not an approximation. It is an engineered setpoint designed to achieve specific material characteristics.
The Role of Temperature Uniformity
In professional applications, temperature uniformity is non-negotiable. The furnace must maintain the target temperature within a very tight tolerance, often as precise as ± 5°F (2.5°C).
Any deviation, or "cold spot," can result in an unevenly fired product with internal stresses, weaknesses, or defects that compromise its structural integrity.
The Consequences of Incorrect Temperatures
The success or failure of a ceramic firing hinges on temperature control. The margin for error is often very small.
The Risk of Over-firing
If the furnace temperature exceeds the material's sintering range, it will begin to melt, bloat, or warp.
The piece will lose its intended shape and structural integrity, often resulting in a complete failure of the product.
The Problem of Under-firing
If the temperature is too low, the particles will not fuse together properly.
The resulting ceramic will be weak, porous, and lack the durability expected of the finished product. It will be fragile and unable to perform its intended function.
Setting the Right Temperature for Your Goal
The correct approach depends entirely on the material you are working with and the outcome you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is low-fire pottery (e.g., earthenware): Your target temperatures will be on the lower end, typically between 1,750°F and 2,100°F (955°C and 1,150°C).
- If your primary focus is high-fire ceramics (e.g., porcelain or stoneware): You will operate at higher temperatures, often exceeding 2,200°F (1,200°C), to achieve vitrification and strength.
- If your primary focus is advanced technical ceramics: You will use precisely engineered temperatures, like the 2,050°F (1,120°C) example, where absolute accuracy and uniformity are critical for performance.
Ultimately, mastering temperature control is the key to transforming raw material into a durable and functional ceramic product.
Summary Table:
| Ceramic Type | Typical Firing Temperature Range | Key Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Fire (Earthenware) | 1,750°F – 2,100°F (955°C – 1,150°C) | Basic sintering and hardening |
| High-Fire (Porcelain/Stoneware) | >2,200°F (>1,200°C) | Vitrification and high strength |
| Advanced Technical Ceramics | ~2,050°F (1,120°C) ±5°F | Precise properties and uniformity |
Achieve perfect ceramic results with precise temperature control. Whether you're firing earthenware, porcelain, or advanced technical ceramics, KINTEK's laboratory furnaces deliver the accuracy and uniformity you need. Our equipment ensures ±5°F tolerance, eliminating cold spots and firing failures. Contact our experts today to find the ideal furnace for your lab's specific ceramic applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is a muffle furnace used for ash determination? Achieve Precise Inorganic Analysis
- How do traditional high-temperature sintering furnaces facilitate YSZ thin films? Achieving the Gold Standard.
- What roles do high-temperature furnaces and quenching devices play in the 475 °C embrittlement of duplex stainless steel?
- What is the role of high-temperature muffle furnaces in the synthesis of NASICON-structured LATP ceramic powder?
- How is a muffle furnace utilized to simulate high-temperature service environments? Mastering Cyclic Heat Treatment
- What are the primary process objectives when using a precision muffle furnace for titanium alloys? Enhance Durability
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in magnetite pellet roasting? Optimize Mineral Phase & Compressive Strength
- What experimental conditions does a Muffle Furnace provide for 1373 K isothermal oxidation tests of coatings?



















