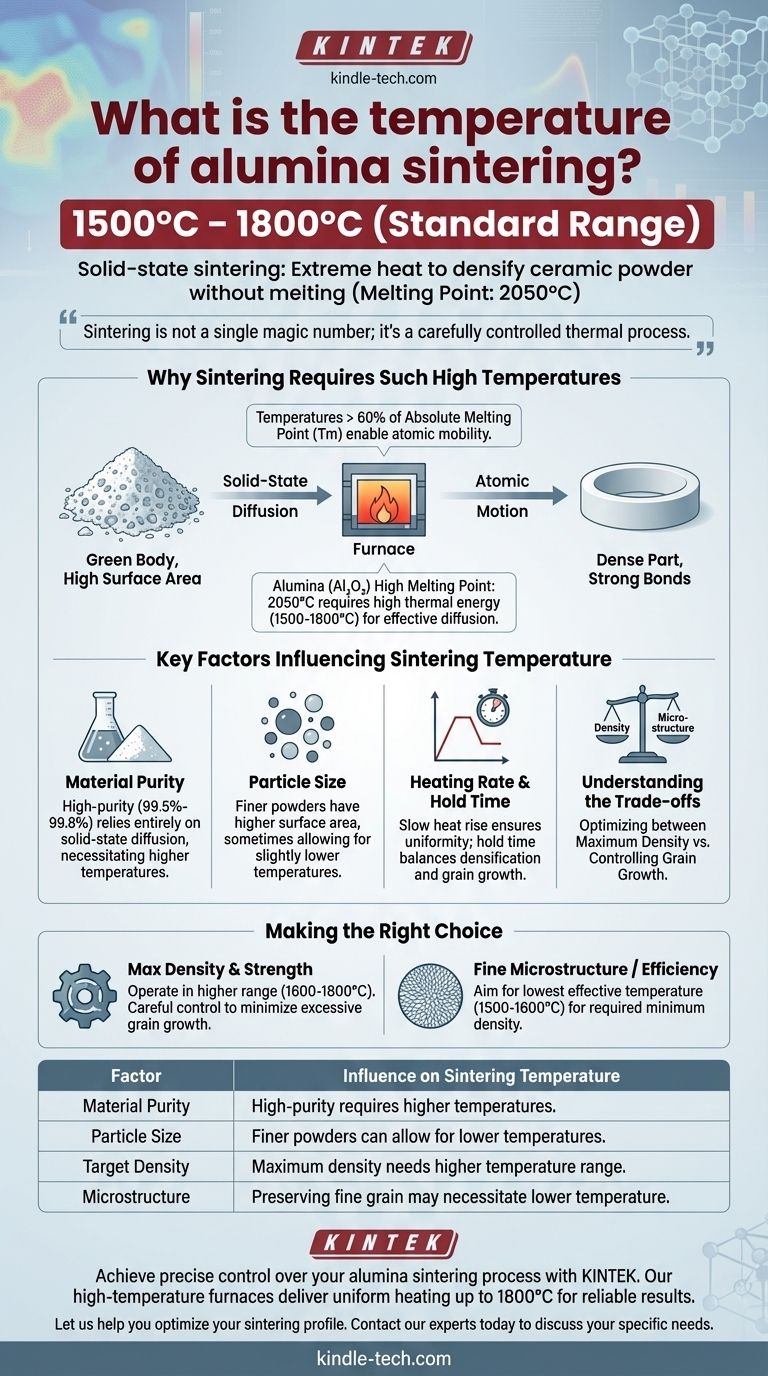
The standard sintering temperature for high-purity alumina is between 1500 °C and 1800 °C. This process, known as solid-state sintering, uses extreme heat to densify the ceramic powder into a solid object without reaching its melting point of 2050 °C. The precise temperature depends heavily on factors like particle size, purity, and the desired final density of the ceramic part.
Sintering is not about a single magic number; it's a carefully controlled thermal process. The goal is to apply enough heat to enable atoms to diffuse and bond, densifying the material, while simultaneously managing the trade-offs between final density and grain structure.

Why Sintering Requires Such High Temperatures
Sintering is fundamentally a process of atomic motion. To transform a loose powder into a dense, solid part, individual atoms must have enough energy to move, eliminate the pores between particles, and form strong chemical bonds. This requires significant thermal energy.
The Principle of Solid-State Diffusion
The primary mechanism at work is solid-state diffusion. At temperatures greater than approximately 60% of a material's absolute melting point (Tm), atoms become mobile enough to move across particle surfaces and through the crystal lattice.
This movement is driven by a reduction in surface energy. The fine particles in the initial "green body" have a very high surface area, which is energetically unfavorable. Heat provides the energy for atoms to rearrange themselves into a denser, lower-energy state, effectively fusing the particles together.
Alumina's High Thermal Requirement
Alumina (Al₂O₃) has exceptionally strong ionic and covalent bonds, making it a very stable material with a high melting point of 2050 °C.
Because of this high melting point, a correspondingly high temperature is needed to initiate effective diffusion. While the general rule suggests a temperature above ~1230 °C (0.6 * 2050 °C), practical densification for alumina requires the much higher range of 1500-1800 °C to achieve the desired properties in a reasonable timeframe.
Key Factors Influencing Sintering Temperature
The ideal sintering temperature is not a fixed value. It is adjusted based on the raw material and the target specifications for the final component.
Material Purity
The purity of the alumina powder is critical. Additives or impurities can act as sintering aids, often forming a liquid phase at lower temperatures that can accelerate densification.
Conversely, for high-purity alumina (99.5% to 99.8%), there are no such aids. The process relies entirely on solid-state diffusion, which necessitates higher temperatures to achieve full density.
Particle Size
Finer starting powders with smaller particle sizes have a higher surface area. This provides a stronger driving force for sintering, which can sometimes allow for slightly lower sintering temperatures or shorter processing times.
Coarser powders require more thermal energy (higher temperatures or longer holds) to achieve the same level of densification.
Heating Rate and Hold Time
The rate at which the temperature is increased (typically 4 °C to 10 °C per minute for technical ceramics) and the duration it is held at the peak temperature are also critical parameters.
A slow heat rise ensures uniform temperature throughout the part, preventing cracks. The hold time at peak temperature is a balancing act; it must be long enough for densification but not so long that it causes undesirable effects.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing the sintering process always involves managing a critical trade-off between achieving maximum density and controlling the microstructure of the final part.
Density vs. Grain Growth
The primary goal of sintering is to eliminate porosity and achieve high density, which is crucial for mechanical strength and other performance characteristics.
However, the same high temperatures and long hold times that promote densification also promote grain growth. If grains become too large, the mechanical properties of the ceramic, such as its toughness and strength, can actually decrease. The ideal process achieves near-full density while maintaining a fine, uniform grain structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sintering profile is essential for achieving the desired material properties for a specific application.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and mechanical strength: You will likely need to operate in the higher end of the temperature range (1600-1800 °C) with a carefully controlled heating rate and hold time to minimize excessive grain growth.
- If your primary focus is preserving a fine microstructure or process efficiency: Aim for the lowest effective temperature (around 1500-1600 °C) that still achieves the required minimum density for your application.
Ultimately, controlling the sintering temperature is the primary lever for engineering the final properties of an alumina ceramic component.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Influence on Sintering Temperature |
|---|---|
| Material Purity | High-purity alumina requires higher temperatures for solid-state diffusion. |
| Particle Size | Finer powders can sometimes allow for slightly lower temperatures. |
| Target Density | Maximum density typically requires the higher end of the temperature range. |
| Microstructure | Preserving a fine grain structure may necessitate a lower temperature. |
Achieve precise control over your alumina sintering process with KINTEK.
The ideal sintering temperature is critical for engineering the final density, strength, and microstructure of your alumina components. KINTEK specializes in high-temperature laboratory furnaces and consumables designed for the exacting demands of technical ceramics. Our equipment delivers the uniform heating and precise temperature control up to 1800°C necessary for reliable, repeatable results.
Let us help you optimize your sintering profile for superior ceramic properties. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the function of a corundum furnace tube in chlorine corrosion tests? Ensure Purity in High-Heat Experiments
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis



















