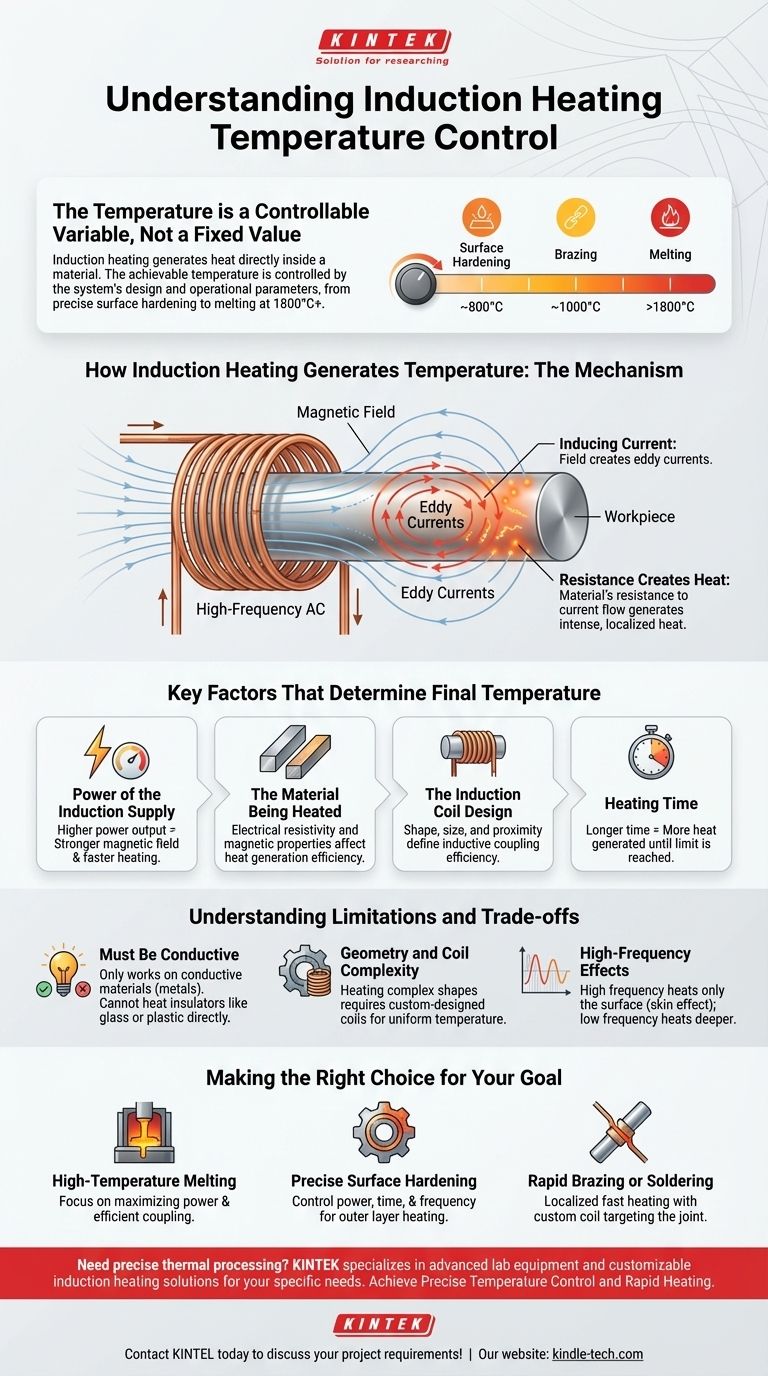
The temperature of induction heating is not a fixed value, but rather the result of a highly controllable process. While an industrial induction furnace can easily reach temperatures of 1800°C (3272°F) or more to melt metals, the technology's true strength is its ability to precisely manage heat. The final temperature is determined by the material being heated, the power of the system, and the design of the induction coil.
The core principle to understand is that induction heating does not have a "set" temperature. It is a method for generating heat directly inside a material, making the achievable temperature a controllable variable based on the system's design and operational parameters.
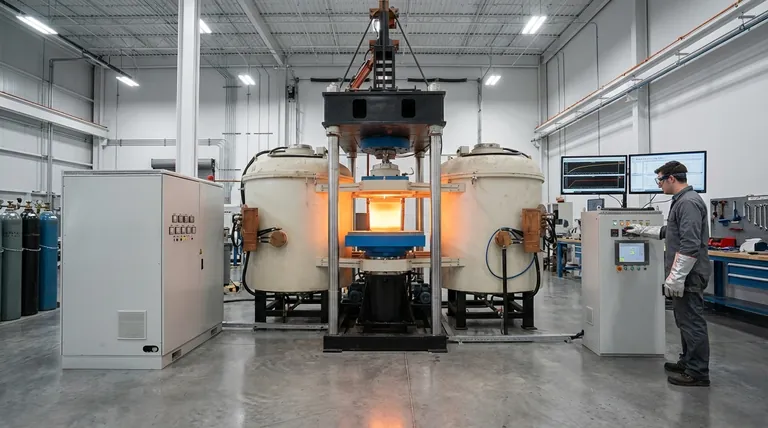

How Induction Heating Generates Temperature
To understand what controls the temperature, you must first understand the mechanism. The process is remarkably elegant and relies on generating heat from within the workpiece itself, rather than applying it from an external source.
The Role of the Magnetic Field
An induction heater uses a coil of conductive material (typically copper) through which a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed. This creates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within and around the coil.
Inducing Current in the Workpiece
When an electrically conductive material, such as a piece of steel, is placed within this magnetic field, the field induces electrical currents inside the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
Resistance Creates Heat
As these eddy currents swirl through the workpiece, they encounter the material's natural electrical resistance. This resistance impedes the flow of the current, and that friction generates intense, localized heat. It is the object's own resistance that causes it to heat up from the inside out.
Key Factors That Determine the Final Temperature
The final temperature of a workpiece is not a fixed limit of the technology but a balance of several key factors. Adjusting these variables allows for precise control over the heating process.
Power of the Induction Supply
This is the most direct factor. A higher power output from the induction unit will generate a stronger magnetic field, induce larger eddy currents, and therefore create heat more rapidly, leading to a higher potential temperature.
The Material Being Heated
A material's electrical resistivity and magnetic properties are critical. Materials with higher resistance will generate heat more effectively for a given amount of induced current. This is why different metals heat at different rates under the same conditions.
The Induction Coil Design
The shape, size, and proximity of the coil to the workpiece define the inductive coupling. A coil that is very close to the part creates a more concentrated magnetic field, transferring energy more efficiently and enabling faster heating to higher temperatures.
Heating Time
Heat is generated as long as the power is applied. The longer the magnetic field is active, the more heat will be generated within the part, causing its temperature to rise until it either melts or loses heat to the environment as fast as it's being generated.
Understanding the Limitations and Trade-offs
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is governed by clear physical principles that create specific constraints.
Material Constraint: Must Be Conductive
This is the most significant limitation. Induction heating only works directly on materials that are electrically conductive, such as metals like steel, copper, and aluminum. It cannot be used to directly heat insulators like glass, plastics, or most ceramics.
Geometry and Coil Complexity
Heating parts with highly complex shapes can be challenging. Achieving uniform temperature requires the magnetic field to be applied evenly, which may necessitate a custom-designed coil that precisely matches the part's geometry.
High-Frequency Effects
The frequency of the alternating current affects how deep the heat penetrates. High frequencies tend to heat only the surface of a part (known as the skin effect), which is ideal for surface hardening but unsuitable if the goal is to heat the entire volume of a large object.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "right" temperature depends entirely on your application. By controlling the factors above, you can tailor the process to a specific industrial need.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature melting or forging: Your main concern will be maximizing power delivery and ensuring efficient coupling with a well-designed coil and furnace.
- If your primary focus is precise surface hardening: You will need to carefully control the power, heating time, and AC frequency to heat only the outer layer to a specific temperature without affecting the core.
- If your primary focus is rapid brazing or soldering: The goal is localized, fast heating, which relies on a custom coil designed to target only the joint area.
Ultimately, the temperature in induction heating is not a limit to be discovered, but a parameter to be controlled.
Summary Table:
| Factor | How It Affects Temperature |
|---|---|
| Power Supply | Higher power generates stronger magnetic fields, enabling faster heating and higher maximum temperatures. |
| Material Properties | Materials with high electrical resistivity heat more efficiently. Metals like steel heat faster than copper. |
| Coil Design | Proper coil geometry and proximity ensure efficient energy transfer, crucial for achieving target temperatures. |
| Heating Time | Temperature rises as long as power is applied, allowing precise control over the final heat level. |
Need precise thermal processing for your lab or production line?
Induction heating's ability to deliver controlled, localized heat is a game-changer for applications from material synthesis to component manufacturing. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction heating systems tailored to your specific needs.
We help you achieve:
- Precise Temperature Control for consistent, repeatable results.
- Rapid and Efficient Heating to accelerate your R&D or production.
- Customizable Solutions with coils designed for your unique workpiece geometry.
Let our experts help you harness the power of induction heating. Contact KINTEL today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum hot press furnace ensure the quality of AlTi diffusion layers? Achieving Pure Al3Ti Intermetallic Bonds
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results
- How does a vacuum hot press (VHP) contribute to the densification of Al-Cu-ZrC composite materials? Key VHP Benefits
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play in the fabrication of CuCrFeMnNi alloys? Achieve High Purity



















