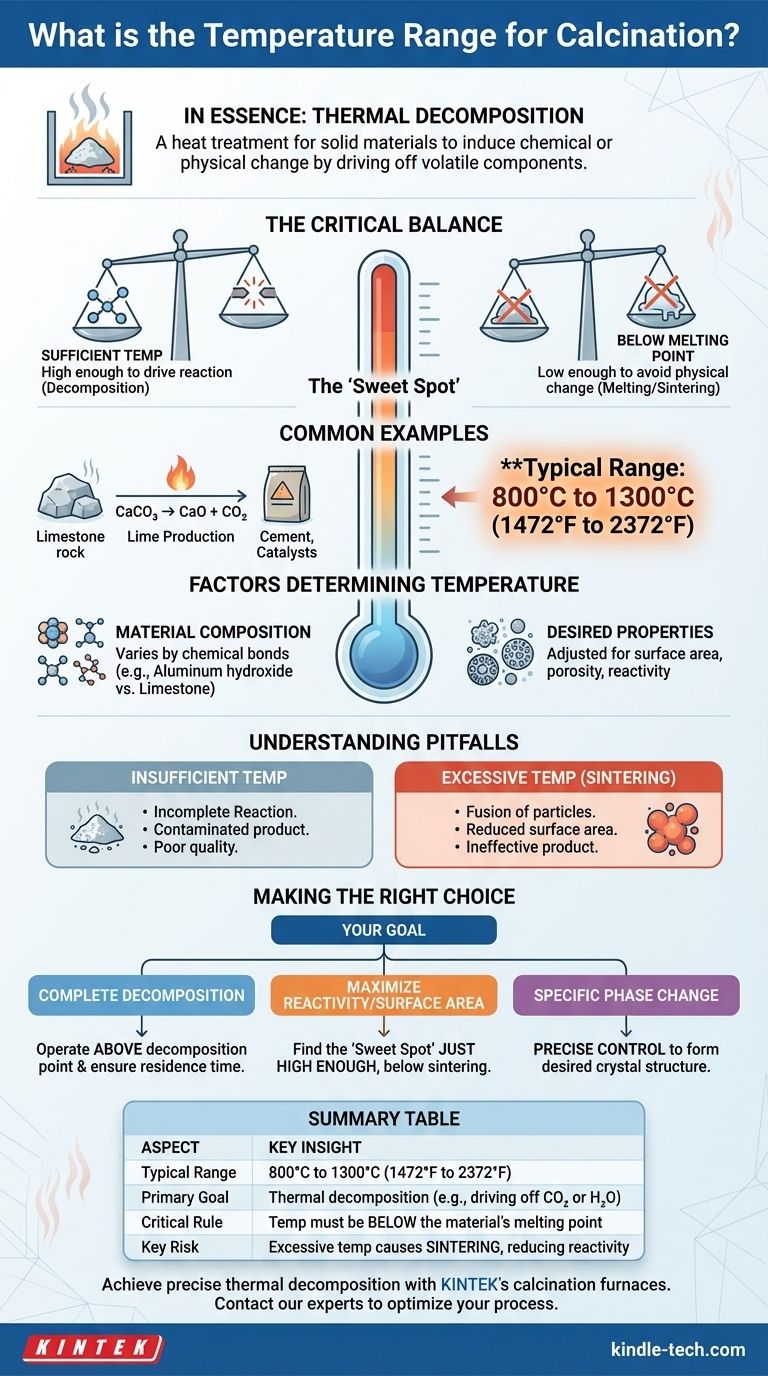
In essence, calcination is a process of thermal decomposition. This is a heat treatment applied to a solid material to bring about a chemical or physical change, typically by driving off volatile components. The required temperature varies significantly by application, but calcination furnaces generally operate in a range from 800°C to 1300°C (1472°F to 2372°F).
The specific temperature for calcination is not a single fixed value but a critical process parameter. It is carefully chosen to be high enough to drive a desired chemical reaction but remain below the material's melting point to avoid unwanted physical changes.

What is Calcination and Why is Temperature Critical?
Calcination is a foundational process in materials science and industry. Understanding why temperature is the primary lever of control is key to achieving the desired outcome.
The Goal: Driving Chemical and Physical Change
The fundamental purpose of calcination is to transform a material. This is often done to remove chemically bound components, like water (dehydration) or carbon dioxide (decarboxylation).
It can also be used to trigger a phase transition, changing the material's crystal structure from one form to another.
The Principle: Decomposition Without Melting
The success of calcination hinges on a simple principle: the temperature must be high enough to break chemical bonds but low enough to avoid melting the material.
Heating a substance to its calcination temperature provides the energy needed for decomposition reactions to occur.
Common Examples of Calcination
One of the most common examples is the production of lime from limestone. Calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) is heated to drive off carbon dioxide (CO₂), leaving behind calcium oxide (CaO), or quicklime.
Other major applications include the production of cement, the removal of water from hydrated minerals to create anhydrous versions, and the preparation of catalysts.
Factors That Determine the Calcination Temperature
The broad 800°C to 1300°C range exists because the precise temperature depends entirely on the material being processed and the desired properties of the final product.
Material Composition
Different chemical compounds have different decomposition temperatures. The bonds holding a molecule together dictate how much thermal energy is needed to break them apart.
For example, the decomposition of aluminum hydroxide requires a different temperature than the decomposition of limestone.
Desired End-Product Properties
Even for the same material, the temperature can be adjusted to fine-tune the final properties.
Slight variations in calcination temperature can significantly alter a product's surface area, porosity, and reactivity, which is especially critical in manufacturing catalysts and absorbents.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Selecting the wrong temperature can lead to an inefficient process or a useless final product. Understanding the potential issues is crucial for process control.
Insufficient Temperature
If the temperature is too low, the decomposition reaction will be incomplete. The final product will be contaminated with the original, unreacted starting material.
This results in poor quality and requires either reprocessing or disposal, both of which are costly.
Excessive Temperature (Sintering)
If the temperature is too high—even if it's still below the melting point—it can cause an unwanted effect called sintering.
Sintering is the fusion of particles, which drastically reduces the material's surface area and reactivity. For applications like catalysts, where high surface area is essential, sintering renders the product ineffective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The optimal calcination temperature is always a function of your end goal. Use these principles to guide your decision-making.
- If your primary focus is complete decomposition: You must operate above the material's specific decomposition point and provide sufficient residence time for the reaction to finish.
- If your primary focus is maximizing surface area or reactivity: You need to find the "sweet spot"—a temperature just high enough for full decomposition but safely below the onset of sintering.
- If your primary focus is inducing a specific phase change: The temperature must be controlled with high precision to form the desired crystal structure without overshooting into an unwanted phase or causing sintering.
Ultimately, mastering calcination is about using temperature as a precise tool to engineer the final properties of your material.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Typical Range | 800°C to 1300°C (1472°F to 2372°F) |
| Primary Goal | Thermal decomposition (e.g., driving off CO₂ or H₂O) |
| Critical Rule | Temperature must be below the material's melting point |
| Key Risk | Excessive temperature causes sintering, reducing reactivity |
| Main Factor | Material composition and desired end-product properties |
Achieve precise thermal decomposition with KINTEK's calcination furnaces.
Selecting the correct temperature is critical for your material's success. Whether you are producing lime, cement, or catalysts, our lab furnaces offer the precise temperature control and uniform heating you need to avoid incomplete reactions or damaging sintering.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment for researchers and industrial professionals who require reliable thermal processing. Let us help you optimize your calcination process for maximum yield and desired material properties.
Contact our thermal experts today to discuss your specific application and furnace requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of pyrolysis? Unlocking Value from Waste vs. Cost & Complexity
- What is the capacity of a rotary furnace? Choose Between Batch or Continuous Processing
- What are the main products formed from the pyrolysis process? A Guide to Bio-char, Bio-oil, and Syngas
- What is the output of the pyrolysis plant? A Flexible Process for Biochar, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the problems with biomass pyrolysis? High Costs & Technical Hurdles Explained
- Why choose pyrolysis? Turn Waste into Valuable Resources with Advanced Thermal Conversion
- What are the disadvantages of fast pyrolysis? The key challenges of bio-oil production
- What is the working principle of rotary furnace? Achieve Continuous, Uniform Thermal Processing



















