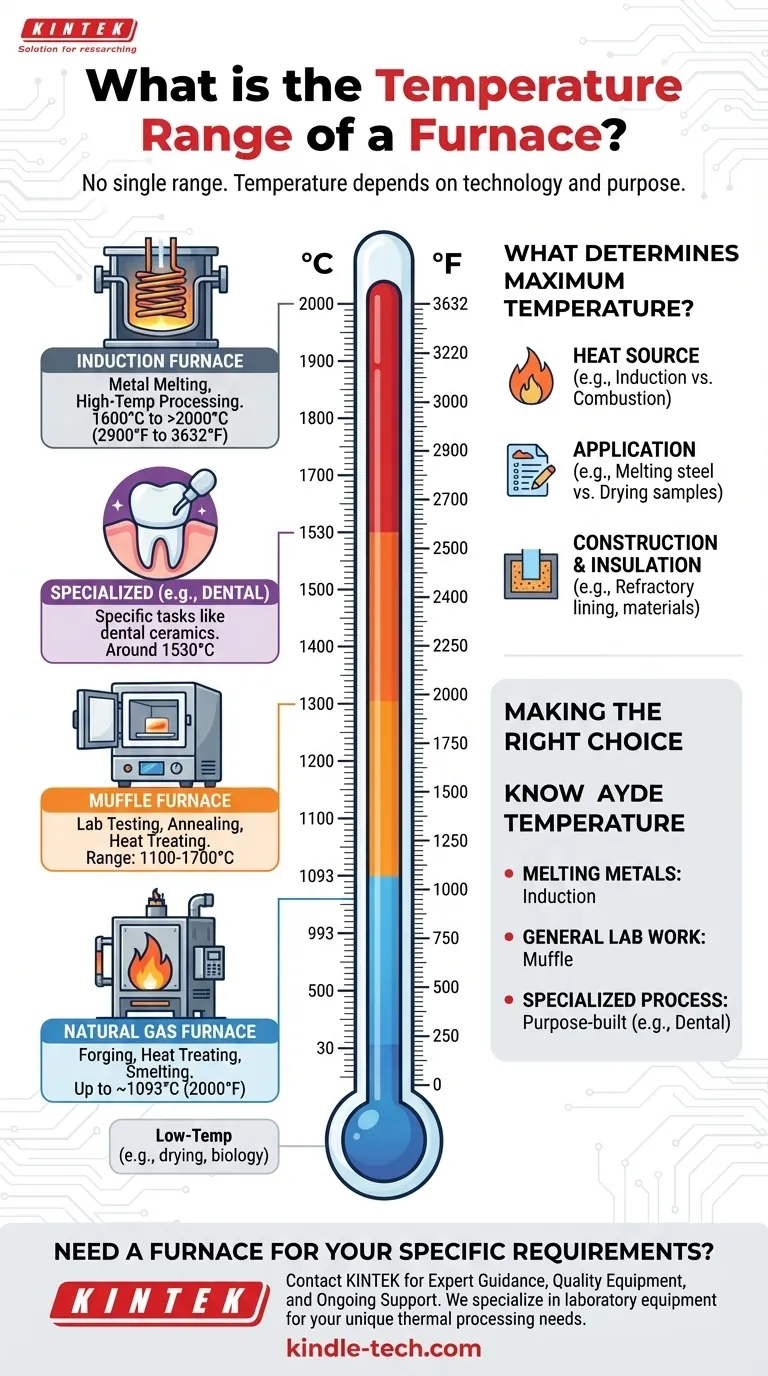
Crucially, there is no single temperature range for a furnace. The term "furnace" covers a vast array of devices, from home heating units to industrial forges, and their operating temperatures vary dramatically based on their technology and purpose. A natural gas furnace might reach around 1093°C (2000°F), while a specialized vacuum induction furnace can exceed 2000°C (3632°F).
The maximum temperature of a furnace is dictated not by a general rule, but by its specific design and application. Understanding the different types—such as induction, muffle, or gas—is essential to understanding their vastly different thermal capabilities.

Common Furnace Types and Their Temperature Ranges
The operational temperature of a furnace is directly linked to its core technology and intended use. A furnace designed for melting high-strength alloys will operate at a fundamentally different level than one used for laboratory sample preparation.
Induction Furnaces
An induction furnace uses electromagnetic induction to heat and melt conductive materials like metal. This technology is known for its ability to achieve extremely high temperatures rapidly and efficiently.
Depending on the specific design, from small melting units to large vacuum furnaces, their maximum temperatures typically range from 1600°C to over 2000°C (2900°F to 3632°F).
Natural Gas Furnaces
These furnaces rely on the combustion of natural gas to generate heat. They are common in industrial settings for processes like forging, heat treating, and smelting.
A typical industrial natural gas furnace can reach temperatures of up to 1093°C (2000°F).
Muffle Furnaces
A muffle furnace insulates the material being heated from the direct flames or heating elements. This creates a more uniform and controlled heating environment, which is ideal for laboratory testing, annealing, and heat-treating applications.
The temperature range for muffle furnaces is quite broad, with different models reaching maximums anywhere from 1100°C to 1700°C (2012°F to 3092°F).
Specialized Application Furnaces
Many furnaces are engineered for a single, highly specific task. A dental furnace, for example, is designed to process materials like zirconium oxides for dental restorations.
These furnaces are optimized for precision temperature control within a specific range, often around 1530°C (2786°F), to achieve the desired material properties.
What Determines a Furnace's Maximum Temperature?
The significant variation in temperature capability is not arbitrary. It is a direct result of fundamental differences in design, energy source, and purpose.
The Heat Source
The method of generating heat is the primary factor. Electromagnetic induction can concentrate immense energy directly into the target material, allowing it to reach higher temperatures than most combustion-based systems, which heat a chamber more broadly.
The Application
A furnace's purpose dictates its required temperature. A furnace for melting steel must obviously reach temperatures far beyond one designed for drying biological samples or firing low-temperature ceramics. The application defines the entire engineering specification.
Construction and Insulation
The materials used to build the furnace, particularly the refractory lining and insulation, determine its ability to contain extreme heat safely and efficiently. High-temperature ceramics and insulating materials are critical for preventing heat loss and structural failure at the upper end of the spectrum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct equipment, you must first define the thermal requirements of your specific process.
- If your primary focus is melting metals at very high temperatures: An induction furnace is the most effective technology, with vacuum models offering the highest purity and temperature capabilities.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory work or heat treating: A muffle furnace provides the controlled, uniform environment you need, with various models available to match your specific temperature requirements.
- If your primary focus is a specialized industrial process: Look for a furnace explicitly designed for that task, such as a dental furnace for ceramics or a forge for metalworking.
Ultimately, understanding the technology behind the furnace is the key to selecting the right tool for any thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Maximum Temperature Range | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Induction Furnace | 1600°C to over 2000°C (2900°F to 3632°F) | Metal melting, high-temperature processing |
| Muffle Furnace | 1100°C to 1700°C (2012°F to 3092°F) | Laboratory testing, annealing, heat treating |
| Natural Gas Furnace | Up to 1093°C (2000°F) | Industrial forging, heat treating, smelting |
| Specialized (e.g., Dental) | Around 1530°C (2786°F) | Specific applications like dental ceramics |
Need a Furnace for Your Specific Temperature Requirements?
Selecting the right furnace is critical for your process success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing laboratory equipment and consumables tailored to your unique thermal processing needs. Whether you require precise temperature control for research or high-temperature capabilities for industrial applications, our experts can help you find the perfect solution.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Get personalized recommendations based on your specific temperature range and application requirements.
- Quality Equipment: Access reliable furnaces from muffle to induction models, ensuring consistent performance and safety.
- Ongoing Support: Benefit from our comprehensive service and maintenance support to keep your lab running smoothly.
Ready to find the perfect furnace for your lab? Contact us today for a consultation and let KINTEK help you achieve optimal thermal processing results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why do we determine ash in food? A Key to Quality, Nutrition & Safety
- Why is a muffle furnace used for CaFe2O4 coating heat resistance? Achieve Precise Thermal Testing Results
- What is the necessity of using a high-temperature box furnace for the 300°C heat treatment? Curing & Adhesion Experts
- Why is precise temperature control in laboratory ovens critical for photocatalytic pigments? Protect Color & Function
- What is the significance of using a high-temperature muffle furnace in the solid-state transformation of CuFe12O19?
- What is a furnace used for in a laboratory? Achieve Precise Material Transformation and Analysis
- What role does a laboratory furnace with an observation window play in refractoriness testing? Real-time Data Accuracy
- What is a muffle furnace used for in pharma? Ensuring Purity and Regulatory Compliance



















