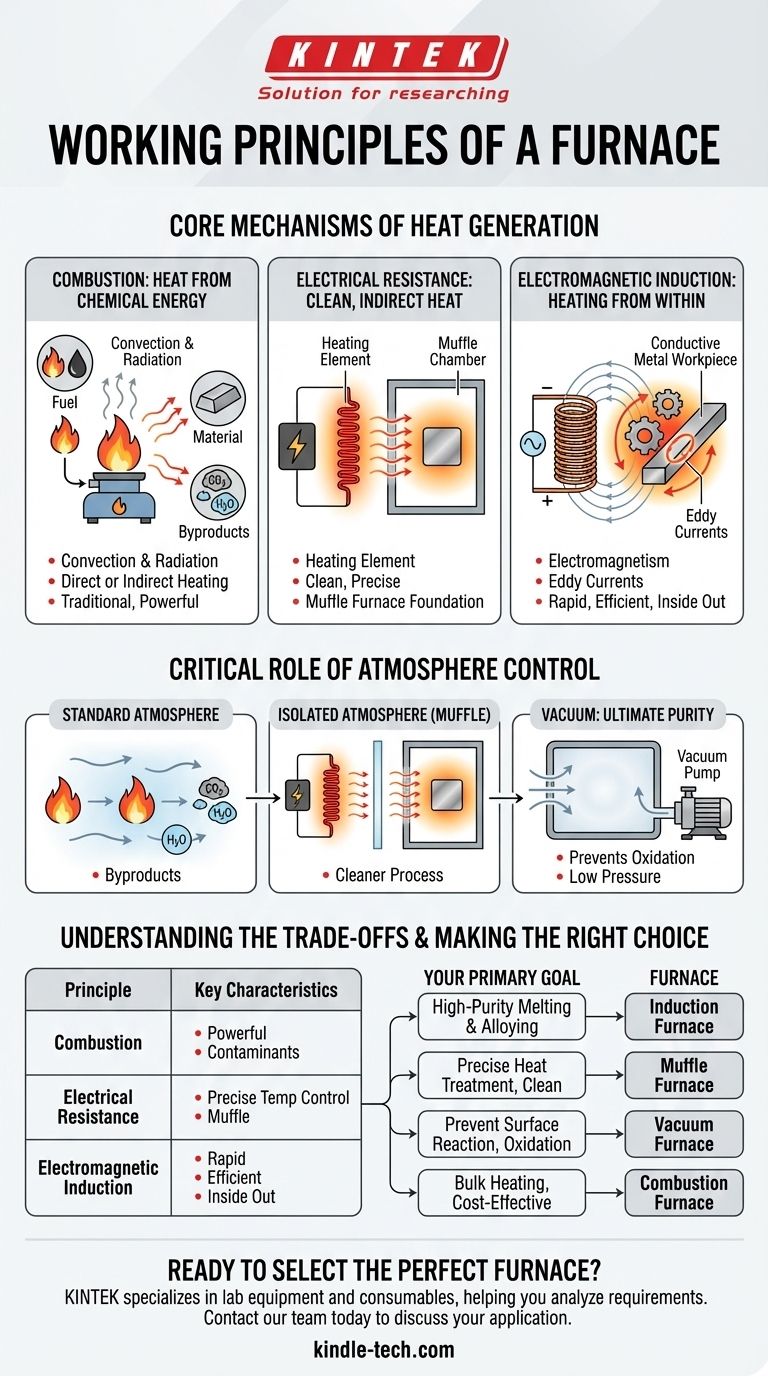
At its core, a furnace works by converting energy into heat and transferring it to a target material. While the fundamental goal is simple, the method used defines the furnace's capabilities and applications. The three primary working principles are the combustion of fuel, electrical resistance heating, and electromagnetic induction.
The specific principle a furnace uses is not just a technical detail; it dictates the precision, efficiency, and purity of the heating process. Understanding the distinction between direct heat generation within the material versus indirect heat application from an external source is the key to choosing the right tool for a specific task.
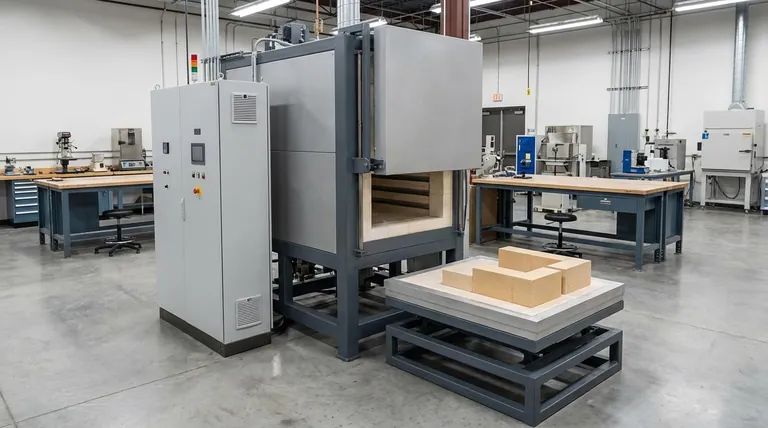

The Core Mechanisms of Heat Generation
Every furnace starts with a source of energy. The method it uses to convert that energy into usable heat is the most important factor in its design and function.
Combustion: Heat from Chemical Energy
The most traditional furnace design works on the principle of combustion. Fuel is burned to produce hot gases.
This heat is then transferred to the material through two primary methods: convection (the movement of the hot gas) and radiation (the emission of thermal energy). Materials can be heated directly by these gases or indirectly by placing them in pipes or containers that are then heated.
Electrical Resistance: Clean, Indirect Heat
Many modern furnaces use the principle of electrical resistance, where electricity is passed through a specialized heating element.
These elements, often made of materials like nichrome, become extremely hot and radiate heat into a chamber. This method is the foundation for the muffle furnace, which uses an insulated chamber to separate the material being heated from the heating elements, preventing direct contact and contamination.
Electromagnetic Induction: Heating from Within
An induction furnace operates on a more advanced principle, using electromagnetism to generate heat directly inside the target material.
An alternating electric current is passed through a copper coil, creating a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field. When a conductive material (like metal) is placed within this field, it induces electrical currents, known as eddy currents, to flow within the material itself. The material's own resistance to these currents generates intense heat, causing it to melt from the inside out.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere Control
The environment inside the furnace is often as important as the temperature. The furnace's design directly impacts the level of atmospheric control possible.
Standard and Isolated Atmospheres
Combustion furnaces inherently introduce byproducts like carbon dioxide and water vapor into the heating environment.
Muffle furnaces improve upon this by creating an isolated chamber. This "muffle" separates the workload from the heating elements and any potential contaminants, providing a cleaner heating process.
Vacuum: The Ultimate Purity
A vacuum furnace is designed for processes where any atmospheric reaction is unacceptable. By removing air and other reactive gases, it creates a low-pressure environment.
This vacuum prevents oxidation and other forms of contamination, which is critical when working with reactive metals or when a perfectly pure surface finish is required. Heating is typically achieved through resistance or radiation within the sealed, vacuum-tight chamber.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single furnace principle is universally superior. The choice always involves a balance of efficiency, control, and material compatibility.
Efficiency and Speed
Induction furnaces are extremely efficient because the heat is generated directly within the workpiece, leading to minimal energy loss and very rapid heating. Combustion furnaces lose a significant amount of heat through exhaust gases.
Precision and Control
Furnaces using electrical principles, such as muffle and induction, offer superior temperature control. When paired with a PID controller and a thermocouple, they can maintain temperatures with remarkable precision. Combustion heating is inherently less precise.
Material and Application
The choice of furnace is fundamentally tied to the material. Induction heating only works on electrically conductive materials. Muffle and combustion furnaces can heat a much wider range of materials, including ceramics and other non-conductors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate technology, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-purity melting and alloying: An induction furnace is the ideal choice due to its direct, rapid, and contaminant-free heating.
- If your primary focus is precise heat treatment in a clean environment: A muffle furnace provides excellent temperature control while isolating the workpiece from the heating elements.
- If your primary focus is preventing any surface reaction like oxidation: A vacuum furnace is the only technology that can provide the necessary inert environment.
- If your primary focus is bulk heating of materials where precision is secondary: A combustion furnace can be a cost-effective and powerful solution.
Ultimately, understanding how a furnace generates and applies heat empowers you to select the precise tool required to achieve your desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Principle | Heat Generation Method | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Combustion | Burning fuel (gas, oil) | Traditional, powerful, can introduce contaminants |
| Electrical Resistance | Current through heating element | Clean, precise temperature control (e.g., Muffle Furnace) |
| Electromagnetic Induction | Eddy currents within conductive material | Rapid, efficient, heats from the inside out |
| Vacuum Environment | Heating in a low-pressure chamber | Prevents oxidation, ensures ultimate purity |
Ready to select the perfect furnace for your specific needs?
Understanding the working principles is the first step. The right furnace technology—be it a clean Muffle Furnace for precise heat treatment, a rapid Induction Furnace for high-purity melting, or a Vacuum Furnace to prevent oxidation—is critical to your success.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you analyze your requirements for material, temperature, and atmosphere control to recommend the ideal furnace solution.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and ensure you get the performance and results you need.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the 4 types of heat treatment steel undergoes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening & Tempering
- What precautions should be taken while heating and cooling the crucible? Prevent Thermal Shock and Ensure Safety
- What do you use a muffle furnace for? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- How does a muffle furnace work? A Guide to Clean, High-Temperature Heating
- What is a muffle furnace for laboratory use? A Guide to Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing



















