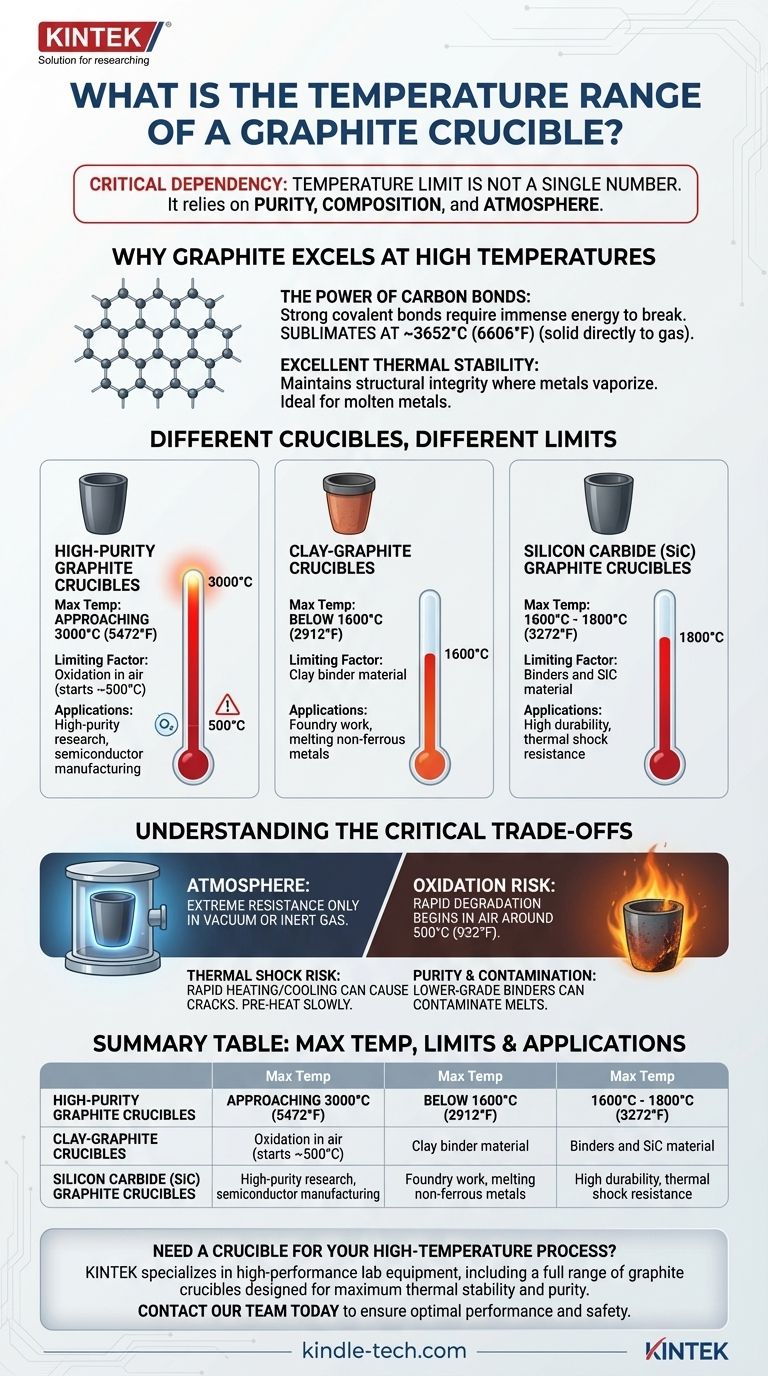
In a controlled, oxygen-free environment, a high-purity graphite crucible can withstand temperatures up to 3000°C (5472°F). However, its practical and safe operating temperature is significantly lower in the presence of air due to oxidation, which begins around 500°C (932°F). The type of crucible, such as clay-graphite or silicon carbide-graphite, also drastically changes its effective temperature limit.
The maximum temperature of a graphite crucible is not a single number. It is critically dependent on two factors: the purity and composition of the crucible and the atmosphere in which it is heated.

Why Graphite Excels at High Temperatures
Graphite is a crystalline form of carbon. Its atoms are arranged in a strong, stable hexagonal lattice, giving it one of the highest melting/sublimation points of any element.
The Power of Carbon Bonds
The strong covalent bonds between carbon atoms require an immense amount of thermal energy to break apart. This is why pure graphite doesn't truly melt at standard pressure but rather sublimates (turns from a solid directly to a gas) at approximately 3652°C (6606°F).
Excellent Thermal Stability
This inherent stability allows graphite to maintain its structural integrity at temperatures that would cause most metals to vaporize. It is an ideal container for molten metals and other high-temperature processes.
Different Crucibles, Different Limits
The term "graphite crucible" can refer to several different products, each with a unique temperature range determined by its composition.
High-Purity Graphite Crucibles
These are made from high-purity, isostatically pressed graphite. They offer the highest performance, with a maximum service temperature approaching 3000°C. They are used for high-temperature research, semiconductor manufacturing, and melting specialty alloys.
Clay-Graphite Crucibles
These are a composite of graphite flakes and binder clays, such as kaolin. They are a common and cost-effective choice for foundries. The clay binder is the limiting factor, typically restricting their use to temperatures below 1600°C (2912°F).
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Graphite Crucibles
These crucibles blend graphite with silicon carbide, offering superior durability and resistance to thermal shock compared to clay-graphite. Their maximum use temperature is generally between 1600°C and 1800°C (3272°F), limited by the binders and the SiC itself.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Using a graphite crucible effectively requires understanding its primary limitation: oxidation.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
Graphite's extreme temperature resistance only applies in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen). In the presence of oxygen (air), graphite begins to oxidize and burn away at a much lower temperature, typically starting around 500°C (932°F).
This oxidation reaction weakens the crucible, causing it to degrade rapidly and potentially fail catastrophically. Protective glazes on some crucibles can slow this process, but they are not a substitute for atmospheric control at very high temperatures.
Thermal Shock Risk
While graphite has good resistance to thermal shock, heating or cooling it too quickly can still cause cracks, especially in clay-bonded variants. It is standard practice to pre-heat crucibles slowly and handle them carefully to prolong their life.
Purity and Contamination
For applications like melting aluminum or precious metals, the purity of the crucible is paramount. Lower-grade crucibles with impurities in their binders can contaminate the melt, affecting the final properties of the cast metal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of crucible must align with your specific material, temperature, and atmospheric conditions.
- If your primary focus is melting common non-ferrous metals (aluminum, brass, copper): A clay-graphite or silicon carbide-graphite crucible is the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is high-purity research or melting reactive metals: A high-purity graphite crucible used within a vacuum or inert gas furnace is essential.
- If your primary focus is hobbyist blacksmithing or casting: Start with a durable and affordable clay-graphite or SiC crucible, always pre-heating it properly before use.
Understanding the material and its environment is the key to successfully working at high temperatures.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Type | Max Temperature (Inert Atmosphere) | Key Limiting Factor | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Graphite | Up to 3000°C (5472°F) | Oxidation in air (starts ~500°C) | High-purity research, semiconductor manufacturing |
| Clay-Graphite | Up to 1600°C (2912°F) | Clay binder material | Foundry work, melting non-ferrous metals |
| Silicon Carbide-Graphite | 1600°C - 1800°C (3272°F) | Binder and SiC material | High durability, thermal shock resistance |
Need a crucible that can handle your specific high-temperature process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including a full range of graphite crucibles designed for maximum thermal stability and purity. Our experts can help you select the perfect crucible for your application—whether you're melting metals, conducting research, or manufacturing semiconductors. Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and ensure optimal performance and safety in your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- What are the benefits of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature & Atmosphere Control
- Why use a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature Uniformity and Atmosphere Control
- What factors influence the general design of a tube furnace? Match Your Process with the Perfect System



















