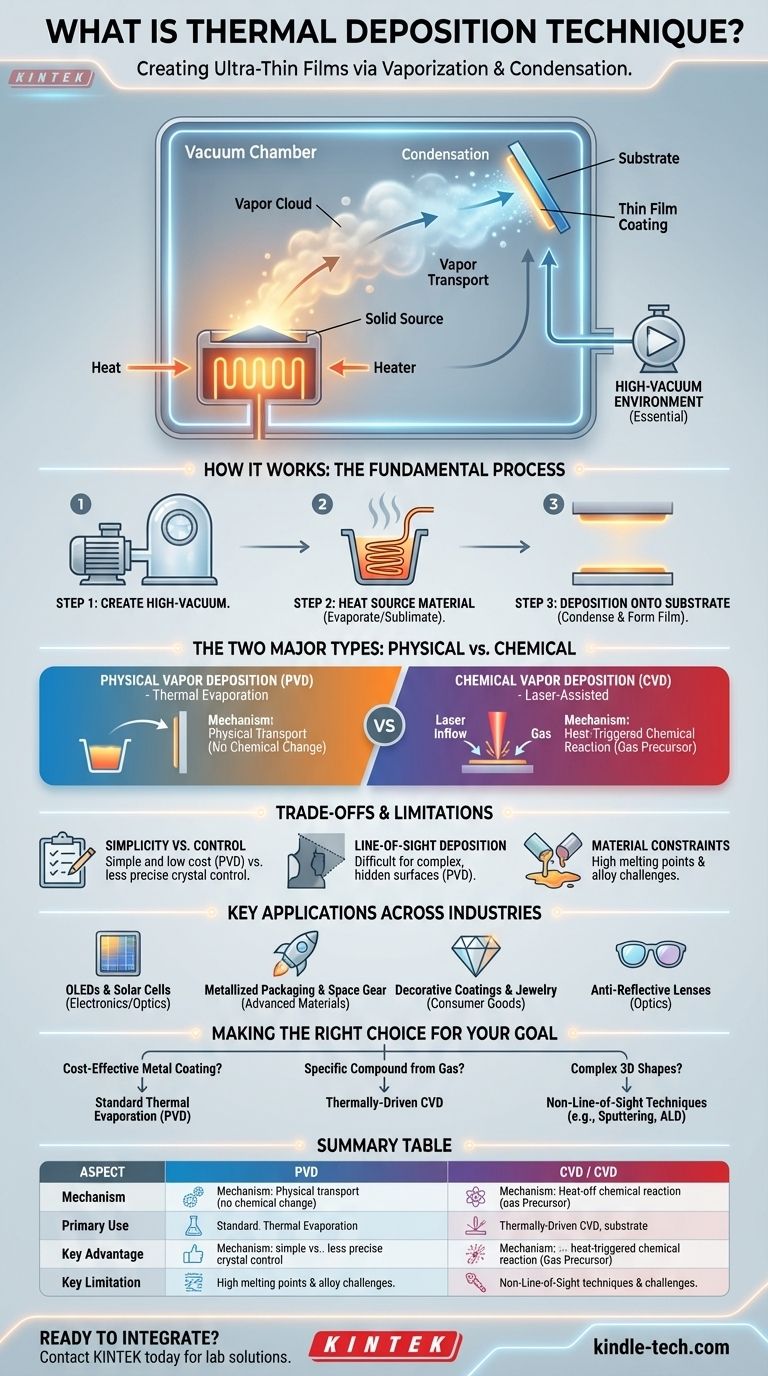
At its core, thermal deposition is a technique for creating ultra-thin films by heating a solid material inside a high-vacuum chamber until it turns into a vapor. This vapor then travels and condenses onto a cooler target surface, known as a substrate, forming a solid, uniform coating. The entire process is a physical transfer of material from a source to a target.
While the concept of "heating and coating" seems simple, the term "thermal deposition" encompasses distinct methods. The key is understanding whether heat is used to physically evaporate a solid source (PVD) or to trigger a chemical reaction from a gas (CVD), as this choice fundamentally dictates the film's properties and potential applications.
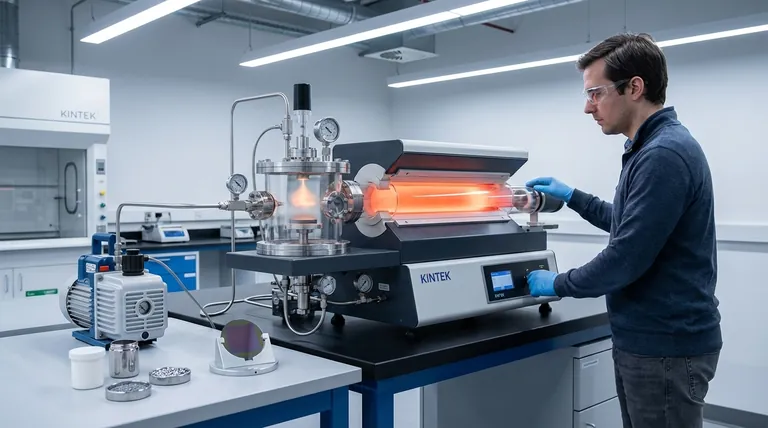

How Thermal Deposition Works: The Fundamental Process
The most common form of thermal deposition, thermal evaporation, relies on a straightforward, three-step physical process. Understanding this sequence is key to grasping how thin films are made.
Step 1: Creating a High-Vacuum Environment
The entire process must occur in a high-vacuum chamber. This vacuum is critical because it removes air and other gas particles that would otherwise collide with the vaporized material, scattering it and preventing it from reaching the substrate in a clean, direct path.
Step 2: Heating the Source Material
The solid source material—often a pure metal like aluminum in the form of wire or pellets—is placed into a holder, such as a ceramic "boat" or a tungsten crucible. An electrical current is passed through this holder, heating it resistively and, in turn, heating the source material until it evaporates or sublimates into a vapor cloud.
Step 3: Deposition onto the Substrate
This vapor cloud expands throughout the vacuum chamber. When the vapor particles strike the cooler substrate (the object being coated), they rapidly lose their thermal energy, condense back into a solid state, and begin to form a thin film. The film's thickness is controlled by the rate of evaporation and the duration of the process.
The Two Major Types of Thermal Deposition
While the term is often used to describe physical evaporation, it's important to distinguish between the two primary mechanisms where heat is the driving force.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): Thermal Evaporation
This is the classic method described above. The source material is physically transported from the source to the substrate without any chemical change.
It is widely used for depositing pure metals, non-metals, and some simple compounds. Its simplicity and cost-effectiveness make it a go-to choice for creating electrically conductive layers on solar cells, OLED displays, and thin-film transistors.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Laser-Assisted
In some advanced techniques, like Laser Chemical Vapor Deposition (LCVD), the mechanism is different. Here, a laser provides localized thermal energy directly to the substrate.
A reactive gas is introduced into the chamber and flows over the heated spot on the substrate. The heat triggers a chemical reaction in the gas, causing it to decompose and deposit a solid film onto the surface. This method is not about physically moving a solid source but about using heat to initiate a chemical transformation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No technique is perfect for every scenario. Thermal deposition has clear advantages in its simplicity and cost but also comes with important limitations.
Simplicity vs. Control
Thermal evaporation is one of the simplest and least expensive PVD methods. However, it offers less precise control over the film's structure (like crystal grain size) compared to more complex techniques like sputtering or molecular beam epitaxy.
Line-of-Sight Deposition
Because the vapor travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate, thermal evaporation is a line-of-sight technique. This makes it difficult to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with undercuts or hidden surfaces.
Material Constraints
Evaporating materials with very high melting points can be challenging and energy-intensive. Furthermore, depositing alloys can be difficult because the constituent metals may have different evaporation rates, leading to a film composition that doesn't match the source alloy.
Key Applications Across Industries
The versatility of thermal deposition has made it a cornerstone technology in numerous fields.
Electronics and Optics
This is a primary application area. The technique is used for creating the ultra-thin metal layers in OLEDs and solar cells, as well as for applying anti-reflective coatings and UV protection layers on optical lenses.
Advanced Materials and Packaging
Its ability to deposit thin layers of aluminum onto polymers is used for metallized food packaging, which provides an excellent barrier to light, moisture, and oxygen. The reflective properties are also utilized in NASA spacesuits, firefighter uniforms, and emergency blankets for thermal management.
Decorative and Consumer Goods
Thin-film coatings are also applied to jewelry, accessories, and other consumer products to achieve specific aesthetic effects, such as metallic or iridescent finishes, at a low cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct deposition method depends entirely on your material, budget, and desired film properties.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective metal coating: Standard thermal evaporation is often the most direct and economical choice for depositing pure metals like aluminum or gold.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific compound from a gas precursor: A thermally-driven Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) method is necessary to provide the energy for the chemical reaction.
- If your primary focus is coating complex 3D shapes uniformly: You must look beyond line-of-sight thermal evaporation to non-line-of-sight techniques like sputtering or Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD).
By understanding the underlying mechanism, you can confidently select the technique that best aligns with your engineering and material science objectives.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Thermal Evaporation (PVD) | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Physical vaporization of a solid source | Heat-triggered chemical reaction from a gas |
| Primary Use | Pure metals, simple compounds (e.g., Al, Au) | Compound films from gas precursors |
| Key Advantage | Simplicity, cost-effectiveness for metals | Can create specific compound structures |
| Key Limitation | Line-of-sight; poor for complex 3D shapes | More complex process and equipment |
Ready to Integrate Thermal Deposition into Your Lab Workflow?
Whether you are developing next-generation OLED displays, enhancing solar cell efficiency, or creating advanced protective coatings, choosing the right deposition equipment is critical. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your thermal deposition needs, from robust thermal evaporation sources to advanced CVD systems.
Our experts can help you select the perfect solution to achieve precise, uniform thin films that meet your specific research and production goals.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and discover how our reliable lab solutions can accelerate your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the pressure in chemical vapor deposition? A Guide to Controlling Film Quality and Rate
- What is Vapour Phase Epitaxy (VPE)? Master High-Purity Semiconductor Growth for Electronics
- What are the different types of thin film coatings? A Guide to Deposition Methods & Materials
- How does the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process work? Master Thin-Film Coating Principles
- What is CVD and what do you mean by polymerization? A Guide to Material Creation Processes
- How does magnetron sputtering work? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How are CVD systems used for molecular sieve modification? Enhance Shape Selectivity & Para-Xylene Yield
- What is the future of CVD diamond? Unlocking Next-Gen Electronics & Thermal Management



















